Abstract
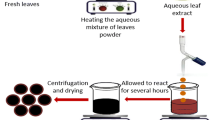
Nanobiotechnology is a fast developing scientific field having several applications in biochemistry, medicine, biology, engineering, etc. and plays a key role in the development and improvement of clean, eco-friendly, non-toxic and cost effective techniques for the synthesis and assembly of metal nanoparticles. One of the foremost green synthesis approaches includes biofabrication of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) using plants and plant products. In the present study, we have synthesized silver nanoparticles using aqueous extract of Indian spice Asafoetida. Their formation was confirmed through UV–Vis spectral peak at 426.4 nm and their stability was also monitored for 3 months at room temperature using dynamic light scattering (DLS). DLS analysis revealed that the particles so formed were not only monodispersed in nature but also stable at room temperature for 3 months with a reported size of 90–95 nm. The characterization techniques revealed that synthesized AgNPs were well distributed with size ranging from 90 to 100 nm. Furthermore, Asafoetida-AgNPs were tested for their anticancer activity against the HepG2 cell line. Cell viability assay was done to check the percentage of viable cells and morphological changes at various test concentrations (0.01, 0.1, 1 and 10 ppm) after 24 and 48 h of exposure. The recorded viable cells at lowest concentration (0.01 ppm) was found to be 58.55% and at highest concentration (10 ppm) it was 40.08% after 24 h. Further, when the percent cell viability was observed at 48 h it was 45.22% and 20.23% at lowest and highest concentrations. Morphological characterization of HepG2 cells after the treatment of Asafoetida-AgNPs showed floating and patchy cells signifying their toxic nature against cancerous cells.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
N.M. Dimitrijevic, D.M. Bartels, C.D. Jonah, K. Takahashi, T. Rajh, Radiolytically induced formation and optical absorption spectra of colloidal silver nanoparticles in supercritical ethane. J. Phys. Chem. B 105(5), 954–959 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0028296
Y. Sun, Y. Yin, B.T. Mayers, T. Herricks, Y. Xia, Uniform silver nanowires synthesis by reducing AgNO3 with ethylene glycol in the presence of seeds and poly (vinyl pyrrolidone). Chem. Mater. 14(11), 4736–4745 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1021/cm020587b
L. Zhang, Y.H. Shen, A.J. Xie, S.K. Li, C. Wang, One-step synthesis of silver nanoparticles in self-assembled multilayered films based on a Keggin structure compound. J. Mater. Chem. 18(11), 1196–1203 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1039/B717151J
V. Kathiravan, S. Ravi, S. Ashokkumar, Synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Melia dubia leaf extract and their in vitro anticancer activity. Spectrochim. Acta A 130, 116–121 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2014.03.107
P. Raveendran, J. Fu, S.L. Wallen, Completely “green” synthesis and stabilization of metal nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125(46), 13940–13941 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja029267j
S. Dhuper, D. Panda, P.L. Nayak, Green synthesis and characterization of zero valent iron nanoparticles from the leaf extract of Mangifera indica. Nano Trends J. Nanotechnol. Appl. 13(2), 16–22 (2012)
D. Philip, Green synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles using Hibiscus rosasinensis. Physica E 42(5), 1417–1424 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physe.2009.11.081
U.B. Jagtap, V.A. Bapat, Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam. seed extract and its antibacterial activity. Indus. Crops Prod. 46, 132–137 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.01.019
S. Ahmed, M. Ahmad, B.L. Swami, S. Ikram, Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Azadirachta indica aqueous leaf extract. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 9(1), 1–7 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrras.2015.06.006
U.K. Sur, B. Ankamwar, S. Karmakar, A. Halder, P. Das, Green synthesis of Silver nanoparticles using the plant extract of Shikakai and Reetha. Mater. Tod. Proc. 5(1), 2321–2329 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2017.09.236
H. Bar, D.K. Bhui, G.P. Sahoo, P. Sarkar, S.P. De, A. Misra, Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using latex of Jatropha curcas. Colloids Surf. A 339(1–3), 134–139 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2009.02.008
P. Prakash, P. Gnanaprakasam, R. Emmanuel, S. Arokiyaraj, M. Saravanan, Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from leaf extract of Mimusops elengi, Linn. for enhanced antibacterial activity against multi drug resistant clinical isolates. Colliods Surf. B 108, 255–259 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.03.017
K. Anandalakshmi, J. Venugobal, V. Ramasamy, Characterization of silver nanoparticles by green synthesis method using Pedalium murex leaf extract and their antibacterial activity. Appl. Nanosci. 6(3), 399–408 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-015-0449-z
S. Botcha, S.D. Prattipati, Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Hyptis suaveolens (L.) Poit leaf extracts, their characterization and cytotoxicity evaluation against PC-3 and MDA-MB 231 cells. Biologia (2019). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-019-00222-1
R. Vaidyanathan, K. Kalishwaralal, S. Gopalram, S. Gurunathan, Nanosilver—the burgeoning therapeutic molecule and its green synthesis. Biotechnol. Adv. 27(6), 924–937 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2009.08.001
J. Sangeetha, J. Sandhya, J. Philip, Biosynthesis and functionalization of silver nanoparticles using Nigella sativa, Dioscorea alata and Ferula asafoetida. Sci. Adv. Mater. 6(8), 1681–1690 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1166/sam.2014.1991
M. Zahin, Studies on antibacterial, antioxidant and antimutagenic activities of certain Indian medicinal plants. Doctoral dissertation, Aligarh Muslim University (2010)
N. Satsangi, S. Preet, Exploring nanobiotechnology in controlling malaria and cancer. IEEE Region 10 Humanitarian Technology Conference (R10-HTC). (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/r10-htc.2016.7906824
T. Mosmann, Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 65(1–2), 55–63 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4
B. Ulug, M.H. Turkdemir, A. Cicek, A. Mete, Role of irradiation in the green synthesis of silver nanoparticles mediated by fig (Ficus carica) leaf extract. Spectrochim. Acta A 13, 153–161 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2014.06.142
M.A. Noginov, G. Zhu, M. Bahoura, J. Adegoke, C.E. Small, B.A. Ritzo, V.P. Drachev, V.M. Shalaev, Enhancement of surface plasmons in an Ag aggregate by optical gain in a dielectric medium. Opt. Lett. 31(20), 3022–3024 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.31.003022
D. Philip, C. Unni, S.A. Aromal, V.K. Vidhu, Murraya koenigii leaf-assisted rapid green synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles. Spectrochim. Acta A 78(2), 899–904 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2010.12.060
D. Raghunandan, B.D. Mahesh, S. Basavaraja, S.D. Balaji, S.Y. Manjunath, A. Venkataraman, Microwave-assisted rapid extracellular synthesis of stable bio-functionalized silver nanoparticles from guava (Psidium guajava) leaf extract. J. Nanopart. Res. 13(5), 2021–2028 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-010-9956-8
S. Preet, N. Satsangi, Size controlled green synthesis of biocompatible silver nanoparticles with enhanced mosquito larvicidal activity. J. Clust. Sci. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-019-01606-8
A. Hamidi, M.E. Yazdi, M.S. Amiri, H.A. Hosseini, M. Darroudi, Biological synthesis of silver nanoparticles in Tribulus terrestris L. extract and evaluation of their photocatalyst, antibacterial, and cytotoxicity effects. Res. Chem. Intermed. 45(5), 2915–2925 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-019-03770-y
M. Anjugam, B. Vaseeharan, A. Iswarya, M. Divya, N.M. Prabhu, K. Sankaranarayanan, Biological synthesis of silver nanoparticles using β-1, 3 glucan binding protein and their antibacterial, antibiofilm and cytotoxic potential. Microb. Pathog. 115, 31–40 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2017.12.003
D.L. Van Hyning, C.F. Zukoski, Formation mechanisms and aggregation behavior of borohydride reduced silver particles. Langmuir 14(24), 7034–7046 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1021/la980325h
B. Molleman, T. Hiemstra, Time, pH, and size dependency of silver nanoparticle dissolution: the road to equilibrium. Environ. Sci. 4(6), 1314–1327 (2017)
D.P. Sakarkar, Morphological study of silver nanoparticles by using titronx-100 [surfactant]. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Res. Stud. 2(3), 5–8 (2013)
S. Kim, J.E. Choi, J. Choi, K.H. Chung, K. Park, J. Yi, D.Y. Ryu, Oxidative stress-dependent toxicity of silver nanoparticles in human hepatoma cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 23(6), 1076–1084 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2009.06.001
K. Kawata, M. Osawa, S. Okabe, In vitro toxicity of silver nanoparticles at noncytotoxic doses to HepG2 human hepatoma cells. Environ. Sci. Technol. 43(15), 6046–6051 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/es900754q
W. Liu, Y. Wu, C. Wang, H.C. Li, T. Wang, C.Y. Liao, G.B. Jiang, Impact of silver nanoparticles on human cells: effect of particle size. Nanotoxicology 4(3), 319–330 (2010). https://doi.org/10.3109/17435390.2010.483745
L. Braydich-Stolle, S. Hussain, J.J. Schlager, M.C. Hofmann, In vitro cytotoxicity of nanoparticles in mammalian germline stem cells. Toxicol. Sci. 88(2), 412–419 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfi256
F. Faedmaleki, F.H. Shirazi, A.A. Salarian, H.A. Ashtiani, H. Rastegar, Toxicity effect of silver nanoparticles on mice liver primary cell culture and HepG2 cell line. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 13(1), 235–242 (2014)
Acknowledgements
Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi is gratefully acknowledged for providing the author (Neh Satsangi, IF130922) with financial assistance in form of INSPIRE fellowship. Author is thankful to National Institute of Oceanography, Goa, Advanced Instrumentation Research Facility (AIRF), JNU, New Delhi and International Centre for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, New Delhi for characterization studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declare that she has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Satsangi, N. Synthesis and Characterization of Biocompatible Silver Nanoparticles for Anticancer Application. J Inorg Organomet Polym 30, 1907–1914 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-019-01372-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-019-01372-0