Abstract
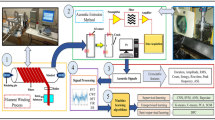
Resin fiber composites reinforcement is used to recover the original mechanical properties of steel tubes subjected to corrosion wall thinning. Pulsed Eddy Current (PEC) technique can perform nondestructive evaluation of this kind of component, due to its capability to penetrate nonmagnetic insulation. Despite the evaluation capability, distinguishing inner surface from outer surface defects is not an easy task for time-domain PEC technique. In this paper, Fast Fourier transform (FFT) in combination with multilayer perceptron (MLP) neural network classifiers are applied to PEC signals and used to detect defects (wall thinning) and also to indicate their position. The tested sample is a carbon steel tube, with 17 mm of composite reinforcement, where two defects were manufactured, one at the inner and another at the outer surface. An automated scanner system is used to obtain C-scan maps, showing the thinning areas. Two feature extraction methods are used to produce the input features for the neural network classifier: the coefficients of the FFT; and the parameters of an exponential curve fitted to the FFT coefficients. The results indicate that the MLP neural network correctly recognized the presence of wall thinning and its location with detection efficiencies of 97.4 and 97.0%, respectively. The PEC technique analysis in frequency-domain associated with a neural network classifier seems to be a promising alternative to identify the position of defects in composite reinforced steel tubes.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rohem, N.R.F., Pacheco, L.J., Budhe, S., Banea, M.D., Sampaio, E.M., Barros, S.: Development and qualification of a new polymeric matrix laminated composite for pipe repair. Compos. Struct. 152, 737–745 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2016.05.091
Duell, J.M., Wilson, J.M., Kessler, M.R.: Analysis of a carbon composite overwrap pipeline repair system. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 85, 782–788 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpvp.2008.08.001
Keller, M.W., Jellison, B.D., Ellison, T.: Moisture effects on the thermal and creep performance of carbon fiber/epoxy composites for structural pipeline repair. Composites 45, 1173–1180 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2012.07.046
Winnik, S.: Corrosion Under Insulation (CUI) Guidelines, Revised edn. Woodhead Publishing Limited, Cambridge (2016)
Ahmed, W.H.: Evaluation of the proximity effect on flow-accelerated corrosion. Ann. Nucl. Energy 37, 598–605 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anucene.2009.12.020
He, Y., Tian, G., Zang, H., Alamin, M., Simm, A., Jackson, P.: Steel corrosion characterization using Pulsed Eddy Current systems. IEEE Sens. J. 12, 2113–2119 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2012.2184280
Yu, Y., Yan, Y., Wang, F., Tian, G., Zhang, D.: An approach to reduce lift-off noise in Pulsed Eddy Current nondestructive technology. NDT E Int. 63, 1–6 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ndteint.2013.12.012
Rourke, M., Li, Y., Roberts, G.: Multi-Tubular Corrosion Inspection Using a Pulsed Eddy Current Logging Tool. In: IPTC 2013, International Petroleum Technology Conference. https://doi.org/10.2523/16645-MS
Tian, G.Y., Sophian, A., Taylor, D., Rudlin, J.: Multiple sensors on Pulsed Eddy Current detection for 3d subsurface crack assessment. IEEE Sens. J. 5, 90–96 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2004.839129
Huang, S., Wang, S.: New Technologies in Electromagnetic Non-destructive Testing, pp 41–79. Springer, Singapore (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-0578-7_2
Park, D.J., Angani, C.S., Kishore, M.B., Vértesy, G., Lee, D.H.: Application of the Pulsed Eddy Current technique to inspect pipelines of nuclear plants. J. Magn. 18, 342–347 (2013). https://doi.org/10.4283/JMAG.2013.18.3.342
Renken, C.J.: The use of personal computer to extract information from Pulsed Eddy Current. Mater. Eval. 59, 356–360 (2001)
Majidnia, S., Rudlin, J., Nilavalan, R.: Investigations on a Pulsed Eddy Current system for flaw detection using an encircling coil on a steel pipe. Insight—Non-Destr. Test. Cond. Monit. 56, 560–565 (2014)
Zeng, Z., Li, Y., Huang, L., Luo, M.: Frequency-domain defect characterization in Pulsed Eddy Current testing. Int. J. Appl. Electromagn. Mech. 45, 621–625 (2014). https://doi.org/10.3233/JAE-141885
Chen, X., Hou, D., Zhao, L., Huang, P., Zhang, G.: Study on defect classification in multi-layer structures based on fisher linear discriminate analysis by using Pulsed Eddy Current technique. NDT E Int. 67, 46–54 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ndteint.2014.07.003
He, Y., Luo, F., Pan, M., Hu, X., Gao, J., Liu, B.: Defect classification based on rectangular Pulsed Eddy Current sensor in different directions. Sens Actuators A 157, 26–31 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2009.11.012
Tian, G.Y., Sophian, A.: Defect classification using a new feature for Pulsed Eddy Current sensors. NDT E Int. 38, 77–82 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ndteint.2004.06.001
Tian, G.Y., He, Y., Adewale, I., Simm, A.: Research on spectral response of Pulsed Eddy Current and NDE applications. Sens. Actuators A 189, 313–320 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2012.10.011
Cheng, W.: Pulsed Eddy Current testing of carbon steel pipes, wall-thinning through insulation and cladding. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 31, 215–224 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10921-012-0137-9
Qiu, X., Zhang, P., Wei, J., Cui, X., Wei, C., Liu, L.: Defect classification by Pulsed Eddy Current technique in con-casting slabs based on spectrum analysis and wavelet decomposition. Sens. Actuators A 203, 272–81 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2013.09.004
Pan, M., He, Y., Tian, G., Chen, D., Luo, F.: PEC frequency band selection for locating defects in two-layer aircraft structures with air gap variations. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 62, 2849–2856 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2013.2239892
Peng, Y., Qiu, X., Wei, J., Li, C., Cui, X.: Defect classification using PEC responses based on power spectral density analysis combined with EMD and EEMD. NDT E Int. 78, 37–5 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ndt&eint.2015.11.003
Kiwa, T., Kawata, T., Yamada, H., Tsukada, K.: Fourier-transformed eddy current technique to visualize cross-sections of conductive materials. NDT E Int. 40, 363–367 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ndteint.2007.01.006
Buck, J., Underhill, P.R., Morelli, J.E., Krause, T.W.: Simultaneous multiparameter measurement in Pulsed Eddy Current steam generator data using artificial neural networks. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 65, 672–679 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2016.2514778
Dolapchiev, I., Brandisky, K.: Crack sizing by using Pulsed Eddy Current technique and neural network. Facta Univ. 19, 371–377 (2006). https://doi.org/10.2298/FUEE0603371D
Xie, S., Chen, Z., Chen, H., Wang, X., Takagi, T., Uchimoto, T.: Sizing of wall thinning defects using Pulsed Eddy Current testing signals based on a hybrid inverse analysis method. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 49, 1653–1656 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2012.2236827
Liu, Z., Forsyth, D.S., Lepine, B.A., Hammad, I., Farahbakhsh, B.: Investigation into classifying 3D Pulsed Eddy Current signals with neural network. Insight—Non-Destruct. Test. Cond. Monit. 45, 608–614 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1784/insi.45.9.608.52940
Arjun, V., Sasi, B., Rao, B.C.P., Mukhopadhyay, C.K., Jayakumar, T.: Optimisation of Pulsed Eddy Current probe for detection of sub-surface defects in stainless steel plates. Sens. Actuators A 226, 69–75 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2015.02.018
Sophian, A., Tian, G.Y., Taylor D Rudlin, J.: A feature extraction technique based on principal component analysis for Pulsed Eddy Current NDT. NDT E Int. 36, 37–41 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0963-8695(02)00069-5
Haykin, S.: Neural Networks and Learning Machines, 3rd edn. Pearson Education, New Jersey (2009)
Diniz, P.S.R., Silva, E.A.B., Netto, S,L.: Digital Signal Processing: System Analysis and Design, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2010)
Tian, L., Yin, C., Cheng, Y., Bai, L.: Successive approximation method for the measurement of thickness using Pulsed Eddy Current. IEEE Int. Instrum. Meas. Technol. Conf. 2015, 848–852 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/I2MTC.2015.7151379
Fletcher, R., Reeves, C.M.: Function minimization by conjugate gradients. Comput. J. 7, 149–154 (1964). https://doi.org/10.1093/comjnl/7.2.149
Simas Filho, E.F., Silva Junior, M.M., Farias, P.C.M.A., Albuquerque, M.C.S., Silva, I.C., Farias, C.T.T.: Flexible decision support system for ultrasound evaluation of fiber-metal laminates implemented in a DSP. NDT E Int. 79, 38–45 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ndteint.2015.12.001
Acknowledgements
The authors thank FAPESB for funding this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Larocca, C.B., Farias, C.T.T., Simas Filho, E.F. et al. Wall Thinning Characterization of Composite Reinforced Steel Tube Using Frequency-Domain PEC Technique and Neural Networks. J Nondestruct Eval 37, 44 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10921-018-0477-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10921-018-0477-1