Abstract
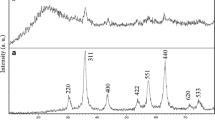
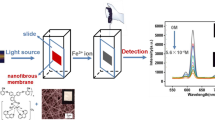
The existence of excessive concentration of iron ion (Fe3+) in water will do harm to the environment and biology. Presently, sensitive and selective determination of Fe3+ directly in real environment samples is still a challenging job because of the high complexity of the sample matrix. In this work, we reported a new sensor system for Fe3+ based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) from upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs) to Rhodamine derivative probe (RhB). The NaYF4: Yb, Er@SiO2@P(NIPAM-co-RhB) nanocomposites was constructed, in which PNIPAm was used as the probe carrier. The nanocomposites can not only be excited by infrared light to avoid the interference of background light in the Fe3+ detection process, but also enhance the detection signal output through temperature control. Under the optimum conditions, the RSD (Relative standard deviation) of actual sample measurements ranges was from 1.95% to 4.96%, with the recovery rate from 97.4% to 103.3%, which showed high reliability for Fe3+ detection. This work could be extended to sensing other target ions or molecules and may promote the widespread use of FRET technique.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The date that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Liang Y, Xu L, Tang K, Guan Y, Wang T, Wang H, William WY (2020) Nitrogen-doped carbon dots used as an “on–off–on” fluorescent sensor for Fe3+ and glutathione detection. Dyes Pigm 178:108358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2020.108358
Li AL, Wang ZL, Wang WY, Liu QS, Sun Y, Wang SF, Gu W (2021) A novel dehydroabietic acid-based fluorescent probe for detection of Fe3+ and Hg2+ ions and its application in live-cell imaging. Microchem J 160:105682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2020.105682
Li B, Gu X, Wang M, Liu X, Xu K (2021) A novel “off-on-off” fluorescent probe for sensing of Fe3+ and F− successively in aqueous solution and its application in cells. Dyes Pigm 194:109637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2021.109637
Latief U, ul Islam, S., Khan, Z. M., Khan, M. S. (2021) A facile green synthesis of functionalized carbon quantum dots as fluorescent probes for a highly selective and sensitive detection of Fe3+ ions. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 262:120132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2021.120132
Khan WA, Arain MB, Bibi H, Tuzen M, Shah N, Zada A (2021) Selective electromembrane extraction and sensitive colorimetric detection of copper (II). Z Phys Chem 235:1113–1128. https://doi.org/10.1515/zpch-2020-1761
Nazir R, Khan M, Rehman RU, Shujah S, Khan M, Ullah M, Zada A, Mahmood N, Ahmad I (2020) Adsorption of selected azo dyes from an aqueous solution by activated carbon derived from Monotheca buxifolia waste seeds. Soil Water Res 15:166–172. https://doi.org/10.17221/59/2019-SWR
Ullah M, Nazir R, Khan M, Khan W, Shah M, Afridi SG, Zada A (2020) The effective removal of heavy metals from water by activated carbon adsorbents of Albizia lebbeck and Melia azedarach seed shells. Soil Water Res 15:30–37. https://doi.org/10.17221/212/2018-SWR
Tang X, Wang Y, Han J, Ni L, Zhang H, Li C, Li J, Qiu Y (2018) A novel fluorescent probe based on biphenyl and rhodamine for multi-metal ion recognition and its application. Dalton Trans 47(10):3378–3387. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7DT04629D
Wang X, Huang J, Wei H, Wu L, Xing H, Zhu J, Kan C (2022) A novel Fe3+ fluorescent probe based on rhodamine derivatives and its application in biological imaging. J Mol Struct 1270:133979. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2022.133979
Geng Y, Chen L, Wan Q, Lian C, Han Y, Wang Y, Zhang C, Huang L, Zhao H, Sun X, He H (2021) A novel [1, 2, 4] triazolo [1, 5-a] pyrimidine derivative as a fluorescence probe for specific detection of Fe3+ ions and application in cell imaging. Anal Chim Acta 1187:339168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2021.339168
Feng X, Li Y, He X, Liu H, Zhao Z, Kwok RT, Elsegood MR, Lam JWY, Tang BZ (2018) A substitution-dependent light-up fluorescence probe for selectively detecting Fe3+ ions and its cell imaging application. Adv Func Mater 28:1802833. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201802833
Tang X, Wang Y, Han J, Ni L, Wang L, Li L, Zhang H, Li C, Li J, Li H (2018) A relay identification fluorescence probe for Fe3+ and phosphate anion and its applications. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 191:172–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2017.10.018
Soleja N, Jairajpuri MA, Queen A, Mohsin M (2019) Genetically encoded FRET based optical sensor for Hg2+ detection and intracellular imaging in living cells. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 46:1669–1683. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-019-02235-w
Marx V (2017) Probes: FRET sensor design and optimization. Nat Methods 14:949–953. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.4434
Chini MK, Kumar V, Maiti B, De P, Satapathi S (2019) A dual “Turn-on/Turn-off” “FRET” sensor for highly sensitive and selective detection of lead and methylene blue based on fluorescent dansyl tagged copolymer and small molecule diketopyrrolopyrrole. Polym Test 79:105997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2019.105997
Wu L, Huang C, Emery BP, Sedgwick AC, Bull SD, He XP, Tian H, Yoon J, Sessler JL, James TD (2020) Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET)-based small-molecule sensors and imaging agents. Chem Soc Rev 49:5110–5139. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9CS00318E
Maniyazagan M, Mariadasse R, Jeyakanthan J, Lokanath NK, Naveen S, Premkumar K, Muthuraja P, Manisankar P, Stalin T (2017) Rhodamine based “turn–on” molecular switch FRET–sensor for cadmium and sulfide ions and live cell imaging study. Sens Actuators B-Chem 238:565–577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.07.102
Ma Y, Pandzic E, Nicovich PR, Yamamoto Y, Kwiatek JM, Pageon SV, Benda A, Rossy J, Gaus K (2017) An intermolecular FRET sensor detects the dynamics of T cell receptor clustering. Nat Commun 8(1):15100–15100. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15100
Tan H, Xie S, Xu J, Li N, Zhang C, Xu L, Zheng J (2017) Branched NaYF4: Yb, Er up-conversion phosphors with luminescent properties for anti-counterfeiting application. Sci Adv Mater 9:2223–2233. https://doi.org/10.1166/sam.2017.3252
Xu L, Liu J, Pei L, Xu Y, Xia Z (2019) Enhanced up-conversion luminescence and optical temperature sensing in graphitic C3N4 quantum dots grafted with BaWO4:Yb3+, Er3+ phosphors. J Mater Chem C 7:6112–6119. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9TC01351B
Lin SL, Chen ZR, Chang CA (2018) Nd3+ sensitized core-shell-shell nanocomposites loaded with ir806 dye for photothermal therapy and up-conversion luminescence imaging by a single wavelength NIR light irradiation. Nanotheranostics 2(3):243–257. https://doi.org/10.7150/ntno.25901
Wu Y, Suo H, He D, Guo C (2018) Highly sensitive up-conversion optical thermometry based on Yb3+-Er3+ co-doped NaLa(MoO4)2 green phosphors. Mater Res Bull 106:14–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2018.05.019
Li K, Zhu D, Lian H (2020) Up-conversion luminescence and optical temperature sensing properties in novel KBaY(MoO4)3:Yb3+, Er3+ materials for temperature sensors. J Alloys Compd 816:152554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.152554
Roh J, Yu H, Jang J (2016) Hexagonal β-NaYF4:Yb3+, Er3+ nanoprism-incorporated upconverting layer in perovskite solar cells for near-infrared sunlight harvesting. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:19847–19852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.152554
Bednarkiewicz A, Nyk M, Samoc M, Strek W (2010) Up-conversion FRET from Er3+/Yb3+: NaYF4 nanophosphor to CdSe quantum dots. J Phys Chem C 114:17535–17541. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp106120d
Cui S, Xu S, Song H, Xu W, Chen X, Zhou D, Yin Z, Han W (2015) Highly sensitive and selective detection of mercury ions based on up-conversion FRET from NaYF4:Yb3+/Er3+ nanophosphors to CdTe quantum dots. RSC Adv 5:99099–99106. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA16200A
Wu S, Duan N, Shi Z, Fang C, Wang Z (2014) Dual fluorescence resonance energy transfer assay between tunable upconversion nanoparticles and controlled gold nanoparticles for the simultaneous detection of Pb2+ and Hg2+. Talanta 128:327–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2014.04.056
Hu J, Yu X, Zhang X, Jing C, Liu T, Hu X, Lu S, Uvdal K, Gao H, Hu Z (2020) Rapid detection of mercury (II) ions and water content by a new rhodamine B-based fluorescent chemosensor. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 241:118657. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2020.118657
Zhu N, Xu J, Ma Q, Geng Y, Li L, Liu S, Liu S, Wang G (2022) Rhodamine-based fluorescent probe for highly selective determination of Hg2+. ACS Omega 7:29236–29245. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.2c03336
Wang L, Ye D, Li W, Liu Y, Li L, Zhang W, Ni L (2017) Fluorescent and colorimetric detection of Fe (III) and Cu (II) by a difunctional rhodamine-based probe. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 183:291–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2017.04.056
Chen Y, Chen B, Han Y (2016) A novel rhodamine-based fluorescent probe for the fluorogenic and chromogenic detection of Pd2+ ions and its application in live-cell imaging. Sens Actuators B Chem 237:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.06.067
Ni J, Li B, Zhang L, Zhao H, Jiang H (2015) A fluorescence turn-on probe based on rhodamine derivative and its functionalized silica material for Hg2+-selective detection. Sens Actuators B Chem 215:174–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.03.057
Cui C, Gao X, Jia X, Jiao Y, Duan C (2021) A rhodamine B-based turn on fluorescent probe for selective recognition of mercury (II) ions. Inorganica Chim Acta 520:120285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2021.120285
Zhang Z, Wang J, Song Y, Wang Z, Dong M, Liu L (2019) Disassembly of Alzheimer’s amyloid fibrils by functional upconversion nanoparticles under near-infrared light irradiation. Colloids Surf B-Biointerfaces 181:341–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.05.053
Xia L, Kong X, Liu X, Tu L, Zhang Y, Chang Y, Liu K, Shen D, Zhao H, Zhang H (2014) An upconversion nanoparticle-Zinc phthalocyanine based nanophotosensitizer for photodynamic therapy. Biomaterials 35:4146–4156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.01.068
Qian H, Guo HC, Ho PC, Mahendran R, Zhang Y (2009) Mesoporous-silica-coated up-conversion fluorescent nanoparticles for photodynamic therapy. Small 5(20):2285–2290. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.200900692
Dai Y, Ma PA, Cheng Z, Kang X, Zhang X, Hou Z, Li C, Yang D, Zhai X, Lin J (2012) Up-conversion cell imaging and pH-induced thermally controlled drug release from NaYF4/Yb3+/Er3+@hydrogel core-shell hybrid microspheres. ACS Nano 6(4):3327–3338. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn300303q
An Z, Xu Y, Li Y, Cao X, Chen Q (2014) Versatile raft dispersion polymerization in cononsolvents for the synthesis of thermoresponsive nanogels with controlled composition, functionality and architecture. Polym Chem 5(21):6244–6255. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4PY00867G
Chen HM, Deng CH, Zhang XM (2010) Synthesis of Fe3O4@SiO2@PMMA core-shell-shell magnetic microspheres for highly efficient enrichment of peptides and proteins for MALDI-ToF MS analysis. Angew Chem Int Ed 49:607–611. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200904885
Wang J, Zhang H, Ni D, Fan W, Qu J, Liu Y, Jin Y, Cui Z, Xu T, Wu Y, Bu W, Yao Z (2016) High-performance upconversion nanoprobes for multimodal MR imaging of acute ischemic stroke. Small 12(26):3591–3600. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201601144
Wang ZJ, Chi W, Han QY, Wang G, Zhang M, Zhang J, Gao W, Zheng H (2017) Metal-enhanced upconversion luminescence of NaYF4: Yb/Er with Ag nanoparticles. Mater Res Bull 88:182–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2016.12.030
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK20190862), and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation funded project (No. 2019M651729).
Funding
The work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK20190862), and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation funded project (No. 2019M651729).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The study conception and design were performed by Xu Tang. Method development and validation were performed by Xu Tang, Yunlong Han and Wencheng Zhou. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Xu Tang. The Schemes 1 and 2 in the manuscript was drawn by Yemei Wang and Wenjing Shen. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no relevant financial or nonfinancial interests to disclose. The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, X., Han, Y., Zhou, W. et al. A FRET Based Composite Sensing Material Based on UCNPs and Rhodamine Derivative for Highly Sensitive and Selective Detection of Fe3+. J Fluoresc 33, 2219–2228 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-023-03223-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-023-03223-1