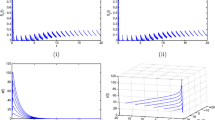
In this paper, we introduce and study a model of a Monod–Haldene type food chain chemostat with seasonally variably pulsed input and washout. We investigate the subsystem with substrate and prey and study the stability of the periodic solutions, which are the boundary periodic solutions of the system. The stability analysis of the boundary periodic solution yields an invasion threshold. By use of standard techniques of bifurcation theory, we prove that above this threshold there are periodic oscillations in substrate, prey and predator. Simple cycles may give way to chaos in a cascade of period-doubling bifurcations. Furthermore, bifurcation diagrams have shown that there exists complexity for the pulsed system including periodic doubling cascade, periodic halving cascade and Pitchfork bifurcations and tangent bifurcations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hale J.K., Somolinos A.S. (1983). J. Math. Biol. 18:255
Hsu S.B. (1980). J. Math. Biol. 18:115
Alessandra G., Oscar D.F., Sergio R. (1998). Bull. Math. Biol. 60:703
Mark K., Sayler G.S., Waltman T.W. (1992). Bull. Math. Biol. 54:619
Eric F., Mark K. (1993). Theorl. Popul. Biol. 44:203
Butler G.J., Hsu S.B., Waltman P. (1985). SIAM J. Appl. Math. 45:435
Lenas P., Pavlou S. (1995). Math. Biosci. 129:111
Pilyugin S.S., Waltman P. (1999). SIAM J. Appl. Math. 59:1157
D. Bainov and P. Simeonor, Impulsive differential equations: periodic solutions and applications. Pitman Monogr. Surv. Pure Appl. Math. 66 (1993).
V. Laksmikantham, D.D. Bainov and P.S. Simeonov, Theory of Impulsive Differential Equations (World Scientific Singapore 1989).
Tang S.Y., Chen L.S. (2002). J. Math. Biol. 44:185
Shulgin B., Stone L., Agur I. (1998). Bull. Math. Biol. 60:1
D’Onofrio A. (2002). Bull. Math. Biol. 60:1
Panetta J.C. (1996). Bull. Math. Biol. 58:425
Liu X.N., Chen L.S. (2003). Chaos Solitons Fractals 16:311
Shuwen Z., Lingzhen D., Lansun C. (2005). Chaos Solitons Fractals 23:631
Wang F., Zhang S., Chen L., Sun J. (2005). Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat. 6(2):169
Cushing J.M. (1997). SIAM J. Appl. Math. 10:384
May R.M. (1974). Science 186:645
Gakkhar S., Naji M.A. (2003). Chaos Solitons Fractal 18:229
Klebanoff A., Hastings A. (1994). J. Math. Biol. 32:427
Neubert M.G., Caswell H. (2000). J. Math. Biol. 41:103
Grebogi C., Ott E., York J.A. (1983). Physica D 7:181
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, F., Pang, G. & Hui, J. Analysis of a Monod–Haldene type food chain chemostat with seasonally variably pulsed input and washout. J Math Chem 43, 601–619 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10910-006-9213-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10910-006-9213-7