Abstract
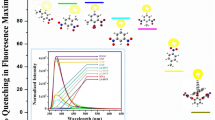
We present the synthesis of a new oxacalix[4]arene system, DMANSOC, wherein two 5-(dimethylamino)-1-naphthalene sulfonamide subunits are attached to the lower rims of the basic oxacalix[4]arene platform. Extensive spectrophotometric studies were conducted to investigate the selectivity and sensitivity of DMANSOC towards nitroaromatic explosives. Detailed analysis of spectrophotometric data, utilizing techniques such as Stern-Volmer, Benesi-Hildebrand, Job’s plot, and interference study, unequivocally demonstrated the effectiveness of DMANSOC as a highly efficient fluorescent sensor for 2,4,6-trinitrophenol explosive (TNP) detection in an aqueous medium. The sensor exhibited a linear concentration range of 7.5 μM to 50 μM, with a low detection limit of 4.64 μM and a high binding affinity of 2.45 × 104 M towards TNP. Furthermore, the efficiency of the sensor in environmental samples contaminated with TNP was evaluated, yielding excellent recovery rates. Complementary DFT calculations and molecular dynamics simulations were performed to elucidate the mechanism behind the selective fluorescence quenching of DMANSOC in the presence of TNP.
Graphical Abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data will be available upon request.
References
Goldman ER, Medintz IL, Whitley JL, Hayhurst A, Clapp AR, Uyeda HT, Deschamps JR, Lassman ME, Mattoussi H (2005) A hybrid quantum dot – antibody fragment fluorescence resonance energy transfer-based TNT sensor. J Am Chem Soc 127(18):6744–6751
Lan A, Li K, Wu H, Olson DH, Emge TJ, Ki W, Hong M, Li J (2009) A luminescent microporous metal–organic framework for the fast and reversible detection of high explosives. Angew Chem 121(13):2370–2374
Enkin N, Sharon E, Golub E, Willner I (2014) Ag nanocluster/DNA hybrids: functional modules for the detection of nitroaromatic and RDX explosives. Nano Lett 14(8):4918–4922
Salinas Y, Martínez-Máñez R, Marcos MD, Sancenón F, Costero AM, Parra M, Gil S (2012) Optical chemosensors and reagents to detect explosives. Chem Soc Rev 41(3):1261–1296
He G, Peng H, Liu T, Yang M, Zhang Y, Fang Y (2009) A novel picric acid film sensor via combination of the surface enrichment effect of chitosan films and the aggregation-induced emission effect of siloles. J Mater Chem 19(39):7347–7353
Wollin K-M, Dieter HH (2005) Toxicological guidelines for monocyclic nitro-, amino-and aminonitroaromatics, nitramines, and nitrate esters in drinking water. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 49(1):18–26
Ju P, Zhang E, Jiang L, Zhang Z, Hou X, Zhang Y, Yang H, Wang J (2018) A novel microporous Tb-MOF fluorescent sensor for highly selective and sensitive detection of picric acid. RSC Adv 8(39):21671–21678
Holmgren E, Ek S, Colmsjö A (2012) Extraction of explosives from soil followed by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry analysis with negative chemical ionization. J Chromatogr A 1222:109–115
Cortada C, Vidal L, Canals A (2011) Determination of nitroaromatic explosives in water samples by direct ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction followed by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Talanta 85(5):2546–2552
Schramm S, Vailhen D, Bridoux MC (2016) Use of experimental design in the investigation of stir bar sorptive extraction followed by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry for the analysis of explosives in water samples. J Chromatogr A 1433:24–33
Babaee S, Beiraghi A (2010) Micellar extraction and high performance liquid chromatography-ultra violet determination of some explosives in water samples. Anal Chim Acta 662(1):9–13
Zang J, Guo CX, Hu F, Yu L, Li CM (2011) Electrochemical detection of ultratrace nitroaromatic explosives using ordered mesoporous carbon. Anal Chim Acta 683(2):187–191
Lee J, Park S, Cho SG, Goh EM, Lee S, Koh S-S, Kim J (2014) Analysis of explosives using corona discharge ionization combined with ion mobility spectrometry–mass spectrometry. Talanta 120:64–70
Tabrizchi M, ILbeigi V (2010) Detection of explosives by positive corona discharge ion mobility spectrometry. J Hazard Mater 176(1–3):692–696
Gares KL, Hufziger KT, Bykov SV, Asher SA (2016) Review of explosive detection methodologies and the emergence of standoff deep UV resonance Raman. J Raman Spectrosc 47(1):124–141
Hakonen A, Andersson PO, Schmidt MS, Rindzevicius T, Käll M (2015) Explosive and chemical threat detection by surface-enhanced Raman scattering: a review. Anal Chim Acta 893:1–13
Meaney MS, McGuffin VL (2008) Investigation of common fluorophores for the detection of nitrated explosives by fluorescence quenching. Anal Chim Acta 610(1):57–67
Tu R, Liu B, Wang Z, Gao D, Wang F, Fang Q, Zhang Z (2008) Amine-capped ZnS – Mn2 + nanocrystals for fluorescence detection of trace TNT explosive. Anal Chem 80(9):3458–3465
Germain ME, Knapp MJ (2009) Optical explosives detection: from color changes to fluorescence turn-on. Chem Soc Rev 38(9):2543–2555
Woodfin RL (2006) Trace chemical sensing of explosives. John Wiley & Sons
Toal SJ, Trogler WC (2006) Polymer sensors for nitroaromatic explosives detection. J Mater Chem 16(28):2871–2883
Hu Z, Deibert BJ, Li J (2014) Luminescent metal–organic frameworks for chemical sensing and explosive detection. Chem Soc Rev 43(16):5815–5840
Desai V, Panchal M, Dey S, Panjwani F, Jain VK (2021) Recent advancements for the recognization of Nitroaromatic Explosives using Calixarene based fluorescent probes. J Fluoresc, 1–13
Mao X, Tian D, Li H (2012) p-Sulfonated calix [6] arene modified graphene as a ‘turn on’fluorescent probe for L-carnitine in living cells. Chem Commun 48(40):4851–4853
Zhang G, Zhu X, Miao F, Tian D, Li H (2012) Design of switchable wettability sensor for paraquat based on clicking calix [4] arene. Org Biomol Chem 10(16):3185–3188
LÜ J, ZHANG, H., and, LU P (2007) Selective Electrochemical Recognition of o-Phenylenediol by a Novel Calix [4] arene derivative. Chin J Chem 25(10):1542–1546
Zhou J, Chen M, Diao G (2013) Calix [4, 6, 8] arenesulfonates functionalized reduced graphene oxide with high supramolecular recognition capability: fabrication and application for enhanced host–guest electrochemical recognition. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5(3):828–836
Miao F, Zhan J, Zou Z, Tian D, Li H (2012) A new Hg2 + fluorescent sensors based on 1, 3-alternate thiacalix [4] arene (L) and the complex of [L + Hg2+] as turn-on sensor for cysteine. Tetrahedron 68(10):2409–2413
Dhir A, Bhalla V, Kumar M (2008) Ratiometric sensing of Hg2 + based on the calix [4] arene of partial cone conformation possessing a dansyl moiety. Org Lett 10(21):4891–4894
Kim HJ, Kim SH, Kim JH, Lee JH, Lee C-H, Kim JS (2009) ICT-based Cu (II)-sensing 9, 10-anthraquinonecalix [4] crown. Tetrahedron Lett 50(23):2782–2786
Ghosh S, Chakrabarty R, Mukherjee PS (2009) Design, synthesis, and characterizations of a series of Pt4 macrocycles and fluorescent sensing of Fe3+/Cu2+/Ni2 + through metal coordination. Inorg Chem 48(2):549–556
Dey S, Kumar A, Mondal PK, Modi KM, Chopra D, Jain VK (2020) An oxacalix [4] arene derived dual sensing fluorescent probe for the detection of as (v) and cr (vi) oxyanions in aqueous media. Dalton Trans 49(22):7459–7466
Kalaiyarasan G, Joseph J, Kumar P (2020) Phosphorus-doped Carbon Quantum Dots as Fluorometric Probes for Iron Detection. ACS Omega 5(35):22278–22288
Kumar RS, Kumar SKA (2019) Highly selective fluorescent chemosensor for the relay detection of Al3 + and picric acid. Inorg Chem Commun 106:165–173
Funding
The authors thank the financial assistance provided by LSRBDRDO, New Delhi, through the project scheme REF. No (LSRB-01/15001/M/LSRB-373/BTB/2020). B. K. S. thanks UGC: Dr. D. S. Kothari Post-Doctoral Fellowship (Project No: F4-2/2006(BSR)/CH/20–21/0113) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Vishv Desai: Lead, Data curation, Writing- Original draft Preparation (First author). Krunal Modi: Formal analysis, Software. Falak Panjwani: Methodology, Visualization. Banabithi Koley Seth: Validation, Investigation. Manoj Vora: Writing- Reviewing and Editing. Jaymin Parikh: Computational study (writing). Vinod K Jain: Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical Approval
Not Applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Desai, V., Modi, K., Panjwani, F. et al. Design and Synthesis of an Efficient Fluorescent Probe Based on Oxacalix[4]arene for the Selective Detection of Trinitrophenol (TNP) Explosives in Aqueous System. J Fluoresc 34, 1219–1228 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-023-03352-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-023-03352-7