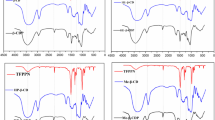
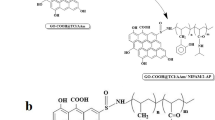
Abstract
Every year, a large amount of waste water containing phenol derivatives is produced in industrial production, which causes serious pollution problem. In the present work, a dually photo- and thermo-responsive adsorbent was developed to remove p-nitrophenol in aqueous solution. N-isopropyl acrylamide was polymerized to build up the thermo-sensitive network of the adsorbent; and cyclodextrin/azobenzene supramolecular complex was grafted on the backbone to act as the photo-responsive adsorbing unit. Under low temperature and 365 nm irradiation, the adsorbent was found in swelling state. In this state, p-nitrophenol was easily caught and removed from aqueous solution by cyclodextrin cavities and azobenzene moieties grafted on the polymer chains. Most interesting, when irradiated at 430 nm, the inclusion of cyclodextrin cavities with azobenzene moieties let freedom of the p-nitrophenol molecules adsorbed previously; at this time if increasing the temperature up to 40 °C, the free p-nitrophenol molecules were forced out owing to the shrinkage of the poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) network. So, without any organic solvent, the adsorbent can be regenerated directly in water. It avoids the secondary pollution caused by traditional regenerating process of adsorbents with organic solvent, which is an important advantage for its practical application of the adsorbent.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Jing, P. Bo, L. Hao, L. Shaohua, Z. Di, Degradation of p-nitrophenol on biochars: role of persistent free radicals. Environ. Sci. Technol. 50, 694 (2016)
Y.X. Yao, H.B. Li, J.Y. Liu, X.L. Tan, J.G. Yu, Removal and adsorption of p-nitrophenol from aqueous solutions using carbon nanotubes and their composites. J. Nanomater. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/571745
S. Hamidouche, O. Bouras, F. Zermane, B. Cheknane, M. Houari, J. Debord, M. Harel, J. Bollinger, M. Baudu, Simultaneous sorption of 4-nitrophenol and 2-nitrophenol on a hybrid geocomposite based on surfactant-modified pillared-clay and activated carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 279, 964–972 (2015)
F. Banat, B. Albashir, S. Alasheh, O. Hayajneh, Adsorption of phenol by bentonite. Environ. Pollut. 107, 391–398 (2000)
P. Yu, Z. Chang, Y. Ma, S. Wang, H. Cao, C. Hua, H. Liu, Separation of p-Nitrophenol and o-Nitrophenol with three-liquid-phase extraction system. Sep. Purif. Technol. 70, 199–206 (2009)
C.S.D. Rodrigues, R.A.C. Borges, V.N. Lima, L.M. Madeira, p-Nitrophenol degradation by Fenton’s oxidation in a bubble column reactor. J. Environ. Manage. 206, 774–785 (2018)
S.R. Subashchandrabose, K. Venkateswarlu, K. Krishnan, R. Naidu, R. Lockington, M. Megharaj, Rhodococcus wratislaviensis strain 9: an efficient p-nitrophenol degrader with a great potential for bioremediation. J. Hazard. Mater. 347, 176–183 (2017)
T. Wang, C. Zhang, S. Chen, Mechanical behaviors of carbon nanoscrolls. J. Nano Nanotechnol. 13, 1136–1140 (2013)
A. Dos Santos, M. Viante, D. Pochapski, A. Downs, C. Almeida, Enhanced removal of p-nitrophenol from aqueous media by montmorillonite clay modified with a cationic surfactant. J. Hazard. Mater. 355, 136–144 (2018)
T. Chen, F. Liu, C. Ling, J. Gao, C. Xu, L. Li, A. Li, Insight into highly efficient coremoval of copper and p-nitrophenol by a newly synthesized polyamine chelating resin from aqueous media: competition and enhancement effect upon site recognition. Environ. Sci. Technol. 47, 13652–13660 (2013)
L. Yang, S. Luo, Y. Li, Y. Xiao, Q. Kang, Q. Cai, High efficient photocatalytic degradation of p-nitrophenol on a unique Cu2O/TiO2 pn heterojunction network catalyst. Environ. Sci. Technol. 44, 7641–7646 (2010)
L. Shao, J. Huang, Controllable synthesis of N-vinylimidazole-modified hyper-cross-linked resins and their efficient adsorption of p-nitrophenol and o-nitrophenol. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 507, 42–50 (2017)
Y. Zhou, X. Liu, L. Tang, F. Zhang, G. Zeng, X. Peng, L. Luo, Y. Deng, Y. Pang, J. Zhang, Insight into highly efficient co-removal of p-nitrophenol and lead by nitrogen-functionalized magnetic ordered mesoporous carbon: performance and modelling. J. Hazard. Mater. 333, 80 (2017)
D. Wang, W. Zhao, Q. Wei, C. Zhao, Y. Zheng, Photoswitchable azobenzene/cyclodextrin host-guest complexes: from UV- to visible/near-IR-light-responsive systems. ChemPhotoChem. 10, 20 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/cptc.201700233
H.M.D. Bandara, S.C. Burdette, Photoisomerization in different classes of azobenzene. Chem. Soc. Rev. 41, 1809–1825 (2012)
H. Zhou, C. Xue, P. Weis, Y. Suzuki, S. Huang, K. Koynov, G.K. Auernhammer, R. Berger, H.-J. Butt, S. Wu, Photoswitching of glass transition temperatures of azobenzene-containing polymers induces reversible solid-to-liquid transitions. Nat. Chem. 9, 145 (2017)
L. Lei, M.S. Johannes, A.L. Pavel, Design and applications of photoresponsive hydrogels. Adv. Mater. 31, 1–17 (2019)
N. Amirmahani, H. Mahdizadeh, M. Malakootian et al., Evaluating nanoparticles decorated on Fe3O4@SiO2-Schiff base (Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS-HBA) in adsorption of ciprofloxacin from aqueous environments. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 30, 3540 (2020)
H. Yamaguchi, Y. Kobayashi, R. Kobayashi, Y. Takashima, A. Hashidzume, A. Harada, Photoswitchable gel assembly based on molecular recognition. Nat. Commun. 3, 603 (2012)
J. Hu, A. Hashidzume, A. Harada, Photoregulated switching of the recognition site of α-cyclodextrin in a side chain polyrotaxane bearing two recognition sites linked with oligo(ethylene glycol). Macromol. Chem. Phys. 212, 1032–1038 (2011)
W. Yuan, J. Shen, W. Guo, Thermoresponse and light-induced reversible self-assembly/disassembly of supra-amphiphiles from azobenzene- and β-cyclodextrin-containing copolymers. Mater. Lett. 134, 259–262 (2014)
M. Chen, S. Nielsen, T. Uyar, S. Zhang, A. Zafar, M. Dong, F. Besenbacher, Electrospun UV-responsive supramolecular nanofibers from a cyclodextrin–azobenzene inclusion complex. J. Mater. Chem. 1, 850–855 (2012)
J. Huang, J.-T. Xu, Z.-Q. Fan, R.-Y. Wang, Z.-Z. Tong, Regulation of the self-assembly morphology of azobenzene-bearing double hydrophobic block copolymers in aqueous solution by shifting the dynamic host-guest complexation. Polym. Chem. 6, 2214 (2015)
H. Ma, Z. Xu, W. Wang, X. Gao, H. Ma, Adsorption and regeneration of leaf-based biochar for p-nitrophenol adsorption from aqueous solution. RSC Adv. 9, 39282–39293 (2019)
B. Zhang, F. Li, T. Wu, D. Sun, Y. Li, Adsorption of p-nitrophenol from aqueous solutions using nanographite oxide. Colloids Surf. A. 464, 78–88 (2015)
K.Y. Andrew Lin, Y.T. Hsieh, Copper-based metal organic framework (MOF), HKUST-1, as an efficient adsorbent to remove p-nitrophenol from water. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 50, 223–228 (2015)
J. Zhou, L. Wang, Z. Zhang, J. Yu, Facile synthesis of alumina hollow microspheres via trisodium citrate-mediated hydrothermal process and their adsorption performances for p-nitrophenol from aqueous solutions. J Colloid Interface. 394, 509–514 (2013)
I.A. Ismail, Thermodynamic and kinetic properties of the adsorption of 4-nitrophenol on graphene from aqueous solution. Can. J. Chem. 93, 150421143704004 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, J., Ren, M., Wang, S. et al. A Smart Adsorbent with Ability of Environmentally Friendly Regeneration for p-Nitrophenol Removal in Aqueous Solution. J Inorg Organomet Polym 31, 2381–2392 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01792-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01792-3