Abstract
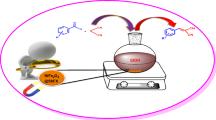
Pristine magnesium spinel ferrite nanoparticles (MgFe2O4, MNPs) were fabricated via sol–gel auto combustion and elucidated by XRD, SEM, EDAX, TEM, FTIR, BET and VSM for structural and physical characteristics. Fabricated MgFe2O4 MNPs found to be an efficient, robust and magnetically separable reusable heterogeneous catalyst for one pot three component solvent free synthesis of biologically important 1,4-dihydropyridines (1, 4 DHP’s) via Hantzsch condensation reaction. This convention was effectively appropriate to an extensive variety physically distinct aryl-aldehydes with ethyl acetoacetate and ammonium acetate to manage the required 1,4-dihydropyridines (1, 4 DHP’s) derivatives. The structural investigations approved the sustainability and reusability of the MgFe2O4, MNPs towards current organic reactions. The novelties of this protocol are operational cleanness, short reaction time, nontoxic, inexpensive and magnetically separable heterogeneous catalyst may perhaps easily be recycled deprived of remarkable decline in catalytic performance.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The synthetic procedures, characterization, and spectral data supporting this article have been uploaded as part of the Electronic supplementary information.
References
D. Das, Multicomponent Reactions in Organic Synthesis Using Copper-Based Nanocatalysts. ChemistrySelect 1, 1959–1980 (2016)
R.S. Varma, Greener and sustainable trends in synthesis of organics and nanomaterials. ACS Publications 4(11), 5866–5878 (2016)
M. Kaushik, A. Moores, New trends in sustainable nanocatalysis: emerging use of earth abundant metals, current opinion in green and sustainable. Chemistry 7, 39–45 (2017)
M.B. Gawande, R. Luque, R. Zboril, The rise of magnetically recyclable nanocatalysts. ChemCatChem 6, 3312–3313 (2014)
A. Maleki, M. Kamalzare, M. Aghaei, Efficient one-pot four-component synthesis of 1, 4-dihydropyridines promoted by magnetite/chitosan as a magnetically recyclable heterogeneous nanocatalyst. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 5, 95–105 (2015)
R. Hudson, Y. Feng, R.S. Varma, A. Moores, Bare magnetic nanoparticles: sustainable synthesis and applications in catalytic organic transformations. Green Chem. 16, 4493–4505 (2014)
R.M. Borade, S.B. Somvanshi, S.B. Kale, R.P. Pawar, K. Jadhav, Spinel zinc ferrite nanoparticles: an active nanocatalyst for microwave irradiated solvent free synthesis of chalcones. Mater. Res. Express 7, 016116 (2020)
A. Hilgeroth, H. Lilie, Structure-activity relationships of first bishydroxymethyl-substituted cage dimeric 4-aryl-1, 4-dihydropyridines as HIV-1 protease inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 38, 495–499 (2003)
C. Han, W. Meng, H. Liu, Y. Liu, J. Tao, DMAP-catalyzed four-component one-pot synthesis of highly functionalized spirooxindole-1, 4-dihydropyridines derivatives in aqueous ethanol. Tetrahedron 70, 8768–8774 (2014)
N. Edraki, A.R. Mehdipour, M. Khoshneviszadeh, R. Miri, Dihydropyridines: evaluation of their current and future pharmacological applications. Drug Discov. Today 14, 1058–1066 (2009)
G.W. Zamponi, Antagonist binding sites of voltage-dependent calcium channels. Drug Dev. Res. 42, 131–143 (1997)
A. Vijesh, A.M. Isloor, S. Peethambar, K. Shivananda, T. Arulmoli, N.A. Isloor, Hantzsch reaction: synthesis and characterization of some new 1, 4-dihydropyridine derivatives as potent antimicrobial and antioxidant agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 46, 5591–5597 (2011)
M. El-Ashmawy, M. El-Sherbeny, N. El-Gohary, Synthesis and antitumor screening of new series of pyrimido-[4, 5-b] quinolines and [1, 2, 4] triazolo [2′, 3′: 3, 4] pyrimido [6, 5-b] quinolines. Med. Chem. Res. 22, 2724–2736 (2013)
S. Bahekar, D. Shinde, Synthesis and anti-inflammatory activity of 1, 4-dihydropyridines. Acta Pharm. 52, 281–287 (2002)
T. Althuis, P. Moore, H. Hess, Development of ethyl 3, 4-dihydro-4-oxopyrimido [4, 5-b] quinoline-2-carboxylate, a new prototype with oral antiallergy activity. J. Med. Chem. 22, 44–48 (1979)
P. Pallavicini, A. Dona, A. Taglietti, P. Minzioni, M. Patrini, G. Dacarro, G. Chirico, L. Sironi, N. Bloise, L. Visai, Self-assembled monolayers of gold nanostars: a convenient tool for near-IR photothermal biofilm eradication. Chem. Commun. 50, 1969–1971 (2014)
H.-A.S. Abbas, H.N. Hafez, A.-R.B. El-Gazzar, Synthesis, in vitro antimicrobial and in vivo antitumor evaluation of novel pyrimidoquinolines and its nucleoside derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 46, 21–30 (2011)
A. Krauze, S. Ģērmane, O. Eberlin, I. Šturms, V. Klusā, G. Duburs, Derivatives of 3-cyano-6-phenyl-4-(3-pyridyl)-pyridine-2 (1H)-thione and their neurotropic activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 34, 301–310 (1999)
S. Gullapalli, P. Ramarao, L-type Ca2+ channel modulation by dihydropyridines potentiates κ-opioid receptor agonist induced acute analgesia and inhibits development of tolerance in rats. Neuropharmacology 42, 467–475 (2002)
A. Hantzsch, Ueber die synthese pyridinartiger verbindungen aus acetessigäther und aldehydammoniak. Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. 215, 1–82 (1882)
J. Yadav, B. Reddy, A. Basak, A. Narsaiah, Three-component coupling reactions in ionic liquids: an improved protocol for the synthesis of 1, 4-dihydropyridines. Green Chem. 5, 60–63 (2003)
M. Anniyappan, D. Muralidharan, P.T. Perumal, Synthesis of Hantzsch 1, 4-dihydropyridines under microwave irradiation. Synth. Commun. 32, 659–663 (2002)
A. Kumar, R.A. Maurya, Efficient synthesis of Hantzsch esters and polyhydroquinoline derivatives in aqueous micelles. Synlett 2008, 883–885 (2008)
G. Giorgi, M.F. Adamo, F. Ponticelli, A. Ventura, Synthesis, structural and conformational properties, and gas phase reactivity of 1, 4-dihydropyridine ester and ketone derivatives. Org. Biomol. Chem. 8, 5339–5344 (2010)
H.G. Alvim, G.A. Bataglion, L.M. Ramos, A.L. de Oliveira, H.C. de Oliveira, M.N. Eberlin, J.L. de Macedo, W.A. da Silva, B.A. Neto, Task-specific ionic liquid incorporating anionic heteropolyacid-catalyzed Hantzsch and Mannich multicomponent reactions. Ionic liquid effect probed by ESI-MS (/MS). Tetrahedron 70, 3306–3313 (2014)
B. Datta, M.A. Pasha, Silica sulfuric acid: an efficient heterogeneous catalyst for the one-pot synthesis of 1, 4-dihydropyridines under mild and solvent-free conditions. Chin. J. Catal. 32, 1180–1184 (2011)
R.M. Borade, P.R. Shinde, S.B. Kale, R.P. Pawar, Preparation, characterization and catalytic application of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles in the synthesis of benzimidazoles, in: AIP Conference Proceedings. (AIP Publishing LLC, 2018), pp. 030194.
P.P. Khirade, A.R. Chavan, S.B. Somvanshi, J.S. Kounsalye, K. Jadhav, Tuning of physical properties of multifunctional Mg-Zn spinel ferrite nanocrystals: a comparative investigations manufactured via conventional ceramic versus green approach sol-gel combustion route. Mater. Res. Express 7, 116102 (2020)
G.-W. Wang, Mechanochemical organic synthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 42, 7668–7700 (2013)
A.M. Romani, Magnesium in health and disease, Interrelations between essential metal ions and human diseases, 49–79 (2013)
A. Rosanoff, C.M. Weaver, R.K. Rude, Suboptimal magnesium status in the United States: are the health consequences underestimated? Nutr. Rev. 70, 153–164 (2012)
L. Teigen, C.J. Boes, An evidence-based review of oral magnesium supplementation in the preventive treatment of migraine. Cephalalgia 35, 912–922 (2015)
V. Vinayak, P.P. Khirade, S.D. Birajdar, D. Sable, K. Jadhav, Structural, microstructural, and magnetic studies on magnesium (Mg2+)-substituted CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 29, 1025–1032 (2016)
K.-W. Jung, S. Lee, Y.J. Lee, Synthesis of novel magnesium ferrite (MgFe2O4)/biochar magnetic composites and its adsorption behavior for phosphate in aqueous solutions. Biores. Technol. 245, 751–759 (2017)
J. Nonkumwong, P. Pakawanit, A. Wipatanawin, P. Jantaratana, S. Ananta, L. Srisombat, Synthesis and cytotoxicity study of magnesium ferrite-gold core-shell nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 61, 123–132 (2016)
P.B. Kharat, S.B. Somvanshi, P.P. Khirade, K. Jadhav, Induction heating analysis of surface-functionalized nanoscale CoFe2O4 for magnetic fluid hyperthermia toward noninvasive cancer treatment. ACS Omega 5, 23378–23384 (2020)
J. Jose, R. Kumar, S. Harilal, G.E. Mathew, D.G.T. Parambi, A. Prabhu, M. Uddin, L. Aleya, H. Kim, B. Mathew, Magnetic nanoparticles for hyperthermia in cancer treatment: an emerging tool. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 27, 19214–19225 (2020)
J. Chandradass, A.H. Jadhav, K.H. Kim, H. Kim, Influence of processing methodology on the structural and magnetic behavior of MgFe2O4 nanopowders. J. Alloy. Compd. 517, 164–169 (2012)
S.B. Somvanshi, S.R. Patade, D.D. Andhare, S.A. Jadhav, M.V. Khedkar, P.B. Kharat, P.P. Khirade, K. Jadhav, Hyperthermic evaluation of oleic acid coated nano-spinel magnesium ferrite: enhancement via hydrophobic-to-hydrophilic surface transformation. J. Alloy. Compd. 835, 155422 (2020)
T. Srinivasan, C. Srivastava, N. Venkataramani, M. Patni, Infrared absorption in spinel ferrites. Bull. Mater. Sci. 6, 1063–1067 (1984)
S. Bhattacharjee, DLS and zeta potential–what they are and what they are not? J. Control. Release 235, 337–351 (2016)
K. DoymuŞ, The effect of ionic electrolytes and pH on the zeta potential of fine coal particles. Turk. J. Chem. 31, 589–597 (2007)
P. Wang, A.A. Keller, Natural and engineered nano and colloidal transport: role of zeta potential in prediction of particle deposition. Langmuir 25, 6856–6862 (2009)
E.F. de la Cruz, Y. Zheng, E. Torres, W. Li, W. Song, K. Burugapalli, Zeta potential of modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes in presence of poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogel. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1452-3981(23)13979-4
C.H. Christensen, J.C. Groen, Chem. Soc. Rev. 37, 2530–2542 (2008)
A. Bamoniri, S. Fouladgar, SnCl4-functionalized nano-Fe3O4 encapsulated-silica particles as a novel heterogeneous solid acid for the synthesis of 1, 4-dihydropyridine derivatives. RSC Adv. 5, 78483–78490 (2015)
J. Safari, F. Azizi, M. Sadeghi, Chitosan nanoparticles as a green and renewable catalyst in the synthesis of 1, 4-dihydropyridine under solvent-free conditions. New J. Chem. 39, 1905–1909 (2015)
S. Igder, A.R. Kiasat, M.R. Shushizadeh, Melamine supported on hydroxyapatite-encapsulated-γ-Fe2O3: a novel superparamagnetic recyclable basic nanocatalyst for the synthesis of 1, 4-dihydropyridines and polyhydroquinolines. Res. Chem. Intermed. 41, 7227–7244 (2015)
T.R. Naik, S. Shivashankar, Heterogeneous bimetallic ZnFe2O4 nanopowder catalyzed synthesis of Hantzsch 1, 4-dihydropyridines in water. Tetrahedron Lett. 57, 4046–4049 (2016)
N. Taheri, F. Heidarizadeh, A. Kiasat, A new magnetically recoverable catalyst promoting the synthesis of 1, 4-dihydropyridine and polyhydroquinoline derivatives via the Hantzsch condensation under solvent-free conditions. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 428, 481–487 (2017)
B. Maleki, A. Mofrad, R. Tayebee, A. Khojastehnezhad, H. Alinezhad, E. Rezaei Seresht, One-pot synthesis of 1, 4-dihydropyridine derivatives catalyzed by silica-coated magnetic NiFe2O4 nanoparticles-supported H14 [NaP5W30O110]. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 87, 2922–2929 (2017)
W. He, Z. Fang, K. Zhang, T. Tu, N. Lv, C. Qiu, K. Guo, A novel micro-flow system under microwave irradiation for continuous synthesis of 1, 4-dihydropyridines in the absence of solvents via Hantzsch reaction. Chem. Eng. J. 331, 161–168 (2018)
E. Pourian, S. Javanshir, Z. Dolatkhah, S. Molaei, A. Maleki, Ultrasonic-assisted preparation, characterization, and use of novel biocompatible core/shell Fe3O4@ GA@ isinglass in the synthesis of 1, 4-dihydropyridine and 4 H-pyran derivatives. ACS Omega 3, 5012–5020 (2018)
A. Maleki, R. Firouzi-Haji, Z. Hajizadeh, Magnetic guanidinylated chitosan nanobiocomposite: a green catalyst for the synthesis of 1, 4-dihydropyridines. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 116, 320–326 (2018)
M. Ghanbari, S. Moradi, M. Setoodehkhah, Fe3O4@SiO2@ADMPT/H6P2W18O62: a novel Wells-Dawson heteropolyacid-based magnetic inorganic–organic nanohybrid material as potent Lewis acid catalyst for the efficient synthesis of 1, 4-dihydopyridines. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 11, 111–124 (2018)
A. Maleki, V. Eskandarpour, J. Rahimi, N. Hamidi, Cellulose matrix embedded copper decorated magnetic bionanocomposite as a green catalyst in the synthesis of dihydropyridines and polyhydroquinolines. Carbohyd. Polym. 208, 251–260 (2019)
H. Alinezhad, M. Tajbakhsh, B. Maleki, F. Pourshaban Oushibi, Acidic ionic liquid [H-NP]HSO4 promoted one-pot synthesis of dihydro-1H-indeno [1, 2-b] pyridines and polysubstituted imidazoles. Polycycl. Aromat. Copds. 40, 1485–1500 (2020)
R. Taheri-Ledari, J. Rahimi, A. Maleki, Synergistic catalytic effect between ultrasound waves and pyrimidine-2, 4-diamine-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles: applied for synthesis of 1, 4-dihydropyridine pharmaceutical derivatives. Ultrason. Sonochem. 59, 104737 (2019)
Z. Hajizadeh, A. Maleki, J. Rahimi, R. Eivazzadeh-Keihan, Halloysite nanotubes modified by Fe3O4 nanoparticles and applied as a natural and efficient nanocatalyst for the symmetricalhantzsch reaction. SILICON 12, 1247–1256 (2020)
P. Wu, L. Feng, Y. Liang, X. Zhang, B. Mahmoudi, M. Kazemnejadi, Magnetic Fe–CO–Mo alloy nano-rods prepared from chemical decomposition of a screw (a top-down approach): an efficient and cheap catalyst for the preparation of dihydropyridine and dihydropyrimidone derivatives. Appl. Catal. A 590, 117301 (2020)
S. Asgharnasl, R. Eivazzadeh-Keihan, F. Radinekiyan, A. Maleki, Preparation of a novel magnetic bionanocomposite based on factionalized chitosan by creatine and its application in the synthesis of polyhydroquinoline, 1, 4-dyhdropyridine and 1, 8-dioxo-decahydroacridine derivatives. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 144, 29–46 (2020)
R.P. Kagne, G.H. Nikam, V.G. Kalalawe, S.N. Niwadange, D.R. Munde, An efficient protocol for synthesis of 1, 4-dihydropyridine derivatives by using graphene oxide nano particles as a catalyst. J. Chem. Chem. Sci. 7, 1064–1070 (2017)
Acknowledgements
The authors are very much indebted to Punyashlok Ahilyadevi Holkar Solapur University for XRD, Materials Research Centre, Malaviya National Institute of Technology (MNIT), Jaipur for TEM and Zeta potential characterization, and Sophisticated Analytical Instrument Facility (SAIF), Panjab University, Chandigarh for NMR and HRMS measurements.
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RMB: Formal analysis, investigation, methodology, data curation, visualization, writing original draft. SBK: investigation, methodology, PPK: formal analysis, visualization, writing—review and editing. KMJ: conceptualization, supervision, RPP: validation, supervision.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Borade, R.M., Kale, S.B., Khirade, P.P. et al. Solvent-Free Synthesis of 1, 4 Dihydropyridines Derivatives via Hantzsch Reaction Employing MgFe2O4 MNPs: An Efficient and Recyclable Heterogeneous Catalyst. J Inorg Organomet Polym 34, 1104–1120 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-023-02858-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-023-02858-8