Abstract
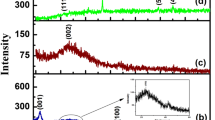
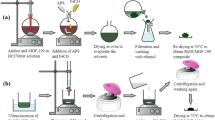
In this paper, a composite material (rGO/Ni/Co) was synthesized by a hydrothermal method and high temperature annealing, and used for the determination of dopamine (DA). Surface morphology and structure of the rGO/Ni/Co were characterized by Scanning electron microscope (SEM), Transmission electron microscope (TEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD). The effects of different pH, scanning rate and interfering substances on the electrochemical properties of dopamine were discussed. The electrochemical test results show that the rGO/Ni/Co/GCE electrode has excellent electrocatalytic activity for dopamine. Under the optimized conditions, the linear range of detection is 10 µmol/L-2250 µmol/L (r = 0.99837), the detection limit is 0.119 µmol/L, and the signal-to-noise ratio is 3. The interference test showed, that most of the ions did not show obvious influence on the detection of DA, indicating that the prepared electrode has selectivity for the detection of DA. Moreover, the composite has good magnetic properties and is convenient for sample separation and recovery.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Sajid, M.K. Nazal, M. Mansha et al., Chemically modified electrodes for electrochemical detection of dopamine in the presence of uric acid and ascorbic acid: a review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 76, 15–29 (2016)
P.Y. Chen, R. Vittal, P.C. Nien et al., Enhancing dopamine detection using a glassy carbon electrode modified with MWCNTs, quercetin, and Nafion®. Biosens. Bioelectron. 24(12), 3504–3509 (2009)
H. Bernheimer, W. Birkmayer, O. Hornykiewicz et al., Brain dopamine and the syndromes of Parkinson and Huntington Clinical, morphological and neurochemical correlations☆. J. Neurol. Sci. 20(4), 415–455 (1973)
W.T. Dauer, S. Przedborski, Parkinson’s disease: mechanisms and models. Neuron 39(6), 889–909 (2003)
Q. Huang, H. Zhang, S. Hu et al., A sensitive and reliable dopamine biosensor was developed based on the Au@ carbon dots–chitosan composite film. Biosens. Bioelectron. 52, 277–280 (2014)
N. Thakur, S. Das Adhikary, M. Kumar et al., Ultrasensitive and highly selective electrochemical detection of dopamine using poly (ionic liquids)–cobalt Polyoxometalate/CNT composite. ACS Omega 3(3), 2966–2973 (2018)
R.M. Wightman, L.J. May, A.C. Michael, Detection of dopamine dynamics in the brain. Analyt. Chem. 60(13), 769A-793A (1988)
L. Li, H. Liu, Y. Shen et al., Electrogenerated chemiluminescence of Au nanoclusters for the detection of dopamine. Anal. Chem. 83(3), 661–665 (2011)
J. Zhao, L. Zhao, C. Lan et al., Graphene quantum dots as effective probes for label-free fluorescence detection of dopamine. Sens. Actuators B 223, 246–251 (2016)
H. Li, C. Li, Z. Yan et al., Simultaneous monitoring multiple neurotransmitters and neuromodulators during cerebral ischemia/reperfusion in rats by microdialysis and capillary electrophoresis. J. Neurosci. Methods 189(2), 162–168 (2010)
W.J. Barreto, S.R.G. Barreto, R.A. Ando et al., Raman, IR, UV–vis and EPR characterization of two copper dioxolene complexes derived from L-dopa and dopamine. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 71(4), 1419–1424 (2008)
E. Cudjoe, J. Pawliszyn, Optimization of solid phase microextraction coatings for liquid chromatography mass spectrometry determination of neurotransmitters. J. Chromatogr. A 1341, 1–7 (2014)
A. Numan, M.M. Shahid, F.S. Omar et al., Facile fabrication of cobalt oxide nanograin-decorated reduced graphene oxide composite as ultrasensitive platform for dopamine detection. Sens. Actuators B 238, 1043–1051 (2017)
M. Altun, M.B. Kamac, A. Bilgi et al., Dopamine biosensor based on screen-printed electrode modified with reduced graphene oxide, polyneutral red and gold nanoparticle. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 100(4), 451–467 (2020)
Q. He, G. Li, X. Liu et al., Morphologically tunable MnO2 nanoparticles fabrication, modelling and their influences on electrochemical sensing performance toward dopamine. Catalysts 2018, 8(8)
N. Thomas, T. Shimna, J. Thomas et al., Nanomolar detection of dopamine at ZnO/graphene modified carbon paste electrode. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym Mater. 29(5), 1728–1737 (2019)
E. Manikandan, G. Kavitha, J. Kennedy, Epitaxial zinc oxide, graphene oxide composite thin-films by laser technique for micro-Raman and enhanced field emission study. Ceram. Int. 40(10), 16065–16070 (2014)
K. Kaviyarasu, E. Manikandan, J. Kennedy et al., Synthesis and analytical applications of photoluminescent carbon nanosheet by exfoliation of graphite oxide without purification. J. Mater. Sci. 27(12), 13080–13085 (2016)
J. Kennedy, F. Fang, J. Futter et al., Synthesis and enhanced field emission of zinc oxide incorporated carbon nanotubes. Diam. Relat. Mater. 71, 79–84 (2017)
K. Krishnamoorthy, M. Veerapandian, K. Yun et al., The chemical and structural analysis of graphene oxide with different degrees of oxidation. Carbon 53, 38–49 (2013)
B.S. TK, A.B. Nair, B.T. Abraham et al., Microwave exfoliated reduced graphene oxide epoxy nanocomposites for high performance applications. Polymer 55(16), 3614–3627 (2014)
K.S. Novoselov, V.I. Fal, L. Colombo et al., A roadmap for graphene. Nature 490(7419), 192 (2012)
C. Sengottaiyan, R. Jayavel, R.G. Shrestha et al., Indium oxide/carbon nanotube/reduced graphene oxide ternary nanocomposite with enhanced electrochemical supercapacitance. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 92(3), 521–528 (2019)
K. Le, Z. Wang, F. Wang et al., Sandwich-like NiCo layered double hydroxide/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite cathodes for high energy density asymmetric supercapacitors. Dalton Trans. 48(16), 5193–5202 (2019)
C.N. Rao, K. Pramoda, Borocarbonitrides, BxCyNz, 2D nanocomposites with novel properties. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 92(2), 441–468 (2019)
M. Idrees, S. Batool, J. Kong et al., Polyborosilazane derived ceramics---nitrogen sulfur dual doped graphene nanocomposite anode for enhanced lithium ion batteries. Electrochimica Acta 2019;925–937
S.K. Kandasamy, K. Kandasamy, Recent advances in electrochemical performances of graphene composite (graphene-polyaniline/polypyrrole/activated carbon/carbon nanotube) electrode materials for supercapacitor: a review. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym Mater. 28(3), 559–584 (2018)
R. Rajendran, L.K. Shrestha, R.M. Kumar et al., Composite nanoarchitectonics for ternary systems of reduced graphene oxide/carbon nanotubes/nickel oxide with enhanced electrochemical capacitor performance. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym Mater. 25(2), 267–274 (2015)
M. Khan, A.B. Yousaf, M. Chen et al., Mixed-phase Pd–Pt bimetallic alloy on graphene oxide with high activity for electrocatalytic applications. J. Power Sources 282, 520–528 (2015)
X.Y. Yan, X.L. Tong, Y.F. Zhang et al., Cuprous oxide nanoparticles dispersed on reduced graphene oxide as an efficient electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction reaction. Chem. Commun. 48(13), 1892–1894 (2012)
C.H. Liu, R.H. Liu, Q.J. Sun et al., Controlled synthesis and synergistic effects of graphene-supported PdAu bimetallic nanoparticles with tunable catalytic properties. Nanoscale 7(14), 6356–6362 (2015)
L. Rout, A. Kumar, R.S. Dhaka et al., Bimetallic Au-Cu alloy nanoparticles on reduced graphene oxide support: synthesis, catalytic activity and investigation of synergistic effect by DFT analysis. Appl. Catal. A 538, 107–122 (2017)
Q. Wang, Z. Zhang, J. Liu et al., Bimetallic non-noble CoNi nanoparticles monodispersed on multiwall carbon nanotubes: highly efficient hydrolysis of ammonia borane. Mater. Chem. Phys. 204, 58–61 (2018)
H.L. Jiang, Q. Xu, Recent progress in synergistic catalysis over heterometallic nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. 21(36), 13705–13725 (2011)
A.B. Vysakh, C.L. Babu, C.P. Vinod, Demonstration of synergistic catalysis in Au@ Ni bimetallic core–shell nanostructures. J. Phys. Chem. C 119(15), 8138–8146 (2015)
M.S. Rahmanifar, H. Hesari, A. Noori et al., A dual Ni/Co-MOF-reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite as a high performance supercapacitor electrode material. Electrochim. Acta 275, 76–86 (2018)
Z. Chen, R. Wu, Y. Liu et al., Ultrafine Co nanoparticles encapsulated in carbon-nanotubes‐grafted graphene sheets as advanced electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction. Adv. Mater. 30(30), 1802011 (2018)
P. Pascariu, I.V. Tudose, M. Suchea et al., Preparation and characterization of Ni, Co doped ZnO nanoparticles for photocatalytic applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 448, 481–488 (2018)
Y. Yusran, D. Xu, Q. Fang et al., MOF-derived Co@ NC nanocatalyst for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol to 4-aminophenol. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 241, 346–354 (2017)
J. Garcia-Torres, C. Crean, E. Vallés, Co-Ni-carbon flexible composite fibres for directional magnetic actuation. Mater. Des. 141, 9–16 (2018)
Y. Fu, H.Y. Yu, C. Jiang et al., NiCo alloy nanoparticles decorated on N-doped carbon nanofibers as highly active and durable oxygen electrocatalyst. Adv. Func. Mater. 28(9), 1705094 (2018)
H. Wang, X. Li, X. Lan et al., Supported ultrafine NiCo bimetallic alloy nanoparticles derived from bimetal–organic frameworks: a highly active catalyst for furfuryl alcohol hydrogenation. ACS Catalysis 8(3), 2121–2128 (2018)
J. Chen, Y. Li, L. Huang et al., High-yield preparation of graphene oxide from small graphite flakes via an improved Hummers method with a simple purification process. Carbon 81, 826–834 (2015)
W.S. Hummers Jr., R.E. Offeman, Preparation of graphitic oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 80(6), 1339–1339 (1958)
Y. Yao, H. Chen, C. Lian et al., Fe, Co, Ni nanocrystals encapsulated in nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes as Fenton-like catalysts for organic pollutant removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 314, 129–139 (2016)
Y. Zhang, N. Zhang, Z.R. Tang et al., Graphene transforms wide band gap ZnS to a visible light photocatalyst. The new role of graphene as a macromolecular photosensitizer. ACS Nano 6(11), 9777–9789 (2012)
Z. Wang, Y. Hu, W. Yang et al., Facile one-step microwave-assisted route towards Ni nanospheres/reduced graphene oxide hybrids for non-enzymatic glucose sensing. Sensors 12(4), 4860–4869 (2012)
G. Jiang, T. Jiang, H. Zhou et al., Preparation of N-doped carbon quantum dots for highly sensitive detection of dopamine by an electrochemical method. RSC Adv 5(12), 9064–9068 (2015)
Z.N. Huang, J. Zou, J. Teng et al., A novel electrochemical sensor based on self-assembled platinum nanochains-multi-walled carbon nanotubes-graphene nanoparticles composite for simultaneous determination of dopamine and ascorbic acid. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 172, 167–175 (2019)
H.S. GJang, D. Kim, C. Lee et al., Nafion coated Au nanoparticle-graphene quantum dot nanocomposite modified working electrode for voltammetric determination of dopamine. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 105, 174–181 (2019)
B. Liu, X. Ouyang, Y. Ding et al., Electrochemical preparation of nickel and copper oxides-decorated graphene composite for simultaneous determination of dopamine, acetaminophen and tryptophan. Talanta 146, 114–121 (2016)
W. Zhang, L. Liu, Y. Li et al., Electrochemical sensing platform based on the biomass-derived microporous carbons for simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid. Biosens. Bioelectron. 121, 96–103 (2018)
K. Krishnamoorthy, V. Sudha, S.M.S. Kumar et al., Simultaneous determination of dopamine and uric acid using copper oxide nano-rice modified electrode. J. Alloys Compd. 748, 338–347 (2018)
W. Liu, J. Qian, K. Wang et al., Magnetically separable Fe3O4 nanoparticles-decorated reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite for catalytic wet hydrogen peroxide oxidation. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym Mater. 23(4), 907–916 (2013)
C. Sengottaiyan, R. Jayavel, R.G. Shrestha et al., Electrochemical supercapacitance properties of reduced graphene oxide/Mn2O3:Co3O4 nanocomposite. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym Mater. 27(2), 576–585 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, Q., Kang, X., Fu, F. et al. The Synthesis of rGO/Ni/Co Composite and Electrochemical Determination of Dopamine. J Inorg Organomet Polym 30, 4269–4277 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01738-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01738-9