Abstract
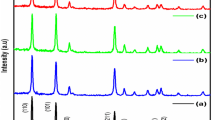
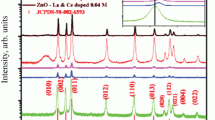
In the present report, synthesis of zinc oxide (ZnO) nano particles (NPs) in pure form, 1 wt% of neodymium (Nd)-doped and 1 wt% of neodymium (Nd) and samarium (Sm) co-doped ZnO NPs in doped form by using simple co-precipitation method (samples namely PZ as pure, NZ as Nd-doped ZnO and NSZ as Nd–Sm co-doped ZnO NPs). Powder X-ray diffraction patterns of all the synthesized samples expose the hexagonal crystal structure of ZnO NPs without any impurity. The various functional groups presented in the synthesized samples were analyzed by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy studies. From Ultraviolet (UV)–Visible Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy (DRS), the band gap was found to be 2.81 eV, 2.90 eV and 3.10 eV respectively for pure, Nd-doped and Nd–Sm co-doped ZnO NPs. Photoluminescence (PL) spectrum displays the broad emission at 393 nm and 450 nm for all the synthesized samples. The agglomeration of flower-like morphology of pure ZnO NPs, flake-like structure of Nd-doped and rod-like morphology of Nd–Sm co-doped ZnO NPs were examined by scanning electron microscopy. The surface chemical composition of samples was carried out with X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The photocatalytic activity of the prepared samples for dye degradation of acid orange 7 (AO-7) and acid red 13 (AR-13) was studied under UV light. The result revealed that, the Nd–Sm co-doped ZnO NPs found to have efficient degradation candidate materials.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.H. Zheng, J.L. Song, Z. Zhao, Q. Jiang, J.S. Lian, Optical and magnetic properties of Nd-doped ZnO nano particles. Cryst. Res. Technol. 47, 1–6 (2012)
A.T. Ravichandran, R. Karthick, A. Robert Xavier, R. Chandramohan, S. Mantha, Influence of Sm doped ZnO Nano particles with enhanced photoluminescence and antibacterial efficiency. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 28, 6643–6648 (2017)
J.-Q. Wen, J.-M. Zhang, G.-X. Chen, H. Wu, X. Yang, The structural, electronic and optical properties of Nd doped ZnO using first-principles calculations. Phys. E: Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physe.2018.01.002
I.L. Raj, S. Valanarasu, K. Hariprasad, J.S. Ponraj, N. Chidhambaram, V. Ganesh, H.E. Ali, Y. Khairy, Enhancement of optoelectronic parameters of Nd-doped ZnO nanowires for photodetector applications. Opt. Mater. 109, 110396 (2020)
H.E. Okur, N. Bulut, T. Ates, O. Kaygili, Structural and optical characterization of Sm-doped ZnO nano particles. Bull. Mater. Sci. 42, 199 (2019)
S.K. Gurav, S.E. Shirsath, R.H. Kadam, D.R. Mane, Low temperature synthesis of Li0.5ZrxCoxFe2.5–2xO4 powder and their characterizations. Powder Technol. 235, 485–492 (2013)
S. Rosari, N.F. Djaja, UV light photo catalytic degradation of organic dyes with Fe-doped ZnO Nano particles. Superlattice Microstruct. 74, 217–233 (2014)
K. Rekha, M. Nirmala, M.G. Nair, A. Anukaliani, Structural, optical, photo catalytic and antibacterial activity of zinc oxide and manganese doped zinc oxide nano particles. Phys. B: Condens. Matter. 405, 3180–3185 (2010)
C. Belkhaoui, N. Mzabi, H. Smaoui, Investigations on structural, optical and dielectric properties of Mn doped ZnO NPs synthesized by co-precipitation method. Mater. Res. Bull. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2018.11.006
S. Tauseef Munawar, F. Yasmeen, K. Hussain, A. Mahmood, M. Hussain, F. Asghar, Iqbal, Synthesis of novel heterostructure ZnO-CdO-CuO nanocomposite: characterization and enhanced sunlight driven photo catalytic activity. Mater. Chem. Phys. 249, 122983 (2020)
T. Sumithra, C. Lydia Pearline, M. John Abel, A. Pramothkumar, P. Fermi Hilbert Inbaraj, J. Joseph, Prince, Studies on structural and optical behavior of SnO2/CuMn2O4 nanocomposite developed via two-step approach for photo catalytic activity Mater. Res. Exp. 6, 115047 (2019)
M.R. Hoffmann, S.T. Martin, W. Choi, D.W. Bahnemann, Environmental applications of semiconductor photocatalysis. Chem. Rev. 95, 69–96 (1995)
M.H. Kahsay, A. Tadesse, D. Rama Devi, N. Belachew, K. Basavaiah, Greensynthesis of zinc oxide nanostructures and investigation of their photo catalytic and bactericidalapplications. RSC Adv. 9(63), 36967–36981 (2019)
A. Shafi, N. Ahmad, S. Sultana, S. Sabir, M.Z. Khan, Ag2S-sensitized NiO-ZnO heterostructures with enhanced visible light photo catalytic activity and acetone sensing property. ACS Omega 4(7), 12905–12918 (2019)
M. Faraz, F.K. Naqvi, M. Shakir, N. Khare, Synthesis of samarium-doped zinc oxide Nano particles with improved photo catalytic performance and recyclability under visible light irradiation. New J. Chem. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/c7nj03927a
N.K. Divya, P.P. Pradyumnan, Enhancement of photo catalytic activity in Nd doped ZnO with an increase in dielectric constant. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 28, 2147–2156 (2017)
M.B. Javaid Akhtar, M. Tahir, H.S. Sagir, Bamufle, Improved photo catalytic performance of Gd and Nd co-doped ZnO nanorods for the degradation of methylene blue. Ceram. Int. 46, 11955–11961 (2020)
Irshad, Ahmad, Inexpensive and quick photocatalytic activity of rare earth (Er, Yb) co-doped ZnO nanoparticles for degradation of methyl orange dye. Sep. Purif. Technol. 227, 115726 (2019)
M. Muneer, M.S. Ba-Abbad, A. Takriff, M.S. Benamor, Nasser, Ebrahim Mahmoudi, Abdul Wahab Mohammad, Synthesis and characterization of Sm3+-doped ZnO nanoparticles via a sol–gel method and their photocatalytic application. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 85, 178–190 (2018)
G. Vijayaprasath, R. Murugan, S. Palanisamy, N.M. Prabhu, T. Mahalingam, Y. Hayakawa, G. Ravi, Structural, optical and antibacterial activity studies of neodymium doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 26, 7564–7576 (2015)
M. Sunil Chauhan, S. Kumar, S.C. Chhoker, V.P.S. Katyal, Awana, Structural, vibrational, optical and magnetic properties of sol–gel derived Nd doped ZnO nano particles. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 24, 5102–5110 (2013)
K. Deepawali Arora, A. Asokan, H. Mahajan, Kaur, D.P. Singh, Structural, optical and magnetic properties of Sm doped ZnO at dilute concentrations. RSC Adv. 6, 78122 (2016)
H. Noei, H. Qiu, Y. Wang, E. Löffler, C. Wöll, M. Muhler, The identification of hydroxyl groups on ZnO Nano particles by infrared spectroscopy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 10, 7092–7097 (2008)
A. Albert Manoharan, R. Chandramohan, R. David Prabu, S. Valanarasu, V. Ganesh, M. Shkir, A. Kathalingam, S. AlFaify, Facile synthesis and characterization of undoped, Mn doped and Nd co-doped CuO nano particles for optoelectronic and magnetic applications. J. Mol. Struct. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2018.06.018
O.M. Ntwaeaborwa, S.J. Mofokeng, V. Kumar, R.E. Kroon, Structural, optical and photoluminescence properties of Eu3+ doped ZnO nano particles. Spectrochem. Acta A: Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 182, 42–49 (2017)
V. Etacheri, R. Roshan, V. Kumar, Mg-doped ZnO nano particles for efficient sunlight-driven photocatalysis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 4, 2717–2725 (2012)
N. Aggarwal, K. Kaur, A. Vasishth, N.K. Verma, Structural, optical and magnetic properties of gadolinium-doped ZnO nano particles. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 27, 13006–13011 (2016)
K.P. Shinde, R.C. Pawar, B.B. Sinha, H.S. Kim, S.S. Oh, K.C. Chung, Study of effect of planetary ball milling on ZnO nano powder synthesized by co-precipitation. J. Alloys Compd. 617(2013), 404–407 (2014)
K.C. Verma, N. Goyal, R.K. Kotnala, Lattice defect-formulated ferromagnetism and UV photo-response in pure and Nd, Sm substituted ZnO thin films. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 21, 12540 (2019)
N. Mohamed Basith, J. Judith Vijaya, L. John Kennedy, M. Bououdina, Structural, optical and room-temperature ferromagnetic properties of Fe-doped CuO nanostructures. Physica E 53, 193–199 (2013)
A. Arulraj, M. Ramesh, B. Subramanian, G. Senguttuvan, In-situ temperature and thickness control grown 2D-MoS2 via pulsed laser ablation for photovoltaic devices. Sol. Energy 174, 286–295 (2018)
R. Karthick, A. Arulraj, M. Ramesh, M. Selvaraj, Free-standing graphene/NiMoS paper as cathode for quasi-solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 530, 179–188 (2018)
J. Zhang, S.J. Deng, S.Y. Liu, J.M. Chen, B.Q. Han, Y. Wang, Y.D. Wang, Preparation and photocatalytic activity of Nd doped ZnO nanoparticles. Mater. Technol. 29(5), 262–268 (2014)
A. Khataee, B. Vahid, S. Saadi, S.W. Joo, Development of an empirical kinetic model for sonocatalytic process using neodymium doped zinc oxide nanoparticles. Ultrason. Sonochem. 29, 146–155 (2016)
D. Ranjith Kumar, K.S. Ranjith, R.T. Rajendra Kumar, Structural, optical, photocurrent and solar driven photocatalytic properties of vertically aligned samarium doped ZnO nanorod arrays. Optik 154, 115–125 (2018)
B. Krishnakumar, B. Subash, M. Swaminathan, AgBr–ZnO– An efficient nano-photocatalyst for the mineralization of acid black 1 with UV light. Sep. Purif. Technol. 85, 35–44 (2012)
B.S. Ong, C. Li, Y. Li, Y. Wu, R. Loutfy, Stable, Solution- Processed, High-Mobility ZnO Thin-Film Transistors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 2750–2751 (2007)
P.G. Freire, R.H. Montes, F.C. Romeiro, S.C. Lemos, R.C. Lima, E.M. Richter, R.A. Munoz, Morphology of ZnO nanoparticles bound to carbon nanotubes affects electrocatalytic oxidation of phenolic compounds. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 223, 557–565 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baskaran, P., Pramothkumar, A. & Mani, P. Enhanced Photo Catalytic Activity of ZnO Nano Particles Co-doped with Rare Earth Elements (Nd and Sm) Under UV Light Illumination. J Inorg Organomet Polym 32, 1668–1680 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-022-02228-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-022-02228-w