Abstract
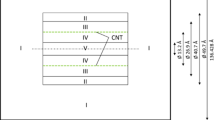
The separation of carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4) mixture is of considerable interest in order to purify natural gas, and one suggestion is that titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanotubes might be exploited to separate a gaseous mixture of methane and carbon dioxide. In this study, we employ both Coulomb’s law and the Lennard–Jones potential to determine the total energy of adsorption CO2 and CH4 into a TiO2 nanotube. The CH4 is a nonpolar molecule, and therefore the Coulombic interaction may be neglected. The total energy of the systems is evaluated utilizing the continuous approximation, which assumes that the two gas molecules are spheres of certain radii, while the tube is modelled as a cylinder. Further, both electrostatic and van der Waals potentials are determined and expressed in the exact analytical formulae. The numerical results predict that a single molecule of CO2 or CH4 can be encapsulated into the tube. On assuming both gases may form clusters with the same proportion of atom species, a cluster of CO2 will not be adsorbed into the tube when its radius exceeds 3.32Å. On the other hand, a cluster of CH4 can be encapsulated into an appropriate radius of TiO2 nanotube. These results indicate that TiO2 nanotubes may be useful in the purification of CH4.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babarao R., Hu Z., Jiang J., Chempath S., Sandler S.I.: Storage and separation of CO2 and CH4 in silicalite, C168 schwarzite, and IRMOF-1: A comparative study from Monte Carlo simulation. Langmuir 23(2), 659–666 (2007)
Huang L., Zhang L., Shao Q., Lu L., Lu X., Jiang S., Shen W.: Simulations of binary mixture adsorption of carbon dioxide and methane in carbon nanotubes: temperature, pressure, and pore size effects. J. Phys. Chem. C 111(32), 11912–11920 (2007)
Peng X., Cao D., Wang W.: Computational study on purification of CO2 from natural gas by C60 intercalated graphite. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 49(18), 8787–8796 (2010)
Matranga C., Chen L., Smith M., Bittner E., Johnson J.K., Bockrath B.: Trapped CO2 in carbon nanotube bundles. J. Phys. Chem. B 107(47), 12930–12941 (2003)
Choi B.-U., Choi D.-K., Lee Y.-W., Lee B.-K., Kim S.-H.: Adsorption equilibria of methane, ethane, ethylene, nitrogen, and hydrogen onto activated carbon. J. Chem. Eng. Data 48(3), 603–607 (2003)
M. Bienfait, P. Zeppenfeld, N. Dupont-Pavlovsky, M. Muris, M.R. Johnson, T. Wilson, M. DePies, O.E. Vilches, Thermodynamics and structure of hydrogen, methane, argon, oxygen, and carbon dioxide adsorbed on single-wall carbon nanotube bundles. Phys. Rev. B 70, 035410 (10pp), (2004)
Peng X., Wang W., Xue R., Shen Z.: Adsorption separation of CH4/CO2 on mesocarbon microbeads: experiment and modeling. AICHE J. 52(3), 994–1003 (2006)
Thorntona A.W., Hilder T.A., Hill A.J., Hill J.M.: Predicting gas diffusion regime within pores of different size, shape and composition. J. Membr. Sci. 336, 101–108 (2009)
Keller J.U., Staudt R.: Gas Adsorption Equilibria: Experimental Methods and Adsorptive Isotherms. Springer, New York (2004)
Catlow C.R.A., Smit B., van Santen R.A.: Computer Modelling of Microporous Materials. Elsevier, Ansterdam (2004)
Kasuga T., Hiramatsu M., Hoson A., Sekino T., Niihara K.: Formation of titanium oxide nanotube. Langmuir 14(12), 3160–3163 (1998)
X. Pan, C. Chen, K. Zhu, Z. Fan, TiO2 nanotubes infiltrated with nanoparticles for dye sensitized solar cells. Nanotechnology 22, 235402 (7pp), (2011)
Swamy V., Gale J.D.: Transferable variable-charge interatomic potential for atomistic simulation of titanium oxides. Phys. Rev. B 62(9), 5406–5412 (2000)
Mayo S.L., Olafson B.D., Goddard W.A. III: A generic force field for molecular simulations. J. Phys. Chem. 94, 8897–8909 (1999)
Hirschfelder J.O., Curtiss C.F., Bird R.B.: Molecular Theory of Gases and Liquids. Wiley, New York (1954)
D. Baowan, W. Triampo, D. Triampo, Encapsulation of TiO2 nanoparticles into single-walled carbon nanotubes. New J. Phys. 11, 093011 (13pp), (2009)
Cox B.J., Thamwattana N., Hill J.M.: Mechanics of atoms and fullerenes in single-walled carbon nanotubes. I. Acceptance and suction energies. Proc. R. Soc. A 463, 461–476 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baowan, D. Modelling of carbon dioxide: methane separation using titanium dioxide nanotubes. J Math Chem 50, 300–309 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10910-011-9917-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10910-011-9917-1