Abstract
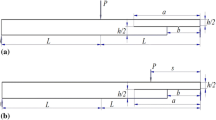
Adhesively bonded external composite patch repairs are one of the most common types of repairs. The shape and form of the damage in the repaired composite and the limits of this damage are interesting topics for researchers. In this direction, the detection of the damage in the patch and damaged main material can be determined by various methods. This study aims to investigate the impact delamination behavior of composite laminates repaired by external patches by using 3D finite element analysis and ultrasonic testing (UT). The non-destructive testing method is preferred for the actual delamination damage caused and the accuracy of the proposed numerical model. The proposed numerical model estimated delamination damage by degrading to material constants according to the delamination damage criterion. UT consisting of pulse-echo and through-transmission (TT) technique was evaluated under different ambient temperatures. These ambient temperatures were chosen due to field and laboratory conditions. Numerical analysis of patched-composites was carried out by using ABAQUS-PYTHON scripting language with VUMAT and 3D Hashin shear and delamination damage model. The effect of the material and thickness of the composite patch affecting the delamination damage under impact was also investigated in order to precisely determine the accuracy of the ultrasonic methods and the proposed numerical model. The damage areas and regions at the top (patch) and bottom (damaged composite plate) faces of the patched composite specimen were in good agreement. Numerical analysis results correctly predicted the delamination areas. The use of patches increased the peak contact force (glass fiber and carbon fiber, respectively) in the unpatched damaged composite by 11\(\%\) and 18\(\%\). The patch material change (from glass fiber to carbon fiber) increased the peak contact force by 6\(\%\). With the increase in patch thickness (glass fiber and carbon fiber, respectively), the peak contact force was increased by 21 and 15\(\%\). Ultrasonic scanning results show that the through-transmission technique is more successful in detecting damage to the back of the plates (volumetric damages), and the pulse-echo technique is more successful in detecting damage to the impact surface of the plate.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tamborrino, R., Palumbo, D., Galietti, U., Aversa, P., Chiozzi, S., Luprano, V.A.M.: Assessment of the effect of defects on mechanical properties of adhesive bonded joints by using non destructive methods. Composites B 91, 337–345 (2016)
Cheng, L., Tian, G.Y.: Comparison of nondestructive testing methods on detection of delaminations in composites. J. Sens. 1–7 (2012)
Sojasi, S., Khodayar, F., Lopez, F., Ibarra-Castando, C., Maldague, X., Vavilov, V.P., Chulkov, A.O.: Infrared testing of CFRP components: comparisons of approaches using the tanimoto criterion. In: NDT in Canada (2015)
Liu, B., Zhang, H., Fernandes, H., Maldague, X.: Quantitative evaluation of pulsed thermography, lock-in thermography and vibrothermography on foreign object defect (fod) in cfrp. Sensors (Switzerland) 16(5), 00 (2016)
Swiderski, W., Hlosta, P.: Non-destructive evaluation of impacted CFRP by IR thermography. Materials (Basel) 12(6), 956 (2019)
Li, Y., Zhang, W., Yang, Z., Zhang, J., Tao, S.: Low-velocity impact damage characterization of carbon fiber reinforced polymer (CFRP) using infrared thermography. Infrared Phys. Technol. 76, 91–102 (2016)
Meola, C., Carlomagno, G.M.: Impact damage in GFRP: new insights with infrared thermography. Composites A 41(12), 1839–1847 (2010)
Safri, S.N.A., Sultan, M.T.H., Yidris, N., Mustapha, F.: Low velocity and high velocity impact test on composite materials—a review. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 3(9), 50–60 (2014)
Yang, B., Huang, Y., Cheng, L.: Defect detection and evaluation of ultrasonic infrared thermography for aerospace CFRP composites. Infrared Phys. Technol. 60, 166–173 (2013)
Gaudenzi, P., Bernabei, M., Dati, E., De Angelis, G., Marrone, M., Lampani, L.: On the evaluation of impact damage on composite materials by comparing different NDI techniques. Compos. Struct. 118, 257–266 (2014)
Zhanga, H., Genest, M., Robitaillec, F., Maldaguea, X., West, L., Joncas, S., Leducd, C.: Infrared thermography and ultrasound c-scan for non-destructive evaluation of 3d carbon fiber materials: a comparative study. In: Thermosense: Thermal Infrared Applications XXXVII, vol. 94850 (2015)
Amenabar, I., Mendikute, A., López-Arraiza, A., Lizaranzu, M., Aurrekoetxea, J.: Comparison and analysis of non-destructive testing techniques suitable for delamination inspection in wind turbine blades. Composites B 42(5), 1298–1305 (2011)
Maio, L., Memmolo, V., Boccardi, S., Meola, C., Ricci, F., Boffa, N.D., Monaco, E.: Ultrasonic and IR thermographic detection of a defect in a multilayered composite plate. Procedia Eng. 167, 71–79 (2016)
Gholizadeh, S.: A review of non-destructive testing methods of composite materials. Procedia Struct. Integrity 1, 50–57 (2016), XV Portugese Conference on Fracture, PCF 2016, 10-12 February 2016, Paco de Arcos, Portugal
Krishna, S.H., Kumar, A., Karthikeyan, P.P., Abilash, M.P., Narayanankutty, N., Sunil Kumar, G., Usha, K.M., Rakesh, S.: Pulsed thermography and ultrasonic non-destructive evaluation of corrugated metallic thermal protection system (MTPS) panel. In: Advances in Metallic Materials and Manufacturing Processes for Strategic Sectors. Materials Science Forum, vol 710, pp. 594–599. Trans Tech Publications Ltd (2012)
Balageas, D., Maldague, X., Burleigh, D., Vavilov, V.P., Oswald-Tranta, B., Roche, J.-M., Pradere, C., Carlomagno, G.M.: Thermal (IR) and other NDT techniques for improved material inspection. J. Nondestr. Eval. 35(1), 18 (2016)
Duan, Y., Zhang, H., Maldague, X.P.V., Ibarra-Castanedo, C., Servais, P., Genest, M., Sfarra, S., Meng, J.: Reliability assessment of pulsed thermography and ultrasonic testing for impact damage of CFRP panels. NDT E Int. 102, 77–83 (2019)
de Castro, D.S.V., Matvieieva, N., Grosso, M., Camerini, C.G., Kotik, H.G., Heuer, H.: Evaluation of mode II delamination area by non-destructive techniques: accuracy and influence on fracture toughness calculation. J. Nondestr. Eval. 40(3), 58 (2021)
Schmutzler, H., Garcia, A., Sato, N., Wittich, H., Nishikawa, M., Rohling, H., Hojo, M., Schulte, K., Fiedler, B.: Influence of delamination characteristics in carbon fibre/epoxy laminates on signal features of pulse thermography. J. Nondestr. Eval. 34(1), 5 (2014)
Montinaro, N., Cerniglia, D., Pitarresi, G.: A numerical study on interlaminar defects characterization in fibre metal laminates with flying laser spot thermography. J. Nondestr. Eval. 37(3), 41 (2018)
Shoja, S., Berbyuk, V., Boström, A.: Delamination detection in composite laminates using low frequency guided waves: numerical simulations. Compos. Struct. 203, 826–834 (2018)
Vavilov, V.P., Burleigh, D.D.: Review of pulsed thermal NDT: physical principles, theory and data processing. NDT E Int. 73, 28–52 (2015)
Caminero, M.A., Garcia-Moreno, I., Rodriguez, G.P., Chacon, J.M.: Internal damage evaluation of composite structures using phased array ultrasonic technique: impact damage assessment in cfrp and 3d printed reinforced composites. Composites B 165, 131–142 (2019)
Kersemans, M., Verboven, E., Segers, J., Hedayatrasa, S., Van Paepegem, W.: Non-destructive testing of composites by ultrasound, local defect resonance and thermography. In: Proceedings ICEM 2018, vol. 2, MDP I (2018)
Kim, G., Hong, S., Jhang, K.-Y., Kim, G.H.: NDE of low-velocity impact damages in composite laminates using ESPI, digital shearography and ultrasound c-scan techniques. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 13(6), 869–876 (2012)
Katunin, A., Dragan, K., Dziendzikowski, M.: Damage identification in aircraft composite structures: a case study using various non-destructive testing techniques. Compos. Struct. 127, 1–9 (2015)
Kazys, R., Demcenko, A., Zukauskas, E., Mazeika, L.: Air-coupled ultrasonic investigation of multi-layered composite materials. Ultrasonics 44, e819–e822 (2006)
Papa, I., Lopresto, V., Simeoli, G., Langella, A., Russo, P.: Ultrasonic damage investigation on woven jute/poly (lactic acid) composites subjected to low velocity impact. Composites B 115, 282–288 (2017)
Ahmed, A., Mohmmed, R., Bingjie, Z., Wei, L.: Noncontact inspection of impact damage properties of woven fabric-reinforced composites after low-velocity impact by using air-coupled ultrasonic technique. J. Ind. Text. 46(3), 809–832 (2016)
Abaqus/Explicit (version 6.14), User’s manual, finite element software. http://www.simulia.com
Ultrasonar Defense and Aviation Technologies Inc.: US DSA deep structure analyzer, automated immersion type ultrasonic scanning system (2020)
Ultrasonar Defense and Aviation Technologies Inc.: 2020, US 1000, ultrasonic pulser receiver automated immersion type ultrasonic scanning and digitizer unit (2020)
Yildiz, F., Ozdemir, A.T., Uluisik, S.: Custom design fruit quality evaluation system with non-destructive testing (NDT) techniques. In: 2018 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Data Processing (IDAP), pp. 1–5 (2018)
Yildiz, F., Ozdemir, A.T., Uluisik, S.: Evaluation performance of ultrasonic testing on fruit quality determination. J. Food Qual. 6810865, 7 (2019)
David, J., Cheeke, N.: Fundamentals and Applications of Ultrasonic Waves. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2002)
Briggs, A.: Acoustic Microscopy. Clarendon Press, Oxford (1992)
Gavrilov, D., Maev, R.G., Almond, D.P.: A review of imaging methods in analysis of works of art: thermographic imaging method in art analysis. Can. J. Phys. 92(4), 341–364 (2014)
Rogers, P.H., Van Buren, A.L.: An exact expression for the Lommel-diffraction correction integral. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 55, 724–728 (1974)
Rodrigoa, G., Angel, M.: The ultrasonic pulse-echo immersion technique and attenuation coefficient of particulate composites. Master’s thesis, University of Rhode Island, Mechanical, Industrial and Systems Engineering (2013)
Berke, M.: Nondestructive Material Testing with Ultrasonics—Introduction to the Basic Principles. Krautkamer GmbH & Company, Cologne (1996)
Wronkowicz, A., Dragan, K., Lis, K.: Assessment of uncertainty in damage evaluation by ultrasonic testing of composite structures. Compos. Struct. 203, 71–84 (2018)
Stenström, C.: Diffuse ultrasonic scattering in advanced composites. Master’s thesis, University of Nebraska-Lincoln (2010)
Martinez, R., Leija, L., Vera, A.: Ultrasonic attenuation in pure water: comparison between through-transmission and pulse-echo techniques. In: 2010 Pan American Health Care Exchanges, pp. 81–84 (2010)
Mix, P.E.: Introduction to Nondestructive Testing: A Training Guide. Wiley, New York (1987)
Kas, O., Kaynak, C.: Ultrasonic (c-scan) and microscopic evaluation of resin transfer molded epoxy composite plates. Polym. Test. 24(1), 114–120 (2005)
Hashin, Z.: Failure criteria for unidirectional fiber composites. J. Appl. Mech. 47(2), 329–334 (1980)
Kapti, S., Sayman, O., Ozen, M., Benli, S.: Experimental and numerical failure analysis of carbon/epoxy laminated composite joints under different conditions. Mater. Des. 31(10), 4933–4942 (2010)
Namala, K.K., Mahajan, P., Bhatnagar, N.: Digital image correlation of low-velocity impact on a glass/epoxy composite. Int. J. Comput. Methods Eng. Sci. Mech. 15(3), 203–217 (2014)
Caliskan, U., Apalak, M.K.: Low speed impact behaviour of adhesively bonded foam-core sandwich t-joints. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 33(3), 217–242 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conficts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caliskan, U., Yildiz, F., Teke, S. et al. Impact-Delamination Detection in Repaired-Composite Laminates Using Numerical and Ultrasonic Method. J Nondestruct Eval 41, 48 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10921-022-00878-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10921-022-00878-x