Abstract
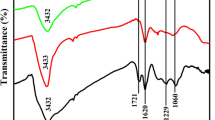
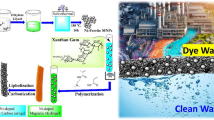
In this study, a novel thermo-responsive polymer was synthesized with efficient grafting of N-isopropylacrylamide as a thermosensitive polymer onto the graphene oxide surface for the efficient removal of phenol and 2,4-dichlorophenol from aqueous solutions. The synthesized polymer was conjugated with 2-allylphenol. Phenol and 2,4-dichlorophenol were monitored by ultra-performance liquid chromatography system equipped with a photodiode array detector. The nanoadsorbent was characterized by different techniques. The nanoadsorbent revealed high adsorption capacity where the removal percentages of 91 and 99% were found under optimal conditions for phenol and 2,4-dichlorophenol, respectively (for phenol; adsorbent dosage = 0.005 g, pH = 8, temperature= 25 °C, contact time = 60 min; for 2,4-dichlorophenol; adsorbent dosage = 0.005 g, pH = 5, temperature = 25 °C, contact time = 10 min). Adsorption of phenol and 2,4-dichlorophenol onto nanoadsorbent followed pseudo-second-order kinetic and Langmuir isotherm models, respectively. The values of ΔG (average value = − 11.39 kJ mol−1 for phenol and 13.42 kJ mol−1 for 2,4-dichlorophenol), ΔH (− 431.72 J mol−1 for phenol and − 15,721.8 J mol−1 for 2,4-dichlorophenol), and ΔS (35.39 J mol−1 K−1 for phenol and − 7.40 J mol−1 K−1 for 2,4-dichlorophenol) confirmed spontaneous and exothermic adsorption. The reusability study indicated that the adsorbent can be reused in the wastewater treatment application. Thermosensitive nanoadsorbent could be used as a low-cost and efficient sorbent for phenol and 2,4-dichlorophenol removal from wastewater samples.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Afsharnia M, Saeidi M, Zarei A, Narooie MR, Biglari H (2016) Phenol removal from aqueous environment by adsorption onto pomegranate peel carbon. Electron Physician 8:3248–3256. https://doi.org/10.19082/3248
Ahmad Panahi H, Sid Kalal H, Moniri E, Nikpour Nezhati M, Taheri Menderjani M, Ranjbar Kelahrodi S, Mahmoudi F (2009) Amberlite XAD-4 functionalized with m-phenylendiamine: synthesis, characterization and applications as extractant for preconcentration and determination of rhodium (III) in water samples by Inductive Couple Plasma Atomic Emission Spectroscopy (ICP-AES). Microchem J 93:49–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2009.04.007
Ain QT, Haq SH, Alshammari A, Al-Mutlaq MA, Naeem Anjum M (2019) The systemic effect of PEG-nGO-induced oxidative stress in vivo in a rodent model. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 10:901–911. https://doi.org/10.3762/bjnano.10.91
Albadarin AB, Charara M, Tarboush BMA, Ahmad MNM, Kurniawan TA, Mu N (2017) Mechanism analysis of tartrazine biosorption onto masau stone, a low cost byproduct from semi-arid regions. J. Mol. Liq. 242:478–483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.07.045
Azizi A, Torabian A, Moniri E, Hassani AH, Ahmad Panahi H (2017) Novel synthesis of graphene oxide with polystyrene for the adsorption of toluene, ethylbenzene and xylenes from wastewater. Desalination Water Treat 74:248–257. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2017.20585
Berizi Z, Hashemi SY, Hadi M, Azari A, Mahvi AH (2016) The study of non-linear kinetics and adsorption isotherm models for acid red 18 from aqueous solutions by magnetite nanoparticles and magnetite nanoparticles modified by sodium alginate. Water Sci Technol 74:1235–1242. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2016.320
Camara M, Liao H, Xu J, Zhang J, Swai R (2019) Molecular dynamics study of the intercalation and conformational transition of poly (N-vinyl caprolactam), a thermosensitive polymer in hydrated Namontmorillonite. Polymer 179:121718. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2019.121718
Carvalho CDO, Rodrigues DLC, Lima EC, Umpierres CS, Chaguezac DFC, Machado FM (2019) Kinetic, equilibrium, and thermodynamic studies on the adsorption of ciprofloxacin by activated carbon produced from Jeriva (Syagrus romanzoffiana). Environ Sci Pollut R 26:4690–4702. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3954-2
Channa AM, Baytak S, Memon SQ, Talpur MY (2019) Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies of removal of phenol from aqueous solution using surface engineered chemistry. Heliyon 5:01852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01852
Chowdhury S, Mishra R, Saha P, Kushwaha P (2011) Adsorption thermodynamics, kinetics and isosteric heat of adsorption of malachite green onto chemically modified rice husk. Desalination 265:159–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.07.047
Chu J, Wang B, Song Y, Zou X, Li C, Yan Y (2012) Selective removal of 2, 4-dichlorophenol by surface molecularly imprinted polymers based on amino-functionalized Fe3O4@SiO2 composites. Adsorpt. Sci Technol 30:409–423. https://doi.org/10.1260/0263-6174.30.5.409
Daneshmoghanlou E, Miralinaghi M, Moniri E, Sadjady S K (2022) Fabrication of a pH-responsive magnetic nanocarrier based on carboxymethyl cellulose-aminated graphene oxide for loading and in-vitro release of curcumin, J Polym Environ (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-022-02467-5.
Dehmani Y, .Alrashdi A A, Lgaz H, Lamhasni T, Abouarnadasse S, Chung L M (2020) Removal of phenol from aqueous solution by adsorption onto hematite (α-Fe2O3): mechanism exploration from both experimental and theoretical studies, Arab J Chem 13: 5474-5486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2020.03.026.
Doskaliyev D, Poulopoulos SG, Yeshmuratov A, Aldyngurova F, Zorpas AA, Inglezakis VJ (2018) Effects of 2-chlorophenol and 2,4,6-trichlorophenol on an activated sludge sequencing batch reactor. Desalination Water Treat 133:283–291. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2018.23065
Dubinin MM (1960) The potential theory of adsorption of gases and vapors for adsorbents with energetically non-uniform surface. Chem Rev 60:235–266. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr60204a006
Freundlich HMF (1906) Über die Adsorption in Lösungen. Z Phys Chem (Leipzig). 57:385–470. https://doi.org/10.1515/zpch-1907-5723
Gurses A, Hassani A, Kıransan M, Acıslı O, Karac S (2014) Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution using by untreated lignite as potential low-cost adsorbent: kinetic, thermodynamic and equilibrium approach. J. Water Process. Eng 2:10–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2014.03.002
Hamrang R, Moniri E, Heydarinasab A, Safaeijavan R (2022) In vitro evaluation of copper sulphide nanoparticles decorated with folic acid/chitosan as a novel pH sensitive nanocarrier for efficient controlled targeted delivery of cytarabine anti-cancer drug. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1002/bab.2355
Hu X, Yu Y, Ren S, Lin N, Wang Y, Zhou J (2018) Highly efficient removal of phenol from aqueous solutions using graphene oxide/Al2O3 composite membrane. J Porous Mater 25:719–726. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-017-0485-z
Huang L, Zhou Y, Guo XQ, Chen ZL (2015) Simultaneous removal of 2, 4-dichlorophenol and Pb (II) from aqueous solution using organoclays: isotherm, kinetics and mechanism. J Ind Eng Chem 22:280–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2014.07.021
Haubold HJ, Mathai AM (2000) The fractional kinetic equation and thermonuclear functions. Astrophys. Space Sci. 273:53–63. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1002695807970
Inglezakis VJ, Malamis S, Omirkhan A, Nauruzbayeva J, Makhtayeva Z, Seidakhmetov T, Kudarova A (2016) Investigating the inhibitory effect of cyanide, phenol and 4- nitrophenol on the activated sludge process employed for the treatment of petroleum wastewater. J. Environ. Manage. 203:825–830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.08.066
Karaca S, Gürses A, Açışl O, Hassani A, Kıranşan M, Yıkılmaz K (2013) Modeling of adsorption isotherms and kinetics of Remazol Red RB adsorption from aqueous solution by modified clay. Desalination Water Treat 51:2726–2739. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2012.749368
Karimi M, Sahandi Zangabad P, Ghasemi A, Amiri M, Bahrami M, Malekzad H, Ghahramanzadeh Asl H, Mahdieh Z, Bozorgomid M, Ghasemi A, Rahmani Taji Boyuk MR, Hamblin MR (2016) Temperature-responsive smart nanocarriers for delivery of therapeutic agents: applications and recent advances. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8:21107–21133. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b00371
Khorshidi P, Shirazi RHSM, Miralinaghi M, Moniri E, Saadi S (2020) Adsorptive removal of mercury (II), copper (II), and lead (II) ions from aqueous solutions using glutathione-functionalized NiFe2O4/graphene oxide composite. Res Chem Intermed 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-020-04164-1
Langmuir I (1918) The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and plat- inum. J Am Chem Soc 40:1361–1403. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja02242a004
Liu J, Fang W, Wang Y, Xing M, Zhang J (2018a) Gold-loaded graphene oxide/PDPB composites for the synchronous removal of Cr(VI) and phenol. Chinese J Catal 39:8–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2067(17)62933-4
Liu Y, Huang S, Zhao X, Zhang Y (2018b) Fabrication of three-dimensional porous β-cyclodextrin/chitosan functionalized graphene oxide hydrogel for methylene blue removal from aqueous solution. Colloids Surf A 539:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2017.11.066
Mohammadi L, Bazrafshan E, Noroozifar M, Ansari-Moghaddam A, Barahuie F, Balarak D (2017) Removing 2,4-dichlorophenol from aqueous environments by heterogeneous catalytic ozonation using synthesized MgO nanoparticles. Water Sci Technol 76:3054–3068. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2017.479
Nekrasova TN, Nazarova OV, Lezov АА, Bezrukova MА, Zolotova YI, Pautov VD, Panarin ЕF (2019) pH- and thermosensitive copolymers of 4-acryloylmorpholine and 2- dialkylaminoethyl methacrylates and silver-containing nanocomposites based on these copolymers. Mater Today Commun 19:196–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2019.01.016
Othman I, Abu Haija M, Ismail I, Hisham Zain J, Banat F (2019) Preparation and catalytic performance of CuFe2O4 nanoparticles supported on reduced graphene oxide (CuFe2O4/rGO) for phenol degradation. Mater Chem Phys 238:121931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.121931
Pan J, Zou X, Wang X, Guan W, Yan Y, Han J (2010) Selective recognition of 2, 4-dichlorophenol from aqueous solution by uniformly sized molecularly imprinted microspheres with β cyclodextrin/attapulgite composites as support. Chem Eng J 162:910–918. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.06.039
Peers AM (1965) Elovich adsorption kinetics and the heterogeneous surface. J. Catal 4:499–503. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9517(65)90054-0
Pieklarz K, Galita G, Tylman M, Maniukiewicz W, Kucharska E, Majsterek I, Modrzejewska Z (2021) Physico-chemical properties and biocompatibility of thermosensitive chitosan lactate and chitosan chloride hydrogels developed for tissue engineering application. J Funct Biomater 12:37. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb12020037
Pourshaban M, Moniri E, Safaeijavan R, Ahmad Panahi H (2021) Kinetics, isotherm, and adsorption mechanism studies of letrozole loaded modified and biosynthesized silver nanoparticles as a drug delivery system: comparison of nonlinear and linear analysis. Korean J Chem Eng 59:493–502. https://doi.org/10.9713/kcer.2021.59.4.493
Reza Soltani E, Tahvildari K, Moniri E, Ahmad Panahi H (2021) NIR-laser triggered drug release from molybdenum disulfide nanosheets modified with thermosensitive polymer for prostate cancer treatment. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-021-02075-1
Rokni E, Shirazi RHSM, Miralinaghi M, Moniri E (2020) Efficient adsorption of anionic dyes onto magnetic graphene oxide coated with polyethylenimine: kinetic, isotherm, and thermodynamic studies. Res. Chem. Intermed. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-020-04090-2
Stroea L, Buruiana T, Buruiana EC (2019) Synthesis and solution properties of thermosensitive hydrophilic imidazolebased copolymers with improved catalytic activity. Mater Chem Phys 223:311–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2018.10.066
Suganya S, Kumar PS (2018) Kinetic and thermodynamic analysis for the redemption of effluents containing Solochrome Black T onto powdered activated carbon: a validation of new solid-liquid phase equilibrium model. J Mol Liq 259:88–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.03.004
Temkin MI (1941) Adsorption equilibrium and kinetics of processes on heterogeneous surfaces and at interaction between adsorbed molecules. Zh Fiz Khim (Russ J Phys Chem). 15:296–332
Torabi Fard N, Tadayon F, Ahmad Panahi H, Moniri E (2022) The synthesis of functionalized graphene oxide by polyester dendrimer as a pH-sensitive nanocarrier for targeted delivery of venlafaxine hydrochloride: central composite design optimization. J. Mol. Liq 349:118149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2021.118149
Wang L, Cheng C, Tapas S, Lei J, Matsuoka M, Zhang J, Zhang F (2015) Carbon dots modified mesoporous organosilica as an adsorbent for the removal of 2,4-dichlorophenol and heavy metal ions. J Mater Chem A 3:13357–13364. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TA01652E
Xu Y, Wei L, Chen X, Zhao J, Wang Y (2021) Application of the liquid–liquid dispersed microextraction based on phase transition behavior of temperature sensitive polymer to rapidly detect 5 BPs in food packaging. Food Chem 347:28960. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128960
Zhong C, He M, Liao H, Chen B, Wang C, Hu B (2016) Polydimethylsiloxane/covalent triazine frameworks coated stir bar sorptive extraction coupled with high performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet detection for the determination of phenols in environmental water samples. J Chromatogr A 1441:8–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2016.02.073
Funding
Islamic Azad University (Science and Research Branch) provided financial support of this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Daryoush Khedri: methodology, conceptualization, investigation, formal analysis, validation, writing-original draft. Amir Hessam Hassani: supervision, project administration, formal analysis, validation, writing-original draft. Elham Moniri: supervision, project administration, formal analysis, validation, writing-original draft. Homayon Ahmad Panahi: project administration, formal analysis, writing-review and editing, investigation. Mehrnoosh Khaleghian: conceptualization, formal analysis, writing-review and editing, investigation.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable .
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Angeles Blanco
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Khedri, D., Hassani, A.H., Moniri, E. et al. Temperature-responsive graphene oxide/N-isopropylacrylamide/2-allylphenol nanocomposite for the removal of phenol and 2,4-dichlorophenol from aqueous solution. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 2494–2508 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22389-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22389-y