Abstract
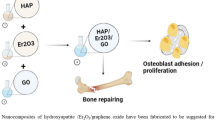
Post-implantation infections are regarded as a major issue in the biomedical field. Further, many investigations are continuous towards developing antibacterial biocompatible materials. In this regard, hydroxyapatite (HAP), erbium oxide (Eu2O3), and graphene oxide (GO) were introduced in nanocomposites combinations, including single, dual, and triple constituents. The nanoparticles of HAP, Eu2O3, and nanosheets of GO are synthesized separately, while dispersed in the nanocomposites simultaneously. The morphological investigation showed that HAP was configured in a rod-like shape while the nano ellipsoidal shape of Eu2O3 was confirmed. The particle size of the ternary nanocomposite containing HAP/Eu2O3/GO reached the length of 40 nm for the rods of HAP and around 28 nm for the length axis of ellipsoidal Eu2O3 nanoparticles. The roughness average increased to be about 54.7 nm for HAP/GO and decreased to 37.9 nm for the ternary nanocomposite. Furthermore, the maximum valley depth (Rv) increased from HAP to the ternary nanocomposite from 188.9 to 189.8 nm. Moreover, the antibacterial activity was measured, whereas the inhibition zone of HAP/Eu2O3/GO reached 13.2 ± 1.1 mm for Escherichia coli and 11.4 ± 0.8 mm for Staphylococcus aureus. The cell viability of the human osteoblast cell lines was evaluated to be 98.5 ± 3% for the ternary composition from 96.8 ± 4% for the pure HAP. The existence of antibacterial activity without showing cytotoxicity against mammalian cells indicates the compatibility of nanocomposites with biomedical applications.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.S. Ambekar, B. Kandasubramanian, Advancements in nanofibers for wound dressing: a review. Eur. Polym. J. 117, 304–336 (2019)
M.F.H.A. El-Kader, M.K. Ahmed, M.T. Elabbasy, M. Afifi, A.A. Menazea, Morphological, ultrasonic mechanical and biological properties of hydroxyapatite layers deposited by pulsed laser deposition on alumina substrates. Surf. Coat. Technol. 409, 126861 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2021.126861
V. Ponnilavan, S. Vasanthavel, R.K. Singh, S. Kannan, Influence of La3+ additions on the phase behaviour and antibacterial properties of ZrO2–SiO2 binary oxides. Ceram. Int. 41, 7632–7639 (2015)
N.H. de Leeuw, Local ordering of hydroxy groups in hydroxyapatite. Chem Commun (2001). https://doi.org/10.1039/b104850n
O. Kaygili, C. Tatar, F. Yakuphanoglu, S. Keser, Nano-crystalline aluminum-containing hydroxyapatite based bioceramics: synthesis and characterization. J. Sol-Gel. Sci. Technol. 65, 105–111 (2012)
L. Wang, H. He, Y. Yu, L. Sun, S. Liu, C. Zhang et al., Morphology-dependent bactericidal activities of Ag/CeO2 catalysts against Escherichia coli. J. Inorg. Biochem. 135, 45–53 (2014)
M.K. Ahmed, S.F. Mansour, R. Al-Wafi, M. Afifi, V. Uskokovic, Gold as a dopant in selenium-containing carbonated hydroxyapatite fillers of nanofibrous epsilon-polycaprolactone scaffolds for tissue engineering. Int. J. Pharm. 577, 118950 (2020)
F. Mohandes, M. Salavati-Niasari, In vitro comparative study of pure hydroxyapatite nanorods and novel polyethylene glycol/graphene oxide/hydroxyapatite nanocomposite. J. Nanopart. Res. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-014-2604-y
L.A. Zavala-Sanchez, G.A. Hirata, E. Novitskaya, K. Karandikar, M. Herrera, O.A. Graeve, Distribution of Eu(2+) and Eu(3+) ions in hydroxyapatite: a cathodoluminescence and raman study. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 1, 1306–1313 (2015)
S.-L. Iconaru, M. Motelica-Heino, D. Predoi, Study on Europium-doped hydroxyapatite nanoparticles by fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and their antimicrobial properties. J. Spectrosc. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/284285
V. Uskokovic, M.A. Iyer, V.M. Wu, One ion to rule them all: combined antibacterial, osteoinductive and anticancer properties of selenite-incorporated hydroxyapatite. J. Mater. Chem. B 5, 1430–1445 (2017)
C. Popa, C. Ciobanu, S. Iconaru, M. Stan, A. Dinischiotu, C. Negrila et al., Systematic investigation and in vitro biocompatibility studies on mesoporous europium doped hydroxyapatite. Open Chem. 12, 1032–1046 (2014)
M.G. Raucci, D. Giugliano, A. Longo, S. Zeppetelli, G. Carotenuto, L. Ambrosio, Comparative facile methods for preparing graphene oxide-hydroxyapatite for bone tissue engineering. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 11, 2204–2216 (2017)
T.A.R.M. Lima, M.E.G. Valerio, X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy and photoluminescence study of multifunctional europium (III)-doped hydroxyapatite in the presence of cationic surfactant medium. J. Lumin. 201, 70–76 (2018)
J.R. Vail, D.L. Burris, W.G. Sawyer, Multifunctionality of single-walled carbon nanotube–polytetrafluoroethylene nanocomposites. Wear 267, 619–624 (2009)
T. Kataoka, S. Abe, M. Tagaya, Surface-engineered design of efficient luminescent europium(III) complex-based hydroxyapatite nanocrystals for rapid hela cancer cell imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 8915–8927 (2019)
S. Chaudhary, P. Sharma, S. Kumar, S.A. Alex, R. Kumar, S.K. Mehta et al., A comparative multi-assay approach to study the toxicity behaviour of Eu2O3 nanoparticles. J. Mol. Liq. 269, 783–795 (2018)
K. Kattel, J.Y. Park, W. Xu, H.G. Kim, E.J. Lee, B.A. Bony et al., Water-soluble ultrasmall Eu2O3 nanoparticles as a fluorescent imaging agent: In vitro and in vivo studies. Colloids Surf. A 394, 85–91 (2012)
S. Stankovich, D.A. Dikin, G.H. Dommett, K.M. Kohlhaas, E.J. Zimney, E.A. Stach et al., Graphene-based composite materials. Nature 442, 282–286 (2006)
M. Li, Q. Liu, Z. Jia, X. Xu, Y. Cheng, Y. Zheng et al., Graphene oxide/hydroxyapatite composite coatings fabricated by electrophoretic nanotechnology for biological applications. Carbon 67, 185–197 (2014)
H. Nosrati, R.S. Mamoory, D.Q.S. Le, C.E. Bünger, Preparation of reduced graphene oxide/hydroxyapatite nanocomposite and evaluation of graphene sheets/hydroxyapatite interface. Diamond Related Mater. 100, 107561 (2019)
L. Feng, Y. Chen, J. Ren, X. Qu, A graphene functionalized electrochemical aptasensor for selective label-free detection of cancer cells. Biomaterials 32, 2930–2937 (2011)
C. Wan, M. Frydrych, B. Chen, Strong and bioactive gelatin–graphene oxide nanocomposites. Soft Matter 7, 6159 (2011)
J.H. Lee, Y.C. Shin, S.M. Lee, O.S. Jin, S.H. Kang, S.W. Hong et al., Enhanced osteogenesis by reduced graphene oxide/hydroxyapatite nanocomposites. Sci. Rep. 5, 18833 (2015)
D. Lahiri, A.P. Benaduce, L. Kos, A. Agarwal, Quantification of carbon nanotube induced adhesion of osteoblast on hydroxyapatite using nano-scratch technique. Nanotechnology 22, 355703 (2011)
M. Afifi, M.K. Ahmed, H.A. Ibrahium, N.S. Awwad, E. Abdel-Fattah, M.Y. Alshahrani, Improvement of physicochemical properties of ternary nanocomposites based on hydroxyapatite/CuO/graphene oxide for biomedical usages. Ceram. Int. 48(3), 3993–4004 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.10.186
Z. Mo, Y. Zhao, R. Guo, P. Liu, T. Xie, Preparation and characterization of graphene/europium oxide composites. Mater. Manuf. Processes 27, 494–498 (2011)
Y. Li, Z. Li, X. Zhou, P. Yang, Detection of nano Eu2O3 in cells and study of its biological effects. Nano Biomed. Eng. (2010). https://doi.org/10.5101/nbe.v2i1.p24-30
M.K. Ahmed, R. Ramadan, M. Afifi, A.A. Menazea, Au-doped carbonated hydroxyapatite sputtered on alumina scaffolds via pulsed laser deposition for biomedical applications. J. Market. Res. 9, 8854–8866 (2020)
M.K. Ahmed, M. Afifi, M.S. Mostafa, A.F. El-kott, H.A. Ibrahium, N.S. Awwad, Crystal structure optimization, ultrasonic properties and morphology of Mg/Se co-dopant into annealed hydroxyapatite for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Res. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-021-00148-y
Z. Liu, J. Tian, C. Yu, Q. Fan, X. Liu, K. Yang et al., Ultrasonic fabrication of SO42—doped g-C3N4/Ag3PO4 composite applied for effective removal of dyestuffs and antibiotics. Mater. Chem. Phys. 240, 122206 (2020)
S. Sivaselvam, P. Premasudha, C. Viswanathan, N. Ponpandian, Enhanced removal of emerging pharmaceutical contaminant ciprofloxacin and pathogen inactivation using morphologically tuned MgO nanostructures. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 8, 104256 (2020)
M. Ramadas, G. Bharath, N. Ponpandian, A.M. Ballamurugan, Investigation on biophysical properties of hydroxyapatite/graphene oxide (HAp/GO) based binary nanocomposite for biomedical applications. Mater. Chem. Phys. 199, 179–184 (2017)
G. Xiong, H. Luo, G. Zuo, K. Ren, Y. Wan, Novel porous graphene oxide and hydroxyapatite nanosheets-reinforced sodium alginate hybrid nanocomposites for medical applications. Mater. Charact. 107, 419–425 (2015)
M.K. Ahmed, M.E. El-Naggar, A. Aldalbahi, M.H. El-Newehy, A.A. Menazea, Methylene blue degradation under visible light of metallic nanoparticles scattered into graphene oxide using laser ablation technique in aqueous solutions. J. Mol. Liq. 315, 113794 (2020)
S.F. Mansour, S.I. El-dek, M. Ismail, M.K. Ahmed, Structure and cell viability of Pd substituted hydroxyapatite nano particles. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 4, 045008 (2018)
M.F. Abdelbar, H.S. El-Sheshtawy, K.R. Shoueir, I. El-Mehasseb, M. Ebeid E-Zeiny, M. El-Kemary, Halogen bond triggered aggregation induced emission in an iodinated cyanine dye for ultra sensitive detection of Ag nanoparticles in tap water and agricultural wastewater. RSC Adv. 8, 24617–24626 (2018)
M.A. Zakria, A.A. Menazea, A.M. Mostafa, E.A. Al-Ashkar, Ultra-thin silver nanoparticles film prepared via pulsed laser deposition: synthesis, characterization, and its catalytic activity on reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Surf. Interfaces (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2020.100438
C.S. Ciobanu, S.L. Iconaru, F. Massuyeau, L.V. Constantin, A. Costescu, D. Predoi, Synthesis, structure, and luminescent properties of europium-doped hydroxyapatite nanocrystalline powders. J. Nanomater. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/942801
S. Rahavi, A. Monshi, R. Emadi, A. Doostmohammadi, H. Akbarian, Determination of crystallite size in synthetic and natural hydroxyapatite: a comparison between XRD and TEM results. Adv. Mater. Res. 620, 28–34 (2012)
B. Gayathri, N. Muthukumarasamy, D. Velauthapillai, S.B. Santhosh, V. Asokan, Magnesium incorporated hydroxyapatite nanoparticles: Preparation, characterization, antibacterial and larvicidal activity. Arab. J. Chem. 11, 645–654 (2018)
U. Rajaji, S. Manavalan, S.M. Chen, S. Chinnapaiyan, T.W. Chen, R.R. Jothi, Facile synthesis and characterization of erbium oxide (Er2O3) nanospheres embellished on reduced graphene oxide nanomatrix for trace-level detection of a hazardous pollutant causing Methemoglobinaemia. Ultrason. Sonochem. 56, 422–429 (2019)
M.J. Lukić, L. Veselinović, M. Stevanović, J. Nunić, G. Dražič, S. Marković et al., Hydroxyapatite nanopowders prepared in the presence of zirconium ions. Mater. Lett. 122, 296–300 (2014)
S. Hiromoto, M. Inoue, T. Taguchi, M. Yamane, N. Ohtsu, In vitro and in vivo biocompatibility and corrosion behaviour of a bioabsorbable magnesium alloy coated with octacalcium phosphate and hydroxyapatite. Acta Biomater. 11, 520–530 (2015)
A. Janković, S. Eraković, M. Mitrić, I.Z. Matić, Z.D. Juranić, G.C.P. Tsui et al., Bioactive hydroxyapatite/graphene composite coating and its corrosion stability in simulated body fluid. J. Alloys Compd. 624, 148–157 (2015)
M.K. Ahmed, R. Ramadan, S.I. El-dek, V. Uskoković, Complex relationship between alumina and selenium-doped carbonated hydroxyapatite as the ceramic additives to electrospun polycaprolactone scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. J. Alloys Compd. 801, 70–81 (2019)
O. Kaygili, S. Keser, N. Bulut, T. Ates, Characterization of Mg-containing hydroxyapatites synthesized by combustion method. Physica B 537, 63–67 (2018)
D. Gopi, D. Rajeswari, S. Ramya, M. Sekar, R.D. Pramod, J. Dwivedi et al., Enhanced corrosion resistance of strontium hydroxyapatite coating on electron beam treated surgical grade stainless steel. Appl. Surf. Sci. 286, 83–90 (2013)
K. Lin, Y. Zhou, Y. Zhou, H. Qu, F. Chen, Y. Zhu et al., Biomimetic hydroxyapatite porous microspheres with co-substituted essential trace elements: surfactant-free hydrothermal synthesis, enhanced degradation and drug release. J. Mater. Chem. 21, 16558 (2011)
S.F. Mansour, S.I. El-Dek, M.K. Ahmed, Physico-mechanical and morphological features of zirconia substituted hydroxyapatite nano crystals. Sci. Rep. 7, 43202 (2017)
V.K. Mishra, B.N. Bhattacharjee, O. Parkash, D. Kumar, S.B. Rai, Mg-doped hydroxyapatite nanoplates for biomedical applications: a surfactant assisted microwave synthesis and spectroscopic investigations. J. Alloys Compd. 614, 283–288 (2014)
A. Menazea, S.A. Abdelbadie, M. Ahmed, Manipulation of AgNPs coated on selenium/carbonated hydroxyapatite/ε-polycaprolactone nano-fibrous via pulsed laser deposition for wound healing applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 508, 145299 (2020)
H. Zhou, J. Lee, Nanoscale hydroxyapatite particles for bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 7, 2769–2781 (2011)
K. Kaviyarasu, K. Kanimozhi, N. Matinise, C. Maria Magdalane, G.T. Mola, J. Kennedy et al., Antiproliferative effects on human lung cell lines A549 activity of cadmium selenide nanoparticles extracted from cytotoxic effects: Investigation of bio-electronic application. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 76, 1012–1025 (2017)
M. Wang, Y. Liu, G. Ren, W. Wang, S. Wu, J. Shen, Bioinspired carbon quantum dots for sensitive fluorescent detection of vitamin B12 in cell system. Anal. Chim. Acta 1032, 154–162 (2018)
S. Kumar, R. Prakash, R.J. Choudhary, D.M. Phase, Structural, XPS and magnetic studies of pulsed laser deposited Fe doped Eu2O3 thin film. Mater. Res. Bull. 70, 392–396 (2015)
H.H. Huang, C.T. Ho, T.H. Lee, T.L. Lee, K.K. Liao, F.L. Chen, Effect of surface roughness of ground titanium on initial cell adhesion. Biomol. Eng. 21, 93–97 (2004)
I.M. Hung, W.J. Shih, M.H. Hon, M.C. Wang, The properties of sintered calcium phosphate with [Ca]/[P] = 1.50. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 13, 13569–13586 (2012)
A. Toloei, V. Stoilov, D. Northwood, The relationship between surface roughness and corrosion, in Proceedings of the ASME 2013 international mechanical engineering congress and exposition. Advanced manufacturing, vol. 2B, (2014)
M.S. Johnsson, G.H. Nancollas, The role of brushite and octacalcium phosphate in apatite formation. Crit. Rev.Oral Biol. Med 3, 61–82 (1992)
A. Carino, C. Ludwig, A. Cervellino, E. Müller, A. Testino, Formation and transformation of calcium phosphate phases under biologically relevant conditions: experiments and modelling. Acta Biomater. 74, 478–488 (2018)
S. Sompech, A. Srion, A. Nuntiya, The effect of ultrasonic treatment on the particle size and specific surface area of LaCoO3. Procedia Eng. 32, 1012–1018 (2012)
K. Kaviyarasu, A. Mariappan, K. Neyvasagam, A. Ayeshamariam, P. Pandi, R.R. Palanichamy et al., Photocatalytic performance and antimicrobial activities of HAp-TiO2 nanocomposite thin films by sol-gel method. Surf. Interfaces 6, 247–255 (2017)
S. Liu, M. Hu, T.H. Zeng, R. Wu, R. Jiang, J. Wei et al., Lateral dimension-dependent antibacterial activity of graphene oxide sheets. Langmuir 28, 12364–12372 (2012)
K. Krishnamoorthy, M. Veerapandian, L.-H. Zhang, K. Yun, S.J. Kim, Antibacterial efficiency of graphene nanosheets against pathogenic bacteria via lipid peroxidation. J. Phys. Chem. C 116, 17280–17287 (2012)
Acknowledgements
The authors appreciate the Deputyship for Research and Innovation, Minsitry of education in Saudi Arabia for funding this research work through the project number : IFP-KKU-2020/11.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmed, M.K., Awwad, N.S., Ibrahium, H.A. et al. Hybrid Nanocomposites of Hydroxyapatite, Eu2O3, Graphene Oxide Via Ultrasonic Power: Microstructure, Morphology Design and Antibacterial for Biomedical Applications. J Inorg Organomet Polym 32, 1786–1799 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-022-02279-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-022-02279-z