Abstract
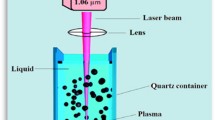
Titanium oxide nanoparticles (TiO2) were produced by pulsed Nd:YAG laser ablation in water under the effect of an external magnetic field. Various techniques such as X-ray diffraction (XRD), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), energy Dispersive X-ray (EDX), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), UV–Vis spectroscopy, and Raman spectroscopy were used to characterize the TiO2 nanoparticles. The XRD analysis of titanium oxide nanoparticles revealed that the synthesized nanoparticles were polycrystalline with mixed of tetragonal anatase and rutile TiO2. Scanning electron microscope shows the formation of spherical nanoparticles and the particles agglomeration decreases and the particle size from increases from 25 to 35 nm when the magnetic field applied. The optical energy gap of TiO2 nanoparticles decreased from 4.6 to 3.4 eV after using the magnetic field during the ablation. Raman studies show the existence of five vibration modes belong to TiO2. The antibacterial effect assay revealed a largest inhibition zone in S. aureus and E. coli, with a more potent effect for TiO2 NPs prepared by magnetic field when compared with that prepared without presence of magnetic field.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
X. Shi et al., Photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B dye with MWCNT/TiO2/C60 composites by a hydrothermal method. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed. 26(1), 65–69 (2011)
F. Barreca, N. Acacia, E. Barletta, D. Spadaro, G. Curro, F. Neri, Titanium oxide nanoparticles prepared by laser ablation in water. Radiat. Eff. Def. Solids 165, 573–578 (2010)
M. Malekshahi Byranvand, A. Nemati Kharat, L. Fatholahi, Z. Malekshahi Beiranvand, A review on synthesis of nano-TiO2 via different methods. J. Nanostruct. 3(1), 1–9 (2013)
A. Bahrami, R. Delshadi, E. Assadpour, S.M. Jafari, L. Williams, Antimicrobial-loaded nanocarriers for food packaging applications. Adv. Coll. Interface Sci. 278, 102140 (2020)
M. Yousefi, A. Ehsani, S.M. Jafari, Lipid-based nano delivery of antimicrobials to control food-borne bacteria. Adv. Coll. Interface Sci. 270, 263–277 (2019)
K.S. Khashan, G.M. Sulaiman, S.A. Hussain, T.R. Marzoog, M.S. Jabir, Synthesis, characterization and evaluation of anti-bacterial, anti-parasitic and anti-cancer activities of aluminum-doped zinc oxide nanoparticles. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 30, 3677–3693 (2020)
K.S. Khashan, G.M. Sulaiman, F.A.K. AbdulAmeer, G. Napolitano, Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of colloidal NiO nanoparticles. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 29(2), 541–546 (2016)
G.M. Sulaiman, A.T. Tawfeeq, M.D. Jaaffer, Biogenic synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using Olea europaea leaf extract and evaluation of their toxicity activities: an in vivo and in vitro study. Biotechnol. Prog. 34(1), 218–230 (2018)
K.S. Khashan, G.M. Sulaiman, S.A. Hussain, T.R. Marzoog, M.S. Jabir, Synthesis, characterization and evaluation of anti-bacterial, anti-parasitic and anti-cancer activities of aluminum-doped zinc oxide nanoparticles. J. Inorg. Organomet Polym. Mater. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01522-9
R.A. Ismail, G.M. Sulaiman, S.A. Abdulrahman, T.R. Marzoog, Antibacterial activity of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles synthesized by laser ablation in liquid. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 53, 286–297 (2015)
P. Russo, R. Liang, R.X. He, Y.N. Zhou, Phase transformation of TiO2 nanoparticles by femtosecond laser ablation in aqueous solutions and deposition on conductive substrates. Nanoscale 9(18), 6167–6177 (2017)
L. Chiodo, M. Salazar, A. Romero, S. Laricchia, F. Sala, A. Rubio, Structure, electronic, and optical properties of TiO2 atomic clusters: an ab initio study. J. Chem. Phys. 135, 244704 (2011)
A. Hernández, W. Hernández, A. Cid, J. García, M. Villanueva, Prediction, and physic-chemical properties of (TiO2)n n = 15–20 clusters and their possible catalytic application: A DFT study. Comput. Mater. Sci. 162, 228–235 (2019)
M. Salazar-Villanueva, A. Hernandez, J. Briones, E. Anota, F. Carrillo, Influence of doping on chain-like TiO2 clusters: a DFT study. Curr. Appl. Phys. 16, 197–206 (2016)
Y. Song, Y. Yang, C.J. Medforth, E. Pereira, A.K. Singh, H. Xu, Y. Jiang, C.J. Brinker, F. van Swol, J.A. Shelnutt, Controlled synthesis of 2-D and 3-D dendritic platinum nanostructures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126(2), 635–645 (2004)
A. Singh, J. Vihinen, E. Frankberg, L. Hyvarinen, M. Honkanen, E. Levanen, Pulsed laser ablation-induced green synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles and application of novel small angle X-ray scattering technique for nanoparticle size and size distribution analysis. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 11(1), 1–9 (2016)
G. Colon, M.C. Hidalgo, J.A. Navio, A novel preparation of high surface area TiO2 nanoparticles from alkoxide precursor and using active carbon as additive. Catal. Today 76(2–4), 91–101 (2002)
V.A. Shakhatov, O.A. Gordeev, Thin film deposition by means of laser ablation of titanium oxide targets in oxygen radiofrequency electrode plasma. High Energy Chem. 42(2), 141–144 (2008)
E. Solati, Z. Aghazadeh, D. Dorranian, Effects of liquid ablation environment on the characteristics of TiO2 Nanoparticles. J. Clust. Sci. 31(5), 961–969 (2020)
A. Nath, S.S. Laha, A. Khare, Synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles via laser ablation at titanium-water interface. Integ. Ferro. 121(1), 58–64 (2010)
N. Attan, H. Nur, J. Efendi, H.O. Lintang, S.L. Lee, I. Sumpono, Well-aligned titanium dioxide with very high length-to-diameter ratio synthesized under magnetic field. Chem. Lett. 41(11), 1468–1470 (2012)
K.H. Jawad, B.A. Hasoon, N.N. Hussein, Biological application of titanium dioxide nanoparticles prepared through laser ablation in liquid. Drug Invent. Today 12, 10 (2019)
E. Giorgetti, M.M. Miranda, S. Caporali, P. Canton, P. Marsili, C. Vergari, F. Giammanco, TiO2 nanoparticles obtained by laser ablation in water: influence of pulse energy and duration on the crystalline phase. J. Alloy Compd. 643, S75–S79 (2015)
E.P. Meagher, G.A. Lager, Polyhedral thermal expansion in the TiO2 polymorphs: refinement of the crystal structures of rutile and brookite at high temperature. Can. Mineral. 17, 77–85 (1979)
H. Seki, N. Ishizawa, N. Mizutani, M. Kato, High temperature structures of the rutile-type oxides, TiO2 and SnO2. Yogyo Kyokai Shi. J. Ceram. Assoc. Jpn. 92, 219 (1984)
C. Ma, O. Tschauner, J.R. Beckett, G.R. Rossman, W. Liu, Panguite (Ti4+, Sc, Al, Mg, Zr, Ca)1.8 O3, a new ultra-refractory titania mineral from the Allende meteorite: Synchrotron micro-diffraction and EBSD. Am. Miner. 97, 1219–1225 (2012)
M. Fusi, V. Russo, C.S. Casari, A.L. Bassi, C.E. Bottani, Titanium oxide nanostructured films by reactive pulsed laser deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 255(10), 5334–5337 (2009)
J. Philip, P.D. Shima, B. Raj, Evidence for enhanced thermal conduction through percolating structures in nanofluids. Nanotechnology 19, 305706 (2008)
R.A. Ismail, A.M. Mousa, K.S. Khashan, M.H. Mohsin, M.K. Hamid, Synthesis of PbI2 nanoparticles by laser ablation in methanol. J. Mater. Sci. 27(10), 10696–10700 (2016)
J. Zhang, P. Zhou, P. Liu, J. Yu, New understanding of the difference of photocatalytic activity among anatase, rutile and brookite TiO2. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 16, 20382–20386 (2014)
R.A. Ismail, K.I. Hassan, O.A. Abdulrazaq, W.H. Abode, Optoelectronic properties of CdTe/Si heterojunction prepared by pulsed Nd: YAG-laser deposition technique. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 10(1), 19–23 (2007)
E.T. Salim, R.A. Ismail, H.T. Halbos, Growth of Nb2O5 film using hydrothermal method: effect of Nb concentration on physical properties. Mater. Res. Express 6, 116429 (2019)
R.A. Ismail, Improved characteristics of sprayed CdO films by rapid thermal annealing. J. Mater. Sci. 20, 1219 (2009)
R.A. Ismail, F.A. Fadhil, Effect of electric field on the properties of bismuth oxide nanoparticles prepared by laser ablation in water. J. Mater. Sci. 25, 1435–1440 (2014)
R.A. Ismail, G.M. Sulaiman, S.A. Abdulrahman, Preparation of iron oxide nanoparticles by laser ablation in DMF under effect of external magnetic field. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 30(206), 1650094 (2016)
R.A. Ismail, K.S. Khashan, R.O. Mahdi, Characterization of high photosensitivity nanostructured 4H-SiC/p-Si heterostructure prepared by laser ablation of silicon in ethanol. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 68, 252–261 (2017)
A. Wypych, I. Bobowska, M. Tracz, A. Opasinska, S. Kadlubowski, A. Krzywania-Kaliszewska, J. Grobelny, P. Wojciechowski, Dielectric properties and characterization of titanium dioxide obtained by different chemistry methods. J. Nanomater. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/124814
L. Wang, C. Hu, L. Shao, The antimicrobial activity of nanoparticles: present situation and prospects for the future. Int. J. Nanomed. 12, 1227–1249 (2017)
J. Jiang, J. Pi, J. Cai, The advancing of zinc oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/1062562
O.A. Rugaie et al., Gold nanoparticles and graphene oxide flakes synergistic partaking in cytosolic bactericidal augmentation: role of ROS and NOX2 activity. Microorganisms 9(1), 101 (2021)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bahjat, H.H., Ismail, R.A., Sulaiman, G.M. et al. Magnetic Field-Assisted Laser Ablation of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles in Water for Anti-Bacterial Applications. J Inorg Organomet Polym 31, 3649–3656 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-021-01973-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-021-01973-8