Abstract
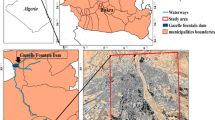
Evaluation and ranking of rural settlements based on the stages of texture deterioration is critical for rural renovation. However, far too little attention has been paid to topic in the literature. This study focuses on the evaluation and ranking of rural settlements based on the stages of texture deterioration. To do so, we use the Overall Weighing (OW) method (a combination of objective weighing methods including Entropy, CRITIC, IDOCRIW, and subjective weighing method including Rank Sum) and the combinative distance-based assessment (CODAS) method as powerful methods in Multi-criteria decision making. The research method is descriptive-applied where data is collected both library and field. The objective data were collected from 260 rural households and fifteen local managers in the deteriorated villages on the Tehran metropolitan fringe through questionnaire forms. Similalry, the subjective data was collected from fifteen elites and scientific experts. The results indicate high rural migration rate factor is superior compared to other indices. Besides, Hesar Kouchak village has a more unfavorable situation than other villages that is followed by other villages including Mazdaran, Qala Boland, Mashhad Firoozkooh, Kabirabad, Yahar, Quinak Rakhshani, Jafarabad Baqraf, Hesar Mehtar, Zavareh Bid, Ramin, Atashan, Vastar, Hasanabad Baqraf, and ultimately Salehabad Sharqi.

Source: The findings of the research


Source: The findings of the research

Source: The findings of the research

Source: The findings of the research

Source: The findings of the research
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Iranian Statistics Center (2011): Population and Housing Census, November 2011.
- Rural Islamic Councils (RIC) are considered as policy-making institutions and Dehyars (rural managers) are considered as the executive arms of rural councils (Emani Jajermi, 2009).
References
Acioly, C. C., Jr. (1999). The International Conference Shelter and Revitalisation of Old and Historic Urban Centres (ICSROHUC) “Institutional and urban management instruments for inner city revitalisation: a brief review with special focus on Brazilian experiences” (pp. 1–25). Institute for Housing and Urban Development Studies-HIS.
Akbari, N., Khoshakhlaq, R., & Mardiha, S. (2013). Measurement and valuation of factors affecting housing choice using a choice experiment method: Viewpoints of households living at old urban textures of Isfahan. The Economic Research, 13(3), 19–47.
Andalib, A. (2007). Renovation process for Tehran city deteriorated areas. Organization of Tehran City Renovation, Office of renovation of deteriorated areas Publishers.
Ástmarsson, B., Anker Jensen, P., & Maslesa, E. (2013). Sustainable renovation of residential buildings and the landlord/tenant dilemma. Energy Policy, 63, 355–362.
Babatunde, M. O., & Ighravwe, D. E. (2019). A CRITIC-TOPSIS framework for hybrid renewable energy systems evaluation under technoeconomic requirements. Journal of Project Management, 4, 1–18. https://doi.org/10.5267/j.jpm.2018.12.001
Badi, I. A., Abdulshahed, A. M., & Shetwanc, A. G. (2018). A case study of supplier selection for a steelmaking company in Libya by using the COmbinative Distance-based ASsessment (CODAS) model. Decision Making: Applications in Management and Engineering, 1(1), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.31181/dmame180101b
Bemanian, M. R., & Rezaei Rad, H. (2012). Assessing Factor Analyst and Delphi Models by use of GIS IN recognizing deterioration in urban fabric (case study of KHaksefid in 4th zone of Tehran). Hoviateshahr, 6, 5–16.
Cereska, A., Zavadskas, E. K., Bucinskas, V., Podvezko, V., & Sutinys, E. (2018). Analysis of steel wire rope diagnostic data applying multi-criteria methods. Applied Sciences, 8(260), 1–22. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8020260
Dadelo, S., Kosareva, N., & Zavadskas, E. K. (2017). Entropy-KEMIRA approach for MCDM problem solution in human resources selection task. International Journal of Information Technology and Decision Making, 19(28), 1–28. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0219622017500274
Dayyani, L., Pourtaheri, M., Eftekhari, A. R., & Ahmadi, H. (2019). The identification and zoning of areas having rural deteriorated textures in the Tehran province by using KDE and GIS. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment, 25(1–2), 475–504. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2018.1523675
Eisenberg, A. M. (2016). Addressing rural blight: lessons from West Virginia and WVLEAP. Journal of Affordable Housing, 24(3), 513–546.
Emani Jajermi H. 2009. Rural manager. Encyclopedia of urban and rural management. Tehran: Ministry of Science, Research and Technology; Ministry of Interior, Iran Municipalities and Rural Management Organization
Faisal, K., & Shaker, A. (2017). Improving the accuracy of urban environmental quality assessment using Geographically-Weighted Regression techniques. Sensors, 17(528), 1–25. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17030528
Gordon, C. (2003). Blighting the way: Urban renewal, economic development, and the elusive definition of blight. Fordham Urban Law Journal, 31(2), 305–337.
Habibi, K., Poor Ahmad, A., Meshkini, A., Asgari, A., & Nazari Adli, S. (2008). Determination of structural/ construction effective factors on the vulnerability of Zanjan’s old town texture using FUZZY LOGIC & GIS. Honar-Ha-Ye-Ziba, 33, 27–36.
Hadaei, A. A., Feizi, V., & Nuroozi, R. (2013). Estimating the potential risks caused by an earthquake in deteriorated textures (case study: Eastern Sangalaj neighborhood in Tehran’s 12th region). Rescue and Relief, 5(3), 1–17.
Hakim, M., & Majedi, H. (2014). Selecting the appropriate approach to reorganize the deteriorated textures. International Journal of Architecture and Urban Development, 4(2), 67–76.
Hamzenejad, M., Shakouri, M., & Shakouri, N. (2018). Investigating and analyzing the condition of the worn texture of Jaffari neighborhood in Tehran with the approach of promoting environmental quality and providing solutions for its organization by using GIS. Journal of Innovative Research in Engineering Sciences, 4(1), 17–29.
Hayes Luce, H. (2000). The meaning of blight: a survey of statutory and case law. Real Property Probate and Trust Journal, 35(2), 389–478.
Ishizaki, T., & Takami, M. (2015). 6th International Building Physics Conference (IBPC) “Deterioration of the wall of a historic stone building in a cold region and measures to protect it.” Energy Procedia, 78, 1371–1376.
Kaili D. 2003. Fuzzy evaluation of urban environmental quality (case study: Wuchang, Wuhan), Master Thesis. International Institute for Geo-information Science and Earth Observation. Urban Planning and Management, Enschede, The Netherlands
Keshavarz Ghorabaee, M., Amiri, M., Zavadskas, E. K., Hooshmand, R., & Antucheviciene, J. (2017). Fuzzy extension of the CODAS method for multi-criteria market segment evaluation. Journal of Business Economics and Management, 18(1), 1–19. https://doi.org/10.3846/16111699.2016.1278559
Keshavarz Ghorabaee, M., Zavadskas, E. K., Turskis, Z., & Antucheviciene, J. (2016). A new Combinative Distance-based Assessment (CODAS) method for multicriteria decision-making. Economic Computation and Economic Cybernetics Studies and Research, 50(3), 25–44.
Lefcoe, G. (2008). Redevelopment takings after Kelo: what’s blight got to do with it? Review of law and social justice, 17(3), 803–851.
Li, P., Qian, H., Howard, K. W. F., & Wu, J. (2015). Building a new and sustainable ‘“Silk Road economic belt.”’ Environment and Earth Science, 74, 7267–7270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4739-2
Li, P., Qian, H., & Zhou, W. (2017). Finding harmony between the environment and humanity: An introduction to the thematic issue of the Silk Road. Environment and Earth Science, 76(105), 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6428-9
Malek Mahmoudi N, Piri M, Daneshfar H, Farahi T, Kazemi A, Karami SA, and Mahvi R. 2012. The epistemology of Tehran province (Trial Experimental)-236, pp 21. Ministry of Education & Training, Research Organization and Educational Planning Publishers, Tehran, I R Iran
Mathew, M., & Sahu, S. (2018). Comparison of new multi-criteria decision making methods for material handling equipment selection. Management Science Letters, 8, 139–150. https://doi.org/10.5267/j.msl.2018.1.004
Mohammad Salehi, Z., Sheikhi, H., & Rahimian, A. A. (2013). Physical–enviromental rehabilitaion of the central core of City textures, toward urban sustainable development (case study: centeral texture of the Khorramabad city). Journal of Urban Studies, 2(7), 73–87.
Morgan B and Gilreath Jr. 2013. A model for quantitatively defining urban blight by using assessment data. Fair & Equitable 3–13
Mostaghim, M., & Masoud, M. (2014). Feasibility of the possible patterns of intervention in the distressed fabric; case study: A Part of Qom city of Iran in central sub-area. Journal of Civil Engineering and Urbanism, 4, 121–132.
Niknami, K., & Dehpahlavan, M. (2013). Formation of the Silk Road in the light of security (case study: the relics and archaeological finds periphery of road, from Semnan to Garmsar). Geopolitics Quarterly, 9(2), 230–255.
Pourahmad, A., & Zarei, J. (2015). Measuring of the life quality in the urban deteriorated texture Area (Case Study: 9th District of Tehran). Journal of Urban Research and Planning, 8(21), 1–18.
Ramachandran A. 2014. Urban renewal-Chetput station area. Thesis. School of architecture and planning campus, Department of planning, Anna University, Chennai, India
Robinson., & Cole. (2007). Urban blight: an analysis of state blight statutes and their implications for eminent domain reform. The National Association of REALTORS® Publishers.
Sabri Emara, A.-A., & Korany, M. S. (2016). An analytical study of building materials and deterioration factors of Farasan heritage houses, and the recommendations of conservation and rehabilitation (German house case study). Urban Planning and Architecture Design for Sustainable Development (UPADSD 14–16 October 2015). Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 216, 561–569.
Samiei, A., & Sayafzadeh, A. (2016). Analysis of the worn-out tissues characteristics and providing of intervention pattern (case study: Eslamshahr city, Tehran). Current Urban Studies, 4, 267–279. https://doi.org/10.4236/cus.2016.43018
Sarmento R, Zorzal FMB, Serafim AJ and Allmenroedr LB. 2000. Urban environmental quality indicators. The Sustainable city. pp 95–102.
SCI (Statistical Center of Iran). 2011. Population and Housing Census, November 2011. Retrieved Apr 2017 from https://www.amar.org.ir/%D8%AE%D8%A7%D9%86%D9%87/%D8%A7%D8%B1%D8%AA%D8%A8%D8%A7%D8%B7-%D8%A8%D8%A7-%D9%85%D8%A7.
Shaker Ardekani, R., & Akhgar, H. (2014). Applying gentrification process for historical texture of Ardakan city, Yazd. Iran. International Journal of Recent Advances in Multidisciplinary Research, 01(03), 014–025.
Shamaei, A., & Pourahmad, A. (2005). Urban rehabilitation and renovation from the Viewpoint of Geography (1st ed.). University of Tehran Publishers.
TG (Tehran Governor). 2013. Statistical yearbook of Tehran province-2012. Tehran Governor, Office of Statistical and Information, and Management and Planning Organization of Tehran Province, Tehran, I R Iran
Trinkūnienė, E., Podvezko, V., Zavadskas, E. K., Jokšienė, I., Vinogradova, I., & Trinkūnas, V. (2017). Evaluation of quality assurance in contractor contracts by multi-attribute decision-making methods. Economic Research-Ekonomska Istraživanja, 30(1), 1152–1180. https://doi.org/10.1080/1331677X.2017.1325616
Varesi, H. R., Taghvaei, M., & Rezaei, N. (2012). Organizing of urban dederiorated texture (case study: Shiraz city). Scientific Specialized Journal of Spatial Planning, 2(2), 129–156.
Vinogradova, I., Podvezko, V., & Zavadskas, E. K. (2018). The recalculation of the weights of Criteria in MCDM Methods using the Bayes Approach. Symmetry, 10(205), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym10060205
Weaver, R. C., & Bagchi-Sen, S. (2013). Spatial analysis of urban decline: The geography of blight. Applied Geography, 40, 61–70.
Zavadskas, E. K., Cavallaro, F., Podvezko, V., Ubarte, I., & Kaklauskas, A. (2017). MCDM assessment of a healthy and safe built environment according to sustainable development principles: A practical neighborhood approach in Vilnius. Sustainability, 9(702), 1–30. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9050702
Zebardast, E., Khalili, A., & Dehghani, M. (2013). Application of factor analysis method in the identification of decayed urban fabrics. Honar-Ha-Ye-Ziba Memari- Va Shahrsazi, 18(2), 27–42. https://doi.org/10.22059/JFAUP.2013.50524
Zhang H and Yang Q. 2008. Geoinformatics 2008 and Joint Conference on GIS and Built Environment: The Built Environment and Its Dynamics “Rural tourism spatial distribution based on multi-criteria decision analysis and GIS”. Proc of SPIE 7144(714425):1–11. doi: https://doi.org/10.1117/12.812825.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The sections (part from literature review and initial data) are from this paper reports the results of a doctoral thesis titled “Pattern presentation for organizing of rural deteriorated textures in the metropolises fringe (case study: the rural areas of Tehran province)” field of Geography and Rural Planning Tarbiat Modares University, supervisor: Dr. Mehdi Pourtaheri, by Leyla Dayyani.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dayyani, L., Pourtaheri, M. & Ahmadi, H. Evaluation of texture deterioration stages of rural settlements on the Tehran metropolitan fringe using the decision-making method of OW and CODAS. J Hous and the Built Environ 37, 241–289 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10901-021-09835-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10901-021-09835-y