Abstract
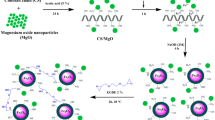
A new biocomposite cross-linked glutaraldehyde-chitosan/MgO/Fe3O4 (CTS-GL/MgO/Fe3O4) adsorbent with magneto-responsiveness was prepared and applied for the removal of reactive blue 19 (RB-19), a synthetic textile dye. The prepared CTS-GL/MgO/Fe3O4 was structurally characterized using spectroscopic (XRD, FTIR, SEM–EDX), and its physicochemical properties were evaluated using potentiometry and pHpzc analyses. The influence of various adsorption parameters (A: CTS-GL/MgO/Fe3O4 dosage; B: initial solution pH; C: process temperature; and D: contact time) on the removal efficiency of RB-19 was statistically optimized using Box-Behnken design (BBD). The analysis of variance (ANOVA) indicates the presence of five significant statistical interactions between the adsorption parameters, as follows: AB, AC, AD, BC, and BD. The equilibrium dye uptake by the Freundlich isotherm model indicates heterogeneous adsorption, while the kinetics of adsorption was well-described by the pseudo-second-order model. The maximum adsorption capacity of CTS-GL/MgO/Fe3O4 towards RB-19 was 193.2 mg/g at 45 °C. This work highlights the development of a recoverable magnetic biocomposite adsorbent with favourable adsorption capacity towards a model textile dye with good separation ability by using an external magnetic field. Moreover, separation of the magnetic adsorbents from the treated solution is easy and convenient apply to continuous flow systems, which is highly preferred for industrial applications.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Jawad AH, Abdulhameed AS, Wilson LD, Hanafah MAKM, Nawawi WI, ALOthman ZA, Khan MR (2021) J Polym Environ 29:2855–2868
Tkaczyk A, Mitrowska K, Posyniak A (2020) Synthetic organic dyes as contaminants of the aquatic environment and their implications for ecosystems: a review. Sci Total Environ 717:137222
Rafaie HA, Yusop NFM, Azmi NF, Abdullah NS, Ramli NIT (2021) Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye solution using different amount of ZnO as a photocatalyst. Sci Lett 15(1):1–12
Rashid RA, Ishak MAM, Mohammed K (2018) Adsorptive removal of methylene blue by commercial coconut shell activated carbon. Sci Lett 12(1):77–101
Malek NNA, Mohammed IA, Reghioua A, Yousif E, Jawad AH (2020) Removal of reactive red 4 dye using chitosan- epichlorohydrin/ TiO2 nanocomposite: application of response surface methodology. Sci Lett 14(1):96–108
Benkhaya S, M’rabet S, El Harfi A (2020) Classifications, properties, recent synthesis and applications of azo dyes. Heliyon 6(1):03271
Li Y, Li Z, Xia Y, Li H, Shi J, Zhang A, Gao L (2020) Fabrication of ternary AgBr/BiPO4/g-C3N4 heterostructure with dual Z-scheme and its visible light photocatalytic activity for Reactive Blue 19. Environ Res 192:110260
Ao C, Zhao J, Li Q, Zhang J, Huang B, Wang Q, Lu C (2020) Biodegradable all-cellulose composite membranes for simultaneous oil/water separation and dye removal from water. Carbohydr Polym 250:116872
Cojocaru C, Clima L (2020) Polymer assisted ultrafiltration of AO7 anionic dye from aqueous solutions: experimental design, multivariate optimization, and molecular docking insights. J Membr Sci 604:118054
Feng Q, Gao B, Yue Q, Guo K (2020) Flocculation performance of papermaking sludge-based flocculants in different dye wastewater treatment: comparison with commercial lignin and coagulants. Chemosphere 262:128416
Varjani S, Rakholiya P, Ng HY, You S, Teixeira JA (2020) Microbial degradation of dyes: an overview. Bioresour Technol 314:123728
Ghaffari Y, Gupta NK, Bae J, Kim KS (2020) One-step fabrication of Fe2O3/Mn2O3 nanocomposite for rapid photodegradation of organic dyes at neutral pH. J Mol Liq 315:113691
Jawad AH, Abdulhameed AS, Reghioua A, Yaseen ZM (2020) Zwitterion composite chitosan-epichlorohydrin/zeolite for adsorption of methylene blue and reactive red 120 dyes. Int J Biol Macromol 163:756–765
Surip SN, Abdulhameed AS, Garba ZN, Syed-Hassan SSA, Ismail K, Jawad AH (2020) H2SO4-treated Malaysian low rank coal for methylene blue dye decolourization and cod reduction: Optimization of adsorption and mechanism study. Surf Interface 21:100641
Upadhyay U, Sreedhar I, Singh SA, Patel CM, Anitha KL (2020) Recent advances in heavy metal removal by chitosan based adsorbents. Carbohydr Polym 251:117000
Liu C, Bai R (2014) Recent advances in chitosan and its derivatives as adsorbents for removal of pollutants from water and wastewater. Curr Opin Chem Eng 4:62–70
Jawad AH, Abdulhameed AS, Malek NNA, ALOthman ZA (2020) Statistical optimization and modeling for color removal and COD reduction of reactive blue 19 dye by mesoporous chitosan-epichlorohydrin/kaolin clay composite. Int J Biol Macromol 164:4218–4230
Saheed IO, Da OW, Suah FBM (2021) Chitosan modifications for adsorption of pollutants-a review. J Hazard Mater. 408:124889
Gul K, Sohni S, Waqar M, Ahmad F, Norulaini NN, Ak MO (2016) Functionalization of magnetic chitosan with graphene oxide for removal of cationic and anionic dyes from aqueous solution. Carbohydr Polym 152:520–531
Jawad AH, Mubarak NSA, Abdulhameed AS (2020) Tunable Schiff’s base-cross-linked chitosan composite for the removal of reactive red 120 dye: adsorption and mechanism study. Int J Biol Macromol 142:732–741
Vakili M, Mojiri A, Zwain HM, Yuan J, Giwa AS, Wang W, Yu G (2019) Effect of beading parameters on cross-linked chitosan adsorptive properties. React Funct Polym 144:104354
Jawad AH, Mubarak NSA, Abdulhameed AS (2020) Hybrid crosslinked chitosan-epichlorohydrin/TiO2 nanocomposite for reactive red 120 dye adsorption: kinetic, isotherm, thermodynamic, and mechanism study. J Polym Environ 28:624–637
Nouh SA, Alsobhi BO, Abou Elfadl A, Benthami K, Khalil KD, Riyadh SM (2020) Structure and thermal investigation of the effect of laser radiation in Chitosan-MgO nanocomposite film. Radiat Eff Defects Solids 175(5–6):422–432
Nga NK, Chau NTT, Viet PH (2020) Preparation and characterization of a chitosan/MgO composite for the effective removal of reactive blue 19 dye from aqueous solution. J Sci 201–202:68–93
Haldorai Y, Shim JJ (2014) An efficient removal of methyl orange dye from aqueous solution by adsorption onto chitosan/MgO composite: a novel reusable adsorbent. Appl Surf Sci 292:447–453
Wang Y, Cen C, Chen J, Fu L (2020) MgO/carboxymethyl chitosan nanocomposite improves thermal stability, waterproof and antibacterial performance for food packaging. Carbohydra Polym 236:116078
Huang YZ, Ji YR, Kang ZW, Li F, Ge SF, Yang DP, Fan XQ (2020) Integrating eggshell-derived CaCO3/MgO nanocomposites and chitosan into a biomimetic scaffold for bone regeneration. Chem Eng J 395:125098
Sundaram CS, Viswanathan N, Meenakshi S (2009) Defluoridation of water using magnesia/chitosan composite. J Hazard Mater 163(2–3):618–624
Patel MK, Ali MA, Zafaryab M, Agrawal VV, Rizvi MMA, Ansari ZA, Malhotra BD (2013) Biocompatible nanostructured magnesium oxide-chitosan platform for genosensing application. Biosens Bioelectron 45:181–188
Riyadh SM, Khalil KD, Aljuhani A (2018) Chitosan-MgO nanocomposite: one pot preparation and its utility as an ecofriendly biocatalyst in the synthesis of thiazoles and [1, 3, 4] thiadiazoles. Nanomaterials 8(11):928
Reddy DHK, Lee SM (2013) Application of magnetic chitosan composites for the removal of toxic metal and dyes from aqueous solutions. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 201:68–93
Dalvand A, Nabizadeh R, Ganjali MR, Khoobi M, Nazmara S, Mahvi AH (2016) Modeling of Reactive Blue 19 azo dye removal from colored textile wastewater using L-arginine-functionalized Fe3O4 nanoparticles: optimization, reusability, kinetic and equilibrium studies. J Magn Magn Mater 404:179–189
Vieira RS, Beppu MM (2006) Interaction of natural and crosslinked chitosan membranes with Hg (II) ions. Colloids Surf A 279(1–3):196–207
Hu YY, Pan C, Zheng X, Hu F, Xu L, Xu G, Peng X (2020) Prediction and optimization of adsorption properties for Cs+ on NiSiO@ NiAlFe LDHs hollow spheres from aqueous solution: kinetics, isotherms, and BBD model. J Hazard Mater 401:123374
Sing KS (1985) Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity (Recommendations 1984). Pure Appl Chem 57(4):603–619
Chen L, Wu P, Chen M, Lai X, Ahmed Z, Zhu N, Liu T (2018) Preparation and characterization of the eco-friendly chitosan/vermiculite biocomposite with excellent removal capacity for cadmium and lead. Appl Clay Sci 159:74–82
dos Santos JM, Pereira CR, Pinto LAA, Frantz T, Lima ÉC, Foletto EL, Dotto GL (2019) Synthesis of a novel CoFe2O4/chitosan magnetic composite for fast adsorption of indigotine blue dye. Carbohydr Polym 217:6–14
Yang Y, Ali N, Khan A, Khan S, Khan S, Khan H, Bilal M (2020) Chitosan-capped ternary metal selenide nanocatalysts for efficient degradation of carcinogenic Congo red dye in sunlight irradiation. Int J Biol Macromol 167:169–181
Jaafari J, Barzanouni H, Mazloomi S, Farahani NAA, Sharafi K, Soleimani P, Haghighat GA (2020) Effective adsorptive removal of reactive dyes by magnetic chitosan nanoparticles: kinetic, isothermal studies and response surface methodology. Int J Boil Macromol 164:344–355
Naeeji N, Shahbazi Y, Shavisi N (2020) Effect of gamma irradiation on physico-mechanical and structural properties of basil seed mucilage-chitosan films containing Ziziphora clinopodioides essential oil and MgO nanoparticles for rainbow trout packaging. J Food Process Preserv 44(10):14781
Pereira MBB, França DB, Araújo RC, Silva Filho EC, Rigaud B, Fonseca MG, Jaber M (2020) Amino hydroxyapatite/chitosan hybrids reticulated with glutaraldehyde at different pH values and their use for diclofenac removal. Carbohyd Polym 236:116036
Jawad AH, Abdulhameed AS (2020) Facile synthesis of crosslinked chitosan-tripolyphosphate/kaolin clay composite for decolourization and COD reduction of remazol brilliant blue R dye: optimization by using response surface methodology. Colloids Surf A 605:125329
Jawad AH, Abdulhameed AS (2020) Statistical modeling of methylene blue dye adsorption by high surface area mesoporous activated carbon from bamboo chip using KOH-assisted thermal activation. Energy Ecol Environ 5(6):456–469
Abdulhameed AS, Mohammad AT, Jawad AH (2019) Application of response surface methodology for enhanced synthesis of chitosan tripolyphosphate/TiO2 nanocomposite and adsorption of reactive orange 16 dye. J Clean Prod 232:43–56
Jawad AH, Malek NNA, Abdulhameed AS, Razuan R (2020) Synthesis of magnetic chitosan-fly Ash/Fe3O4 composite for adsorption of reactive orange 16 Dye: optimization by Box-Behnken design. J Polym Environ 28(3):1068–1082
Kausar A, Sher F, Hazafa A, Javed A, Sillanpää M, Iqbal M (2020) Biocomposite of sodium-alginate with acidified clay for wastewater treatment: kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. Int J Biol Macromol 161:1272–1285
Kalhori EM, Al-Musawi TJ, Ghahramani E, Kazemian H, Zarrabi M (2017) Enhancement of the adsorption capacity of the light-weight expanded clay aggregate surface for the metronidazole antibiotic by coating with MgO nanoparticles: studies on the kinetic, isotherm, and effects of environmental parameters. Chemosphere 175:8–20
Njoku VO, Islam MA, Asif M, Hameed BH (2014) Preparation of mesoporous activated carbon from coconut frond for the adsorption of carbofuran insecticide. J Anal Appl Pyrol 110:172–180
Lagergren S (1898) Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption geloster stoffe. Vet Akad Handl 24:1–39
Ho YS, McKay G (1998) Sorption of dye from aqueous solution by peat. Chem Eng J 70:115–124
Huang L, Yang Z, Lei D, Liu F, He Y, Wang H, Luo J (2020) Experimental and modeling studies for adsorbing different species of fluoride using lanthanum-aluminum perovskite. Chemosphere 263:128089
Langmuir I (1918) The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J Am Chem Soc 40:1361–1403
Freundlich HMF (1906) Over the adsorption in solution. J Phys Chem 57:385–471
Temkin MI (1940) Kinetics of ammonia synthesis on promoted iron catalysts. Acta Physiochim URSS 12:327–356
Chen J, Hu H, Yang J, Xue H, Tian Y, Fan K, Liu Y (2020) Removal behaviors and mechanisms for series of azo dye wastewater by novel nano constructed macro-architectures material. Bioresour Technol 322:124556
Vijayaraghavan K, Won SW, Yun YS (2009) Treatment of complex Remazol dye effluent using sawdust-and coal-based activated carbons. J Hazard Mater 167(1–3):790–796
Janaki V, Oh BT, Shanthi K, Lee KJ, Ramasamy AK, Kamala-Kannan S (2012) Polyaniline/chitosan composite: an eco-friendly polymer for enhanced removal of dyes from aqueous solution. Synth Met 162(11–12):974–980
Phan DN, Rebia RA, Saito Y, Kharaghani D, Khatri M, Tanaka T, Kim IS (2020) Zinc oxide nanoparticles attached to polyacrylonitrile nanofibers with hinokitiol as gluing agent for synergistic antibacterial activities and effective dye removal. J Ind Eng Chem 85:258–268
Nair V, Panigrahy A, Vinu R (2014) Development of novel chitosan–lignin composites for adsorption of dyes and metal ions from wastewater. Chem Eng J 254:491–502
Abbasi M (2017) Synthesis and characterization of magnetic nanocomposite of chitosan/ SiO2/carbon nanotubes and its application for dyes removal. J Clean Prod 145:105–113
Chinoune K, Bentaleb K, Bouberka Z, Nadim A, Maschke U (2016) Adsorption of reactive dyes from aqueous solution by dirty bentonite. Appl Clay Sci 123:64–75
Silva MM, Oliveira MM, Avelino MC, Fonseca MG, Almeida RK, Silva Filho EC (2012) Adsorption of an industrial anionic dye by modified-KSF-montmorillonite: evaluation of the kinetic, thermodynamic and equilibrium data. Chem Eng J 203:259–268
Mate CJ, Mishra S (2020) Synthesis of borax cross-linked Jhingan gum hydrogel for remediation of Remazol Brilliant Blue R (RBBR) dye from water: adsorption isotherm, kinetic, thermodynamic and biodegradation studies. Int J Biol Macromol 151:677–690
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Ministry of Higher Education (MOHE), Malaysia, for funding this project under Fundamental Research Grant Scheme (FRGS) no. (Ref: FRGS/1/2019/STG01/UITM/02/3). The authors would like to thank the Faculty of Applied Sciences, Universiti Teknologi MARA, Shah Alam for all facilities. The authors would like to thank Mrs. Nurfarah Farini Binti Muhamad Kamarazzaman, Penolong Pegawai Sains (Assistant Science Officer) at Applied Sciences, Universiti Teknologi MARA, Shah Alam for facilitating XRD analysis. Zeid A. ALOthman is grateful to the Researchers Supporting Project No. (RSP-2021/1), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Funding
This work was supported by Ministry of Higher Education (MOHE) under Fundamental Research Grant Scheme (FRGS) no. (Ref: FRGS/1/2019/STG01/ UITM/02/3), and Researchers Supporting Project No. (RSP-2021/1), King Saud University, Riyadh Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by AHJ, RS, ASA, SSAS-H, ZAA, LDW. The first draft of the manuscript was written by AHJ, RS, ASA and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jawad, A.H., Rangabhashiyam, S., Abdulhameed, A.S. et al. Process Optimization and Adsorptive Mechanism for Reactive Blue 19 Dye by Magnetic Crosslinked Chitosan/MgO/Fe3O4 Biocomposite. J Polym Environ 30, 2759–2773 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-022-02382-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-022-02382-9