Abstract
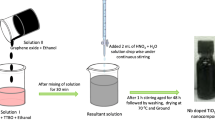
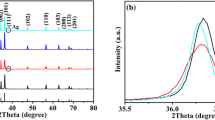
In this work, a series of Al-doped ZnO nanoparticles-reduced graphene oxide (AZO–RGO) nanocomposites were successfully synthesized by loading AZO nanoparticles (AZO NPs) on the graphene oxide sheets via in situ and low temperature solvothermal method. Several techniques were utilized to characterize the resultant nanocomposites including scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), atomic force microscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and FT-Infra Red (FT-IR) analyses. SEM and TEM studies showed that AZO NPs have been formed on RGO surface, confirming the formation of AZO–RGO nanocomposites. XPS, FT-IR, and XRD analyses revealed that the oxygen-containing functional groups can prepare as anchoring sites for capturing AZO NPs on RGO surface. Moreover, it was observed that these nanoparticles have wurtzite structure. The photo-catalysis results showed that the 5% AZO–RGO nanocomposite has a higher efficiency than that of pure ZnO and ZnO–RGO samples for removing methyl orange dye from water under visible light irradiation. The enhancement in the photocatalytic activity can be attributed to the increase of surface area of AZO–RGO nanocomposites in comparison with pure ZnO. Furthermore, the existing of Al dopants and RGO sheets in the prepared samples can effectively decrease the charge recombination process in the AZO–RGO nanocomposites.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Ahmad, E. Ahmed, Y. Zhang, N.R. Khalid, J. Xu, M. Ullah, Z. Hong, Preparation of highly efficient Al-doped ZnO photocatalyst by combustion synthesis. Curr. Appl. Phys. 13, 697–704 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2012.11.008
O. Akhavan, R. Azimirad, S. Safa, Functionalized carbon nanotubes in ZnO thin films for photoinactivation of bacteria. Mater. Chem. Phys. 130, 598–602 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2011.07.030
S.S. Alias, A.B. Ismail, A.A. Mohamad, Effect of pH on ZnO nanoparticle properties synthesized by sol–gel centrifugation. J. Alloy. Compd. 499, 231–237 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.03.174
F.A. Alshamsi, A.S. Albadwawi, M.M. Alnuaimi, M.A. Rauf, S.S. Ashraf, Comparative efficiencies of the degradation of Crystal Violet using UV/hydrogen peroxide and Fenton’s reagent. Dyes Pigm. 74, 283–287 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2006.02.016
S. Ameen, H.-K. Seo, M. Shaheer Akhtar, H.S. Shin, Novel graphene/polyaniline nanocomposites and its photocatalytic activity toward the degradation of rose Bengal dye. Chem. Eng. J. 210, 220–228 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.08.035
S. Ameen, M.S. Akhtar, H.-K. Seo, H.S. Shin, Advanced ZnO–graphene oxide nanohybrid and its photocatalytic. Appl. Mater. Lett. 100, 261–265 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2013.03.012
R. Beura, P. Thangadurai, Structural, optical and photocatalytic properties of graphene-ZnO nanocomposites for varied compositions. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 102, 168–177 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2016.11.024
I.Y.Y. Bu, Highly conductive and transparent reduced graphene oxide/aluminium doped zinc oxide nanocomposite for the next generation solar cell. Appl. Opt. Mater. 36, 299–303 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2013.09.012
Y. Bu, Z. Chen, W. Li, B. Hou, Highly efficient photocatalytic performance of graphene–ZnO quasi-shell–core composite material. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 5, 12361–12368 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/am403149g
D. Chen et al., Graphene-wrapped ZnO nanospheres as a photocatalyst for high performance photocatalysis. Thin Solid Films 574, 1–9 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2014.11.051
A.B. Djurisic, Y.H. Leung, A.M.C. Ng, Strategies for improving the efficiency of semiconductor metal oxide photocatalysis. Mater. Horiz. 1, 400–410 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4MH00031E
S. Gayathri, P. Jayabal, M. Kottaisamy, V. Ramakrishnan, Synthesis of ZnO decorated graphene nanocomposite for enhanced photocatalytic properties. J. Appl. Phys. 115, 173504 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4874877
R. Georgekutty, M.K. Seery, S.C. Pillai, A highly efficient Ag-ZnO photocatalyst: synthesis, properties, and mechanism. J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 13563–13570 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp802729a
O. Gezici, M. Küçükosmanoğlu, A. Ayar, The adsorption behavior of crystal violet in functionalized sporopollenin-mediated column arrangements. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 304, 307–316 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2006.09.048
Y. Gong, T. Andelman, G. Neumark, S. O’Brien, I. Kuskovsky, Origin of defect-related green emission from ZnO nanoparticles: effect of surface modification. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2, 297–302 (2007)
G. Gu, J. Cheng, X. Li, W. Ni, Q. Guan, G. Qu, B. Wang, Facile synthesis of graphene supported ultralong TiO2 nanofibers from the commercial titania for high performance lithium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 3, 6642–6648 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TA00523J
H.-L. Guo, P. Su, X. Kang, S.-K. Ning, Synthesis and characterization of nitrogen-doped graphene hydrogels by hydrothermal route with urea as reducing-doping agents. J. Mater. Chem. A 1, 2248–2255 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/C2TA00887D
J. He, C. Niu, C. Yang, J. Wang, X. Su, Reduced graphene oxide anchored with zinc oxide nanoparticles with enhanced photocatalytic activity and gas sensing properties. RSC Adv. 4, 60253–60259 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA12707B
N. Herring, S. Almahoudi, C. Olson, M.S. El-Shall, Enhanced photocatalytic activity of ZnO–graphene nanocomposites prepared by microwave synthesis. J. Nanopart. Res. 14, 1–13 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-1277-7
L. Hu, X. Hu, X. Wu, C. Du, Y. Dai, J. Deng, Density functional calculation of transition metal adatom adsorption on graphene. Physica B 405, 3337–3341 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2010.05.001
W.S. Hummers, R.E. Offeman, Preparation of graphitic oxide. Am. Chem. Soc. 80, 1339–1339 (1958). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01539a017
M. Isik, N.M. Gasanly, Thermoluminescence properties of Al doped ZnO nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 44, 13929–13933 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.04.241
P. Jantawasu, T. Sreethawong, S. Chavadej, Photocatalytic activity of nanocrystalline mesoporous-assembled TiO2 photocatalyst for degradation of methyl orange monoazo dye in aqueous wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 155, 223–233 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.07.036
S.H. Jeong, S. Kho, D. Jung, S.B. Lee, J.H. Boo, Deposition of aluminum-doped zinc oxide films by RF magnetron sputtering and study of their surface characteristics. Surf. Coat. Technol. 174–175, 187–192 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0257-8972(03)00600-5
S.A. Khayatian, A. Kompany, N. Shahtahmassebi, A.K. Zak, Preparation and characterization of Al doped ZnO NPs/graphene nanocomposites synthesized by a facile one-step solvothermal method. Ceram. Int. 42, 110–115 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.08.008
Y.C. Ko, H.Y. Fang, D.H. Chen, Fabrication of Ag/ZnO/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite for SERS detection and multiway killing of bacteria. J. Alloy. Compd. 695, 1145–1153 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.10.241
H.J. Lee, J.H. Kim, S.S. Park, S.S. Hong, G.D. Lee, Degradation kinetics for photocatalytic reaction of methyl orange over Al-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 25, 199–206 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2014.10.035
X. Li, Q. Wang, Y. Zhao, W. Wu, J. Chen, H. Meng, Green synthesis and photo-catalytic performances for ZnO-reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 411, 69–75 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2013.08.050
P. Liu, Y. Huang, L. Wang, A facile synthesis of reduced graphene oxide with Zn powder under acidic condition. Mater. Lett. 91, 125–128 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2012.09.085
S. Liu, H. Sun, S. Liu, S. Wang, Graphene facilitated visible light photodegradation of methylene blue over titanium dioxide photocatalysts. Chem. Eng. J. 214, 298–303 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.10.058
X. Liu, J. Zhang, L. Wang, T. Yang, X. Guo, S. Wu, S. Wang, 3D hierarchically porous ZnO structures and their functionalization by Au nanoparticles for gas sensors. J. Mater. Chem. 21, 349–356 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1039/C0JM01800G
X. Liu et al., UV-assisted photocatalytic synthesis of ZnO–reduced graphene oxide composites with enhanced photocatalytic activity in reduction of Cr(VI). Chem. Eng. J. 183, 238–243 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.12.068
M. Louhichi, S. Romdhane, A. Fkiri, L.S. Smiri, H. Bouchriha, Structural and photoluminescence properties of Al-doped zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized in polyol. Appl. Surf. Sci. 356, 998–1004 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.08.202
Q.-P. Luo, X.-Y. Yu, B.-X. Lei, H.-Y. Chen, D.-B. Kuang, C.-Y. Su, Reduced graphene oxide-hierarchical ZnO hollow sphere composites with enhanced photocurrent and photocatalytic activity. J. Phys. Chem. C 116, 8111–8117 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp2113329
R. Lv et al., Facile synthesis of ZnO nanorods grown on graphene sheets and its enhanced photocatalytic efficiency. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 90, 550–558 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.4347
N. Neves, A. Lagoa, J. Calado, A.M.B. do Rego, E. Fortunato, R. Martins, I. Ferreira, Al-doped ZnO nanostructured powders by emulsion detonation synthesis—Improving materials for high quality sputtering targets manufacturing. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 34, 2325–2338 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2014.02.019
A.A. Ogwu, E. Bouquerel, O. Ademosu, S. Moh, E. Crossan, F. Placido, The influence of rf power and oxygen flow rate during deposition on the optical transmittance of copper oxide thin films prepared by reactive magnetron sputtering. J. Phys. D 38, 266 (2005)
Y. Peng, J. Ji, D. Chen, Ultrasound assisted synthesis of ZnO/reduced graphene oxide composites with enhanced photocatalytic activity and anti-photocorrosion. Appl. Surf. Sci. 356, 762–768 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.08.070
J. Qin, X. Zhang, C. Yang, M. Cao, M. Ma, R. Liu, ZnO microspheres-reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite for photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye. Appl. Surf. Sci. 392, 196–203 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.09.043
L.S. Roselin, R. Selvin, Photocatalytic degradation of reactive orange 16 dye in a ZnO coated thin film flow photoreactor. Sci. Adv. Mater. 3, 251–258 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1166/sam.2011.1151
P.P. Sahay, R.K. Nath, Al-doped ZnO thin films as methanol sensors. Sens. Actuators B 134, 654–659 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2008.06.006
B. Saravanakumar, R. Mohan, S.-J. Kim, Facile synthesis of graphene/ZnO nanocomposites by low temperature hydrothermal method. Mater. Res. Bull. 48, 878–883 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2012.11.048
J.-C. Sin, S.-M. Lam, K.-T. Lee, A.R. Mohamed, Preparation and photocatalytic properties of visible light-driven samarium-doped ZnO nanorods. Ceram. Int. 39, 5833–5843 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.01.004
R.K. Singhal et al., Room temperature ferromagnetism in Mn-doped dilute ZnO semiconductor: An electronic structure study using X-ray photoemission. J. Alloy. Compd. 477, 379–385 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2008.10.005
Y.M. Slokar, A.M. Le Marechal, Methods of decoloration of textile wastewaters. Dyes Pigm. 37, 335–356 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0143-7208(97)00075-2
G. Srinet, R. Kumar, V. Sajal, Effects of aluminium doping on structural and photoluminescence properties of ZnO nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 40, 4025–4031 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.08.055
S. Stankovich, R.D. Piner, X. Chen, N. Wu, S.T. Nguyen, R.S. Ruoff, Stable aqueous dispersions of graphitic nanoplatelets via the reduction of exfoliated graphite oxide in the presence of poly(sodium 4-styrenesulfonate. J. Mater. Chem. 16, 155–158 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1039/B512799H
V. Subramanian, E.E. Wolf, P.V. Kamat, Green emission to probe photoinduced charging events in ZnO–Au nanoparticles. charge distribution and fermi-level equilibration. J. Phys. Chem. B 107, 7479–7485 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0275037
H. Sun, S. Wang, H.M. Ang, M.O. Tadé, Q. Li, Halogen element modified titanium dioxide for visible light photocatalysis. Chem. Eng. J. 162, 437–447 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.05.069
S. Suwanboon, P. Amornpitoksuk, A. Haidoux, J.C. Tedenac, Structural and optical properties of undoped and aluminium doped zinc oxide nanoparticles via precipitation method at low temperature. J. Alloy. Compd. 462, 335–339 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2007.08.048
L. Sygellou, G. Paterakis, C. Galiotis, D. Tasis, Work function tuning of reduced graphene oxide thin films. J. Phys. Chem. C 120, 281–290 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b09234
Tassalit D, Laoufi AN, Bentahar F (2011) Photocatalytic deterioration of tylosin in an aqueous suspension using UV/TiO2. Sci. Adv. Mater. 3:944–948 https://doi.org/10.1166/sam.2011.1243
Y. Tian, B. Chang, J. Fu, F. Xi, X. Dong, Yellow–colored mesoporous pure titania and its high stability in visible light photocatalysis. Powder Technol. 245, 227–232 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2013.04.036
K. Ullah, Z.-D. Meng, S. Ye, L. Zhu, W.-C. Oh, Synthesis and characterization of novel PbS–graphene/TiO2 composite with enhanced photocatalytic activity. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 20, 1035–1042 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2013.06.040
J. Ungelenk, C. Feldmann, Synthesis of faceted [small beta]-SnWO4 microcrystals with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic properties. Chem. Commun. 48, 7838–7840 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CC33224H
J. Wang, T. Tsuzuki, B. Tang, X. Hou, L. Sun, X. Wang, Reduced graphene oxide/ZnO composite: reusable adsorbent for pollutant management. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 4, 3084–3090 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/am300445f
M. Wang et al., Optical and photoluminescent properties of sol-gel Al-doped ZnO thin films. Mater. Lett. 61, 1118–1121 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2006.06.065
B. Weng, J. Wu, N. Zhang, Y.-J. Xu, Observing the role of graphene in boosting the two-electron reduction of oxygen in graphene–WO3 nanorod photocatalysts. Langmuir 30, 5574–5584 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/la4048566
P. Worajittiphon, K. Pingmuang, B. Inceesungvorn, N. Wetchakun, S. Phanichphant, Enhancing the photocatalytic activity of ZnO nanoparticles for efficient rhodamine B degradation by functionalised graphene nanoplatelets. Ceram. Int. 41, 1885–1889 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.09.023
Q. Xiao, L. Ouyang, Photocatalytic photodegradation of xanthate over Zn1−xMnxO under visible light irradiation. J. Alloy. Compd. 479, L4–L7 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2008.12.085
Q. Xiao, J. Zhang, C. Xiao, X. Tan, Photocatalytic decolorization of methylene blue over Zn1 – xCoxO under visible light irradiation. Mater. Sci. Eng. 142, 121–125 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2007.06.021
D. Yang et al., Chemical analysis of graphene oxide films after heat and chemical treatments by X-ray photoelectron and Micro-Raman spectroscopy. Carbon 47, 145–152 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2008.09.045
N.R. Yogamalar, A.C. Bose, Absorption–emission study of hydrothermally grown Al:ZnO nanostructures. J. Alloy. Compd. 509, 8493–8500 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2011.06.012
J. Yu, J. Jin, B. Cheng, M. Jaroniec, A noble metal-free reduced graphene oxide-CdS nanorod composite for the enhanced visible-light photocatalytic reduction of CO2 to solar fuel. J. Mater. Chem. A 2, 3407–3416 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C3TA14493C
D. Zeng, P. Gong, Y. Chen, C. Wang, D.-L. Peng, Preparation of multi-branched Au–ZnO hybrid nanocrystals on graphene for enhanced photocatalytic performance. Mater. Lett. 161, 379–383 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2015.08.153
L. Zhang, N. Li, H. Jiu, G. Qi, Y. Huang, ZnO-reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites as efficient photocatalysts for photocatalytic reduction of CO2. Ceram. Int. 41, 6256–6262 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.01.044
L. Zhang et al., Significantly enhanced photocatalytic activities and charge separation mechanism of Pd-decorated ZnO–graphene oxide nanocomposites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 3623–3629 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/am405872r
Y. Zheng, L. Zheng, Y. Zhan, X. Lin, Q. Zheng, K. Wei, Ag/ZnO heterostructure nanocrystals: synthesis, characterization and photocatalysis. Inorg. Chem. 46, 6980–6986 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1021/ic700688f
J.B. Zhong, J.Z. Li, X.Y. He, J. Zeng, Y. Lu, W. Hu, K. Lin, Improved photocatalytic performance of Pd-doped ZnO. Curr. Appl. Phys. 12, 998–1001 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2012.01.003
G. Zhou, D.-W. Wang, L.-C. Yin, N. Li, F. Li, H.-M. Cheng, Oxygen bridges between NiO nanosheets and graphene for improvement of lithium storage. ACS Nano 6, 3214–3223 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn300098m
X. Zhou, T. Shi, H. Zhou, Hydrothermal preparation of ZnO-reduced graphene oxide hybrid with high performance in photocatalytic degradation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 258, 6204–6211 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.02.131
F. Zou, Y. Yu, N. Cao, L. Wu, J. Zhi, A novel approach for synthesis of TiO2–graphene nanocomposites and their photoelectrical properties. Scr. Mater. 64, 621–624 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2010.12.003
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Research Involving Human Participants and/or Animal
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khayatian, S.A., Kompany, A., Shahtahmassebi, N. et al. Enhanced Photocatalytic Performance of Al-Doped ZnO NPs-Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite for Removing of Methyl Orange Dye from Water Under Visible-Light Irradiation. J Inorg Organomet Polym 28, 2677–2688 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-018-0940-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-018-0940-6