Abstract
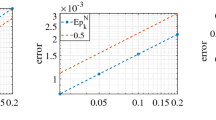
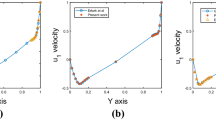
In this paper, we consider numerical analysis for a fully discrete scheme for the stochastic Stokes–Darcy equations with multiplicative noise. Implicit Euler scheme is used for the time discretization, and interior penalty discontinuous Galerkin (IPDG) scheme based on the BDM\(_1\)–P\(_0\) finite element space is used for the space discretization. Physical interface conditions are imposed to couple the fluid equations in free fluid and porous media regions. It is proved that the implicit Euler scheme for the stochastic Stokes–Darcy equations is unconditionally stable. Under usual assumptions for the multiplicative noise and regularity of the velocity, we present the optimal convergence analysis in both time and space discretizations. Moreover, our stability result and error estimates for the velocity are independent of pressure. Numerical results are given to verify the theoretical analysis.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this manuscript.
References
Ambartsumyan, I., Khattatov, E., Wang, C., Yotov, I.: Stochastic multiscale flux basis for Stokes–Darcy flows. J. Comput. Phys. 401, 109011 (2020)
Arbogast, T., Brunson, D.S.: A computational method for approximating a Darcy–Stokes system governing a vuggy porous media. Comput. Geosci. 11, 207–218 (2007)
Arbogast, T., Lehr, H.L.: Homogenization of a Darcy–Stokes system modeling vuggy porous media. Comput. Geosci. 10, 291–302 (2006)
Beavers, G.S., Joseph, D.D.: Boundary conditions at a naturally permeable wall. J. Fluid Mech. 30, 197–207 (1967)
Breit, D., Dogson, A.: Convergence rates for the numerical approximation of the 2D stochastic Navier–Stokes equations. Numer. Math. 147, 553–578 (2021)
Camano, J., Gatica, G.N., Oyarzua, R., Ruiz-Baier, R., Venegas, P.: New fully-mixed finite element methods for the Stokes–Darcy coupling. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 295, 362–395 (2015)
Cao, Y., Gunzburger, M., Hu, X., Hua, F., Wang, X., Zhao, W.: Finite element approximation for Stokes–Darcy flow with Beavers–Joseph interface conditions. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 47, 4239–4256 (2010)
Carelli, E., Hausenblas, E., Prohl, A.: Time-splitting methods to solve the stochastic incompressible Stokes equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 50, 2917–2939 (2012)
Carelli, E., Prohl, A.: Rates of convergence for discretizations of the stochastic incompressible Navier–Stokes equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 50, 2467–2496 (2012)
Chandesris, M., Jamet, D.: Boundary conditions at a planar fluid porous interface for a Poiseuille flow. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 49, 2137–2150 (2006)
Chen, H., Wang, X.-P.: A one-domain approach for modeling and simulation of free fluid over a porous media. J. Comput. Phys. 259, 650–671 (2014)
Ciarlet, P.G.: The Finite Element Method for Elliptic Problems. North-Holland, Amsterdam (1978)
Da Prato, G., Zabczyk, J.: Stochastic Equations in Infinite Dimensions. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1992)
Dixon, J., McKee, S.: Weakly singular Gronwall inequalities. ZAMM Z. Angew. Math. Mech. 66, 535–544 (1986)
Ervin, V.J., Jenkins, E.W., Sun, S.: Coupled generalized nonlinear Stokes flow with flow through a porous media. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 47, 929–952 (2009)
Feng, X., Prohl, A., Vo, L.: Optimally convergent mixed finite element methods for the stochastic Stokes equations. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 41, 2280–2310 (2021)
Feng, X., Qiu, H.: Analysis of fully discrete mixed finite element methods for time-dependent stochastic Stokes equations with multiplicative noise. J. Sci. Comput. 88, 1–25 (2021)
Feng, X., Vo, L.: Analysis of Chorin-type projection methods for the stochastic Stokes equations with general multiplicative noises. Stoch. PDE: Anal. Comp. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40072-021-00228-4
Gao, Y., He, X., Mei, L., Yang, X.: Decoupled, linear, and energy stable finite element method for the Cahn–Hilliard–Navier–Stokes–Darcy phase field model. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 40, B110–B137 (2018)
Goyeau, B., Lhuillier, D., Gobin, D., Velarde, M.G.: Momentum transport at a fluid–porous interface. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 46, 4071–4081 (2003)
Han, D., He, X., Wang, Q., Wu, Y.: Existence and weak-strong uniqueness of solutions to the Cahn–Hilliard–Navier–Stokes–Darcy system in superposed free flow and porous media. Nonlinear Anal. 211, 112411 (2021)
Hanspal, N.S., Waghode, A.N., Nassehi, V., Wakeman, R.J.: Numerical analysis of coupled Stokes/Darcy flow in industrial filtrations. Transp. Porous Media 64, 73–101 (2006)
Hausenblas, E., Randrianasolo, T.A.: Time-discretization of stochastic 2-D Navier–Stokes equations with a penalty-projection method. Numer. Math. 143, 339–378 (2019)
Heywood, J.G., Rannacher, R.: Finite element approximation of the nonstationary Navier–Stokes problem. I. Regularity of solutions and second-order error estimates for spatial discretization. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 19, 275–311 (1982)
Kanschat, G., Rivière, B.: A strongly conservative finite element method for the coupling of Stokes and Darcy flow. J. Comput. Phys. 229, 5933–5943 (2010)
Karper, T., Mardal, K.-A., Winther, R.: Unified finite element discretizations of coupled Darcy–Stokes flow. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 25, 311–326 (2009)
Kruse, R.: Strong and Weak Approximation of Semilinear Stochastic Evolution Equations. Springer, Berlin (2014)
Kuksin, S., Shirikyan, A.: Mathematics of Two-Dimensional Turbulence. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2012)
Kumar, P., Luo, P., Gaspar, F.J., Oosterlee, C.W.: A multigrid multilevel Monte Carlo method for transport in the Darcy–Stokes system. J. Comput. Phys. 371, 382–408 (2018)
Liu, W., Röckner, M.: Stochastic Partial Differential Equations: An Introduction. Springer, Berlin (2015)
Lord, G.J., Powell, C.E., Shardlow, T.: An Introduction to Computational Stochastic PDEs: Galerkin Approximation and Finite Elements. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2014)
Márquez, A., Meddahi, S., Sayas, F.-J.: Strong coupling of finite element methods for the Stokes–Darcy problem. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 35, 969–988 (2015)
Nield, D.A.: The Beavers-Joseph boundary condition and related matters: a historical and critical note. Trans. Porous Media 78, 537–540 (2009)
Nield, D.A., Bejan, A.: Convection in Porous Media, 3rd edn. Springer, New York (2006)
Roman, L.J., Sarkis, M.: Stochastic Galerkin method for elliptic SPDEs: a white noise approach. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B 6, 941–955 (2006)
Saffman, P.G.: On the boundary condition at the interface of a porous media. Stud. Appl. Math. 1, 93–101 (1971)
Tartakovsky, A.M., Tartakovsky, D.M., Meakin, P.: Stochastic Langevin model for flow and transport in porous media. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 044502 (2008)
Yang, Z., Li, X., He, X., Ming, J.: A stochastic collocation method based on sparse grids for a stochastic Stokes–Darcy model. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. S 15, 893–912 (2022)
Yang, Z., Ming, J., Qiu, C., Li, M., He, X.: A multigrid multilevel Monte Carlo method for Stokes–Darcy model with random hydraulic conductivity and Beavers–Joseph condition. J. Sci. Comput. 90, 68 (2022)
Zhang, D.: Stochastic Methods for Flow in Porous Media: Coping with Uncertainties. Academic Press, London (2002)
Funding
This work was supported by the NSF of China (Grant Nos. 12122115, 11771363, 12271457).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xiang, Y., Huang, C. & Chen, H. Optimal Convergence Analysis of a Fully Discrete Scheme for the Stochastic Stokes–Darcy Equations. J Sci Comput 94, 13 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-022-02057-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-022-02057-6
Keywords
- Stochastic Stokes–Darcy equations
- Multiplicative noise
- Wiener process
- Implicit scheme
- Stability estimate
- Convergence analysis
- IPDG scheme