Abstract
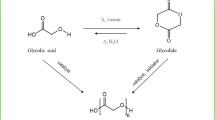
The synthesis of high-molecular-weight lactic acid based polymers by chain linked polymerization was investigated. Lactic acid based hydroxyl terminated telechelic prepolymer was synthesized and then the molecular weight was increased by chain linked polymerization using methylene diphenyldiisocyanate. All polymerizations were carried out in the melt, using tin octoate as catalyst. The products were characterized by Differential scanning calorimetry, nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and size exclusion chromatography. With the increase in diisocyanate concentration, an increase in the glass transition temperature, molecular weight and molecular weight distribution was observed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gupta AP, Kumar V (2007) Eur Polym J 43(10):4053
Dutta J, Dutta PK (2006) Everyman’s Sci XLI(2):103
Woo SI, Kim BO, Jun HS, Chang HN (1995) Polym Bull 35(4):415
Kricheldorf HR, Kreiser-Saunders I, Boettcher C (1995) Polymer 36(6):1253
Hiltunen K, Seppala JV, Harkonen M (1997) J Appl Polym Sci 63(8):1091
Pitt CG, Gu Z-W, Ingram P, Hendren RW (1987) J Polym Sci A Polym Chem 25(4):955
Storey RF, Wiggins JS, Puckett AD (1994) J Polym Sci A Polym Chem 32(12):2345
Hiltunen K, Seppala JV, Harkonen M (1997) J Appl Polym Sci 64(5):865
Hiltunen K, Harkonen M, Seppala JV, Vaananen T (1996) Macromolecules 29(27):8677
Tuominen J, Kylma J, Kapanen A, Venelampi O, Itävaara M, Seppälä J (2002) Biomacromolecules 3(3):445
Rehman I, Andrews EH, Smith R (1996) J Mater Sci Mater in Med 7(1):17
Kylma J, Tuominen J, Helminen A, Seppala J (2001) Polymer 42(8):3333
Zhong W, Ge J, Gu Z, Li W, Chen X, Zang Y, Yang Y (1999) J Appl Polym Sci 74(10):2546
Gu SY, Yang M, Yu T, Ren TB, Ren J (2008) Polym Int 57(8):982
Tuominen J, Kylma J, Seppala J (2002) Polymer 43(1):3
Kylma J, Harkonen M, Seppala JV (1997) J Appl Polym Sci 63(13):1865
Cohn D, Hotovely-Salomon A (2005) Polymer 46(7):2068
Borda J, Bodnar I, Keki S, Sipos L, Zsuga M (2000) J Polym Sci A Polym Chem 38(16):2925
Baiardo M, Frisoni G, Scandola M, Rimelen M, Lips D, Ruffieux K, Wintermantel E (2003) J Appl Polym Sci 90(7):1731
Gupta AP, Kumar V (2010) Des Monomers Polym 13(1):65
Acknowledgments
Authors acknowledge the support of the SAIF facility at Punjab University for the NMR studies and SICART-CVM, VV Nagar for the SEC studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, A.P., Dev, A. & Kumar, V. Studies of Novel Chain Linked Biodegradable Polymers. J Polym Environ 20, 514–518 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-011-0402-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-011-0402-5