Abstract
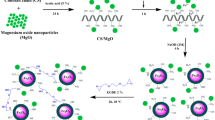
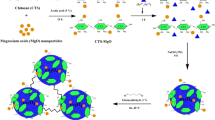
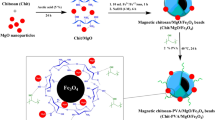
In this work, a magnetic cross-linked chitosan-benzil/organoclay/Fe3O4 biocomposite (CHI-BZI/OC/Fe3O4) was synthesized as a bio-adsorbent for the removal of remazol brilliant blue R (RBBR) dye from aquatic environment. The adsorption factors i.e., CHI-BZI/OC/Fe3O4 dosage, pH, and time were statistically optimized using the Box-Behnken design (BBD). The highest RBBR removal efficiency of 90.9% was achieved at a CHI-BZI/OC/Fe3O4 dosage of 0.1 g/100 mL, initial solution pH of 4.0, and contact time of 20 min. The RBBR adsorption onto the CHI-BZI/OC/Fe3O4 matched the pseudo-second-order kinetic (PSO). Moreover, equilibrium study was conducted and the best fit to the adsoption expsrimantal data was described by Langmuir isotherm model. The adsorption capacity of CHI-BZI/OC/Fe3O4 for RBBR was determined to be 102.9 mg/g. This work contributes to the advancement of environmentally friendly and sustainable methods for treating dye-contaminated water, showcasing the potential of biocomposite materials as effective adsorbents in the field of water purification.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
M.E. Mahmoud, A.M. El-Ghanam, S.R. Saad, Fast and efficient adsorptive capture of Congo red and Erythromycin pollutants by a novel nanobiosorbent from crosslinked nanosilica with nanobiochar and chitosan. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 158, 111557 (2023)
A.M. Hameed, Synthesis of Si/Cu Amorphous Adsorbent for Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue Dye from Aqueous Media. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 30(8), 2881–2889 (2020)
R. Al-Tohamy, S.S. Ali, F. Li, K.M. Okasha, Y.A.G. Mahmoud, T. Elsamahy, J. Sun, A critical review on the treatment of dye-containing wastewater: Ecotoxicological and health concerns of textile dyes and possible remediation approaches for environmental safety. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 231, 113160 (2022)
A. Kalra, A. Gupta, Recent advances in decolourization of dyes using iron nanoparticles: A mini review. Mater. Today: Proc. 36, 689–696 (2021)
A. Shahinpour, B. Tanhaei, A. Ayati, H. Beiki, M. Sillanpää, Binary dyes adsorption onto novel designed magnetic clay-biopolymer hydrogel involves characterization and adsorption performance: Kinetic, equilibrium, thermodynamic, and adsorption mechanism. J. Mol. Liq. 366, 120303 (2022)
A. Belcaid, B.H. Beakou, S. Bouhsina, A. Anouar, Insight into adsorptive removal of methylene blue, malachite green, and rhodamine B dyes by cassava peel biochar (Manihot esculenta Crantz) in single, binary, and ternary systems: competitive adsorption study and theoretical calculations. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 14, 7783–7806 (2022)
J. Hou, K. Wang, R. Weng, L. Li, Y. Liu, J. Sheng, Y. Song, Purification of dye-contaminated water using Si-doped mesoporous Fe3O4 prepared with rice husk SBA-15 as a template: behavior and mechanism. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 14, 985–999 (2022)
C. Lu, J. Yang, A. Khan, J. Yang, Q. Li, G. Wang, A highly efficient technique to simultaneously remove acidic and basic dyes using magnetic ion-exchange microbeads. J. Environ. Manage. 304, 114173 (2022)
T. Pei, M. Deng, C. Ma, H. Yan, A. Zhu, L. Ye, Q. Zhang, Loose nanofiltration membranes based on interfacial glutaraldehyde-amine polymerization for fast and highly selective dye/salt separation. Chem. Eng. J. 450, 138057 (2022)
M. Ikram, M. Naeem, M. Zahoor, M.M. Hanafiah, A.A. Oyekanmi, R. Ullah, N. Gulfam, Biological degradation of the azo dye basic orange 2 by Escherichia coli: A sustainable and ecofriendly approach for the treatment of textile wastewater. Water 14(13), 2063 (2022)
J. Kalita, B. Das, S.S. Dhar, Synergistic effect of iron and copper in hydroxyapatite nanorods for Fenton-like oxidation of organic dye. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 643, 128750 (2022)
U. Ewuzie, O.D. Saliu, K. Dulta, S. Ogunniyi, A.O. Bajeh, K.O. Iwuozor, J.O. Ighalo, A review on treatment technologies for printing and dyeing wastewater (PDW). J. Water Process Eng. 50, 103273 (2022)
S. Afzal, S. Hassan, Z. Imran, S. Aminullah. Chitosan Based Polymer Membrane Modified with CuO/Graphene Oxide Nanoparticles: Novel Synthesis, Characterization and Enhanced Methyl Orange Removal. J. Inorg. Organomet.Polym. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-024-03008-4
H. Zhu, S. Chen, H. Duan, J. He, Y. Luo, Removal of anionic and cationic dyes using porous chitosan/carboxymethyl cellulose-PEG hydrogels: Optimization, adsorption kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamics studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 231, 123213 (2023)
M.E. El-Naggar, E.K. Radwan, H.R. Rashdan, S.T. El-Wakeel, A.A. Koryam, A. Sabt, Simultaneous removal of Pb2+ and direct red 31 dye from contaminated water using N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-2-oxo-2 H-chromene-3-carboxamide loaded chitosan nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 12(29), 18923–18935 (2022)
A.S. Abdulhameed, A.H. Jawad, M. Ridwan, T. Khadiran, L.D. Wilson, Z.M. Yaseen, Chitosan/carbon-doped TiO2 composite for adsorption of two anionic dyes in solution and gaseous SO2 capture: experimental modeling and optimization. J. Polym. Environ. 30(11), 4619–4636 (2022)
A. Benettayeb, S. Ghosh, M. Usman, F.Z. Seihoub, I. Sohoo, C.H. Chia, M. Sillanpää, Some well-known alginate and chitosan modifications used in adsorption: A review. Water 14(9), 1353 (2022)
M. Keshvardoostchokami, M. Majidi, A. Zamani, B. Liu, A review on the use of chitosan and chitosan derivatives as the bio-adsorbents for the water treatment: Removal of nitrogen-containing pollutants. Carbohydr. Polym. 273, 118625 (2021)
U. Filipkowska, T. Jóźwiak, Application of chemically-cross-linked chitosan for the removal of Reactive Black 5 and Reactive Yellow 84 dyes from aqueous solutions. J. Polym. Eng. 33(8), 735–747 (2013)
N. I. Normi, A. S. Abdulhameed, S. N. Surip, Z. A. ALOthman, L. D. Wilson, A. H. Jawad. Benzil Schiff Base Side-Chain Polymer-Crosslinked Chitosan Via Hydrothermal Process for Reactive Orange 16 Dye Removal: An Optimized and Comparative Study with Chitosan. J. Polym. Environ. 31(5) (2023) 1986–2004.
E. M. Abd El-Monaem, A. S. Eltaweil, H. M. Elshishini, M. Hosny, M. M. Abou Alsoaud, N. F. Attia, A. M. Omer. Sustainable adsorptive removal of antibiotic residues by chitosan composites: An insight into current developments and future recommendations. Arab. J. Chem. 15(5) (2022) 103743.
X.Q. Liu, X.X. Zhao, Y. Liu, T.A. Zhang, Review on preparation and adsorption properties of chitosan and chitosan composites. Polym. Bull. 79(4), 2633–2665 (2022)
S. Pandey, S.B. Mishra, Organic–inorganic hybrid of chitosan/organoclay bionanocomposites for hexavalent chromium uptake. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 361(2), 509–520 (2011)
S. Mao, M. Gao, Functional organoclays for removal of heavy metal ions from water: A review. J. Mol. Liquids 334, 116143 (2021)
T. Shen, M. Gao, Gemini surfactant modified organo-clays for removal of organic pollutants from water: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 375, 121910 (2019)
T. De Oliveira, M. Boussafir, L. Fougère, E. Destandau, Y. Sugahara, R. Guégan, Use of a clay mineral and its nonionic and cationic organoclay derivatives for the removal of pharmaceuticals from rural wastewater effluents. Chemosphere 259, 127480 (2020)
M.B. de Farias, M.P. Spaolonzi, M.G.C. Silva, M.G.A. Vieira, Fixed-bed adsorption of bisphenol A onto organoclay: Characterization, mathematical modelling and theoretical calculation of DFT-based chemical descriptors. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 9(5), 106103 (2021)
K. Fang, L. Deng, J. Yin, T. Yang, J. Li, W. He, Recent advances in starch-based magnetic adsorbents for the removal of contaminants from wastewater: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 218, 909–929 (2022)
G.D.V. Brião, J.R. de Andrade, M.G.C. da Silva, M.G.A. Vieira, Removal of toxic metals from water using chitosan-based magnetic adsorbents. A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 18, 1145–1168 (2020)
A.R. Sedaghatian, A. Marjani, A.H. Joshaghani, R. Mohammad-Rezaei, Synthesis of magnetic graphene quantum dots–chitosan nanocomposite: an efficient adsorbent for removal of Pb2+ from aqueous solution. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 19(11), 11447–11458 (2022)
K.S. Sing, Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity (Recommendations 1984). Pure Appl. Chem. 57(4), 603–619 (1985)
S. Korde, S. Tandekar, R.M. Jugade, Novel mesoporous chitosan-zirconia-ferrosoferric oxide as magnetic composite for defluoridation of water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 8(5), 104360 (2020)
K. Ssekatawa, D.K. Byarugaba, E.M. Wampande, T.N. Moja, E. Nxumalo, M. Maaza, J.B. Kirabira, Isolation and characterization of chitosan from Ugandan edible mushrooms. Nile perch scales and banana weevils for biomedical applications. Sci. Rep. 11(1), 4116 (2021)
M.A. Hefnawy, S.S. Medany, R.M. El-Sherif, S.A. Fadlallah, Green synthesis of NiO/Fe3O4@ chitosan composite catalyst based on graphite for urea electro-oxidation. Mater. Chem. Phys. 290, 126603 (2022)
S. Barkhordari, A. Alizadeh, M. Yadollahi, H. Namazi, One-pot synthesis of magnetic chitosan/iron oxide bio-nanocomposite hydrogel beads as drug delivery systems. Soft Mater. 19(4), 373–381 (2021)
Z.M. Şenol, N. Gürsoy, S. Şimşek, A. Özer, N. Karakuş, Removal of food dyes from aqueous solution by chitosan-vermiculite beads. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 148, 635–646 (2020)
U. Malayoglu, Removal of heavy metals by biopolymer (chitosan)/nanoclay composites. Sep. Sci. Technol. 53(17), 2741–2749 (2018)
E. Asgari, A. Sheikhmohammadi, J. Yeganeh, Application of the Fe3O4-chitosan nano-adsorbent for the adsorption of metronidazole from wastewater: Optimization, kinetic, thermodynamic and equilibrium studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 164, 694–706 (2020)
T. Thomas, A.K. Thalla, Nutmeg seed shell biochar as an effective adsorbent for removal of remazol brilliant blue reactive dye: kinetic, isotherm, and thermodynamic study. Energy Sources, Part A: Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects 44(1), 893–911 (2022)
Z. Alhalili, Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles CuO NPs from Eucalyptus Globoulus leaf extract: Adsorption and design of experiments. Arab. J. Chem. 15(5), 103739 (2022)
B.F. Shahandashty, N. Fallah, B. Nasernejad, Industrial wastewater treatment: Case study on copper removal from colloidal liquid using coagulation. J. Water Process Eng. 53, 103712 (2023)
A.H. Jawad, B.H. Hameed, A.S. Abdulhameed, Synthesis of biohybrid magnetic chitosan-polyvinyl alcohol/MgO nanocomposite blend for remazol brilliant blue R dye adsorption: Solo and collective parametric optimization. Polym. Bull. 80(5), 4927–4947 (2023)
Y. Ji, W. Zhang, H. Yang, F. Ma, F. Xu, Green synthesis of poly (pyrrole methane) for enhanced adsorption of anionic and cationic dyes from aqueous solution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 590, 396–406 (2021)
S. Lagergren, Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption geloster stoffe. Vet. Akad. Handl. 24, 1–39 (1898)
Y.S. Ho, G. McKay, Sorption of dye from aqueous solution by peat. Chem. Eng. J. 70, 115–124 (1998)
P.S. Pauletto, J.O. Gonçalves, L.A.A. Pinto, G.L. Dotto, N.P.G. Salau, Single and competitive dye adsorption onto chitosan–based hybrid hydrogels using artificial neural network modeling. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 560, 722–729 (2020)
I. Langmuir, The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 40, 1361–1403 (1918)
H.M.F. Freundlich, Over the adsorption in solution. J. Phys. Chem. 57, 385–471 (1906)
M.I. Temkin, Kinetics of ammonia synthesis on promoted iron catalysts. Acta Physiochim. URSS. 12, 327–356 (1940)
S. Pai, M.S. Kini, G. Rangasamy, R. Selvaraj, Mesoporous calcium hydroxide nanoparticle synthesis from waste bivalve clamshells and evaluation of its adsorptive potential for the removal of Acid Blue 113 dye. Chemosphere 313, 137476 (2022)
Z. M. Zain, A. S. Abdulhameed, A. H. Jawad, Z. A. ALOthman, Z. M. Yaseen. A pH-sensitive surface of chitosan/sepiolite clay/algae biocomposite for the removal of malachite green and remazol brilliant blue R dyes: Optimization and adsorption mechanism study. J. Polym. Environ. 31(2) (2023) 501–518.
D.N. Phan, R.A. Rebia, Y. Saito, D. Kharaghani, M. Khatri, T. Tanaka, I.S. Kim, Zinc oxide nanoparticles attached to polyacrylonitrile nanofibers with hinokitiol as gluing agent for synergistic antibacterial activities and effective dye removal. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 85, 258–268 (2020)
V. Nair, A. Panigrahy, R. Vinu, Development of novel chitosan–lignin composites for adsorption of dyes and metal ions from wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 254, 491–502 (2014)
B. Balci, F.E. Erkurt, M. Basibuyuk, F. Budak, Z. Zaimoglu, E.S. Turan, S. Yilmaz, Removal of Reactive Blue 19 from simulated textile wastewater by Powdered Activated Carbon/Maghemite composite. Sep. Sci. Technol. 57(9), 1408–1426 (2022)
M. Abbasi, Synthesis and characterization of magnetic nanocomposite of chitosan/ SiO2/carbon nanotubes and its application for dyes removal. J. Clean. Prod. 145, 105–113 (2017)
M. Khapre, A. Shekhawat, D. Saravanan, S. Pandey, R. Jugade, Mesoporous Fe–Al-doped cellulose for the efficient removal of reactive dyes. Mater. Adv. 3(7), 3278–3285 (2022)
M. M. Silva, M. M. Oliveira, M. C. Avelino, M. G. Fonseca, R. K. Almeida, E. C. Silva Filho. Adsorption of an industrial anionic dye by modified-KSF-montmorillonite: evaluation of the kinetic, thermodynamic and equilibrium data. Chem. Eng. J. 203 (2012) 259–268.
C.J. Mate, S. Mishra, Synthesis of borax cross-linked Jhingan gum hydrogel for remediation of Remazol Brilliant Blue R (RBBR) dye from water: adsorption isotherm, kinetic, thermodynamic and biodegradation studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 151, 677–690 (2020)
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Faculty of Applied Sciences, Universiti Teknologi MARA (UiTM) Shah Alam, Malaysia for the research facilities. The author Ahmad Hapiz is thankful to the Government of West Nusa Tenggara (NTB) Province, Indonesia, as well as the Education Development Institute (LPP) NTB and the Regional Research and Innovation Agency (BRIDA) NTB for providing a fully funded scholarship. The author (Ruihong Wu) would like to thank Hengshui University for its scientific research funding (2023ZRZ01). The author (Zeid A. ALOthman) is grateful to the Researchers Supporting Project No. (RSP2024R1), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Funding
The author (Ruihong Wu) would like to thank Hengshui University for its scientific research funding (2023ZRZ01). The author (Zeid A. ALOthman) is thankful to the Researchers Supporting Project No. (RSP2024R1), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Ali H. Jawad, Ahmed Saud Abdulhameed, Ahmad Hapiz, Salis Awal Musa, Ruihong Wu, and Zeid A. ALOthman. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Ahmed Saud Abdulhameed, Ahmad Hapiz, Ali H. Jawad, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent to Publish
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jawad, A.H., Abdulhameed, A.S., Hapiz, A. et al. Fabrication of Magnetic Chitosan-Benzil Biopolymer with Organoclay for Remazol Brilliant Blue R Dye Removal: a Statistical Modeling and Adsorption Mechanism. J Inorg Organomet Polym (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-024-03120-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-024-03120-5