Abstract
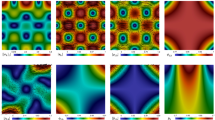
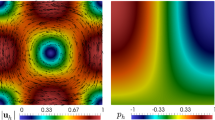
In this paper we introduce and analyze new Banach spaces-based mixed finite element methods for the stationary nonlinear problem arising from the coupling of the convective Brinkman-Forchheimer equations with a double diffusion phenomenon. Besides the velocity and pressure variables, the symmetric stress and the skew-symmetric vorticity tensors are introduced as auxiliary unknowns of the fluid. Thus, the incompressibility condition allows to eliminate the pressure, which, along with the velocity gradient and the shear stress, can be computed afterwards via postprocessing formulae depending on the velocity and the aforementioned new tensors. Regarding the diffusive part of the coupled model, and additionally to the temperature and concentration of the solute, their gradients and pseudoheat/pseudodiffusion vectors are incorporated as further unknowns as well. The resulting mixed variational formulation, settled within a Banach spaces framework, consists of a nonlinear perturbation of, in turn, a nonlinearly perturbed saddle-point scheme, coupled with a usual saddle-point system. A fixed-point strategy, combined with classical and recent solvability results for suitable linearizations of the decoupled problems, including in particular, the Banach-Nečas-Babuška theorem and the Babuška-Brezzi theory, are employed to prove, jointly with the Banach fixed-point theorem, the well-posedness of the continuous and discrete formulations. Both PEERS and AFW elements of order \(\ell \geqslant 0\) for the fluid variables, and piecewise polynomials of degree \(\leqslant \ell \) together with Raviart-Thomas elements of order \(\ell \) for the unknowns of the diffusion equations, constitute feasible choices for the Galerkin scheme. In turn, optimal a priori error estimates, including those for the postprocessed unknowns, are derived, and corresponding rates of convergence are established. Finally, several numerical experiments confirming the latter and illustrating the good performance of the proposed methods, are reported.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
References
Adams, S., Cockburn, B.: A mixed finite element for elasticity in three dimensions. J. Sci. Comput. 25, 515–521 (2005)
Alnaes, M.S., Blechta, J., Hake, J., Johansson, A., Kehlet, B., Logg, A., Richardson, C., Ring, J., Rognes, M.E., Wells, G.N.: The FEniCS project version 1.5. Arch. Numer. Softw. 3, 9–23 (2015)
Alzahrani, A.K.: Importance of Darcy-Forchheimer porous medium in \(3\)D convective flow of carbon nanotubes. Phys. Lett. A 382(40), 2938–2943 (2018)
Arnold, D.N., Brezzi, F., Douglas, J.: PEERS: a new mixed finite element method for plane elasticity. Jpn. J. Appl. Math. 1, 347–367 (1984)
Arnold, D.N., Falk, R.S., Winther, R.: Mixed finite element methods for linear elasticity with weakly imposed symmetry. Math. Comput. 76(260), 1699–1723 (2007)
Arnold, D.N., Winther, R.: Mixed finite elements for elasticity. Numer. Math. 92(3), 401–419 (2002)
Benavides, G.A., Caucao, S., Gatica, G.N., Hopper, A.A.: A new non-augmented and momentum-conserving fully-mixed finite element method for a coupled flow-transport problem. Calcolo 59(1), 6 (2022)
Bhatti, M.M., Zeeshan, A., Ellahi, R., Shit, G.C.: Mathematical modeling of heat and mass transfer effects on MHD peristaltic propulsion of two-phase flow through a Darcy-Brinkman-Forchheimer porous medium. Adv. Powder Technol. 29(5), 1189–1197 (2018)
Brezzi, F., Fortin, M.: Mixed and Hybrid Finite Element Methods. Springer Series in Computational Mathematics, vol. 15. Springer-Verlag, New York (1991)
Camaño, J., García, C., Oyarzúa, R.: Analysis of a momentum conservative mixed-FEM for the stationary Navier-Stokes problem. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 37(5), 2895–2923 (2021)
Camaño, J., Muñoz, C., Oyarzúa, R.: Numerical analysis of a dual-mixed problem in non-standard Banach spaces. Electron. Trans. Numer. Anal. 48, 114–130 (2018)
Caucao, S., Colmenares, E., Gatica, G.N., Inzunza, C.: A Banach spaces-based fully-mixed finite element method for the stationary chemotaxis-Navier-Stokes problem. Comput. Math. Appl. 145, 65–89 (2023)
Caucao, S., Esparza, J.: An augmented mixed FEM for the convective Brinkman-Forchheimer problem: a priori and a posteriori error analysis. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 438, 115517 (2024)
Caucao, S., Gatica, G.N., Gatica, L.F.: A Banach spaces-based mixed finite element method for the stationary convective Brinkman-Forchheimer problem. Calcolo. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10092-023-00544-2
Caucao, S., Gatica, G.N., Ortega, J.P.: A fully-mixed formulation in Banach spaces for the coupling of the steady Brinkman-Forchheimer and double-diffusion equations. ESAIM Math. Model. Numer. Anal. 55(6), 2725–2758 (2021)
Caucao, S., Gatica, G.N., Ortega, J.P.: A posteriori error analysis of a Banach spaces-based fully mixed FEM for double-diffusive convection in a fluid-saturated porous medium. Comput. Geosci. 27(2), 289–316 (2023)
Caucao, S., Gatica, G.N., Oyarzúa, R., Sánchez, N.: A fully-mixed formulation for the steady double-diffusive convection system based upon Brinkman-Forchheimer equations. J. Sci. Comput. 85(2), 44 (2020)
Caucao, S., Oyarzúa, R., Villa-Fuentes, S., Yotov, I.: A three-field Banach spaces-based mixed formulation for the unsteady Brinkman-Forchheimer equations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 394, 114895 (2022)
Celebi, A.O., Kalantarov, V.K., Ugurlu, D.: Continuous dependence for the convective Brinkman-Forchheimer equations. Appl. Anal. 84(9), 877–888 (2005)
Colmenares, E., Gatica, G.N., Moraga, S.: A Banach spaces-based analysis of a new fully-mixed finite element method for the Boussinesq problem. ESAIM Math. Model. Numer. Anal. 54(5), 1525–1568 (2020)
Correa, C.I., Gatica, G.N.: On the continuous and discrete well-posedness of perturbed saddle-point formulations in Banach spaces. Comput. Math. Appl. 117, 14–23 (2022)
Correa, C.I., Gatica, G.N., Ruiz-Baier, R.: New mixed finite element methods for the coupled Stokes and Poisson-Nernst-Planck equations in Banach spaces. ESAIM Math. Model. Numer. Anal. 57(3), 1511–1551 (2023)
Ern, A., Guermond, J.-L.: Theory and Practice of Finite Elements. Applied Mathematical Sciences, vol. 159. Springer-Verlag, New York (2004)
Faulkner, J., Hu, B.X., Kish, S., Hua, F.: Laboratory analog and numerical study of ground water flow and solute transport in a karst aquifer with conduit and matrix domains. J. Contam. Hydrol. 110(1–2), 34–44 (2009)
Gatica, G.N.: A simple introduction to the mixed finite element method. In: Theory and Applications. Springer Briefs in Mathematics. Springer, Cham (2014)
Gatica, G.N., Inzunza, C.: On the well-posedness of Banach spaces-based mixed formulations for the nearly incompressible Navier-Lamé and Stokes equations. Comput. Math. Appl. 102, 87–94 (2021)
Gatica, G.N., Núñez, N., Ruiz-Baier, R.: New non-augmented mixed finite element methods for the Navier-Stokes-Brinkman equations using Banach spaces. J. Numer. Math. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1515/jnma-2022-0073
Gatica, G.N., Núñez, N., Ruiz-Baier, R.: Mixed-primal methods for natural convection driven phase change with Navier-Stokes-Brinkman equations. J. Sci. Comput. 95(3), 79 (2023)
Gatica, G.N., Oyarzúa, R., Ruiz-Baier, R., Sobral, Y.: Banach spaces-based analysis of a fully-mixed finite element method for the steady-state model of fluidized beds. Comput. Math. Appl. 84, 244–276 (2021)
GDR-MiDi. On dense granular flows. Eur. J. Phys. E 14, 341–365 (2004)
Glowinski, R., Marrocco, A.: Sur l’approximation, par éléments finis d’ordre un, et la résolution, par pénalisations-dualité d’une classe de problémes de Dirichlet non lineaires. Rev. Fr. Autom. Inform. Rech. Opér. Anal Numér. 9(2), 41–76 (1975)
Hecht, F.: New development in FreeFem++. J. Numer. Math. 20, 251–265 (2012)
Kaloni, P.N., Guo, J.: Steady nonlinear double-diffusive convection in a porous medium based upon the Brinkman-Forchheimer model. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 204(1), 138–155 (1996)
Liu, D., Li, K.: Mixed finite element for two-dimensional incompressible convective Brinkman-Forchheimer equations. Appl. Math. Mech. (Engl. Ed.) 40(6), 889–910 (2019)
Lonsing, M., Verfuürth, R.: On the stability of BDMS and PEERS elements. Numer. Math. 99(1), 131–140 (2004)
Ôtani, M., Uchida, S.: Global solvability of some double-diffusive convection system coupled with Brinkman-Forchheimer equations. Lib. Math. 33(1), 79–107 (2013)
Safi, S., Benissaad, S.: Double-diffusive convection in an anisotropic porous layer using the Darcy-Brinkman-Forchheimer formulation. Arch. Mech. 70(1), 89–102 (2018)
Zhao, C., You, Y.: Approximation of the incompressible convective Brinkman-Forchheimer equations. J. Evol. Equ. 12(4), 767–788 (2012)
Zhuang, Y.J., Yu, H.Z., Zhu, Q.Y.: A thermal non-equilibrium model for \(3\)D double diffusive convection of power-law fluids with chemical reaction in the porous medium. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 115–B, 670–694 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This research was partially supported by ANID-Chile through Centro de Modelamiento Matemático (FB210005), Anillo of Computational Mathematics for Desalination Processes (ACT210087), and Fondecyt project 11220393; by Centro de Investigación en Ingeniería Matemática (CI\(^2\)MA), Universidad de Concepción; and by Grupo de Investigación en Análisis Numérico y Cálculo Científico (GIANuC\(^2\)), Universidad Católica de la Santísima Concepción.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Carrasco, S., Caucao, S. & Gatica, G.N. New Mixed Finite Element Methods for the Coupled Convective Brinkman-Forchheimer and Double-Diffusion Equations. J Sci Comput 97, 61 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-023-02371-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-023-02371-7
Keywords
- Convective Brinkman–Forchheimer
- Stress-vorticity tensor-velocity formulation
- Double diffusion
- Fixed point theory
- Mixed finite element methods
- A priori error analysis