Abstract
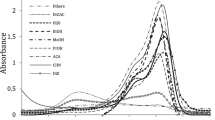
The ground and the singlet excited state pyridinic protonation of 9-methyl-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole, MBC, in water-N,N-dimethylformamide mixtures has been studied by absorption, steady state and time resolved fluorescence measurements. These proton transfer reactions elapse by a stepwise mechanism modulated by different hydrogen bonded adducts and exciplexes formed by water molecules and the pyridinic nitrogen atom of the MBC. Based in the present and previous studies, a general mechanistic Scheme for the ground and the singlet excited state MBC pyridinic protonation has been proposed. Accordingly, in the ground state, upon increasing the water proportion of the water-N,N-dimethylformamide mixtures, a hydrogen bonded complex, HBC, its hydrogen bonded proton transfer complex, PTC, a pre-cationic complex, PC, and the cation, C, are progressively formed. In the excited state, MBC, HBC and PC behave as independent fluorophores. Excited state cations, C*, are mainly formed by direct excitation of the ground state cations and, in minor proportion, by the excited state reaction of the PTC* through the CL* exciplex.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramovitch RA, Spencer ID (1964) The carbolines. Adv. Heterocycl. Chem. 3(1):79–207. doi:10.1016/S0065-2725(08)60542-5
Allen JRF, Holmstedt BR (1980) The simple 3-carboline alkaloids. Phytochem 19:1573–1982. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(00)83773-5
Balón M, Muñoz MA, Guardado P, Hidalgo J, Carmona C (1994) Photophysics and photochemistry of betacarbolines. Trends Photochem. Photobiol. 3(1):117–138
Bloom H, Barchas J, Sandler M, Usdin E (1982) Beta-carbolines and Tetrahydroisoquinolines, Progress in Clinical and Biological Research. Vol 90. Alan R. Liss Inc, New York
Braestrup C, Nielsen M, Olsen CE (1980) Urinary and brain β-caboline-3-carboxylates as potent inhibitors of brain benzodiazepine receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77(4):2288–2292. doi:10.1073/pnas.77.4.2288
Carlini EA (2003) Plants and the central nervous system. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 75(3):501–512. doi:10.1016/S0091-3057(03)00112-6
Meester C (1995) Genotoxic potential of β-carbolines: a review. Mutat. Res. 339:139–153
Tamura S, Konakahara T, Komatsu H, Ozaki T, Ohta Y, Takeuchi H (1998) Synthesis of β-carboline derivatives and their interaction with duplex-DNA. Heterocycles 48(12):2477–2480
Balón M, Muñoz MA, Carmona C, Guardado P, Galán M (1999) A fluorescence study of the molecular interactions of harmine with the nucleobases, their nucleosides and mononucleotides. Biophys. Chem. 80(1):41–52. doi:10.1016/S0301-4622(99)00059-9
Cao R, Peng W, Chen H, Ma Y, Liu X, Hou X, Guan H, Xu A (2005) DNA binding properties of 9-substituted harmine derivatives. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 338(3):1557–1563. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.10.121
Hudson JB, Towers GH (1991) Therapeutic potential of plantphotosensitizers. Pharmacol. Ther. 49(3):81–122. doi:10.1016/0163-7258(91)90055-Q
Shimoi K, Kawabata H, Tomita I (1992) Enhancing effect of heterocyclic amines and β-carbolines on UV or chemically induced mutagenesis in E. coli. Mutat. Res. 268(2):287–295. doi:10.1016/0027-5107(92)90234-S
Guan H, Liu X, Peng W, Cao R, Ma Y, Chen H, Xu A (2006) β-Carboline derivatives: Novel photosensitizers that intercalate into DNA to cause direct DNA damage in photodynamic therapy. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 342(3):894–901. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.02.035
Balón M, Hidalgo J, Guardado P, Muñoz MA, Carmona C (1993) Acid–base and spectral properties of betacarbolines. Part 2. Dehydro and fully aromatic betacarbolines. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 2:99–104. doi:10.1039/p29930000099
Sakuros R, Ghiggino KP (1982) Excited state proton transfer in betacarboline. J. Photochem. 18(1):1–8. doi:10.1016/0047-2670(82)80002-6
Wolfbeis OV, Fürlinger E, Wintersteiger R (1982) Solvent and pH-dependence of the absorption and fluorescence spectra of Harman: Detection of three ground state and four excited state species. Monatsh. Chem. 113:509–517. doi:10.1007/BF00799926
Dias A, Varela AP, Miguel MG, Maçanita AL, Becker RS (1992) Beta-carboline photosensitizers 1. Photophysics, kinetics and excited-state equilibria in organic solvents, and theoretical calculations. J. Phys. Chem. 96(25):10290–10296. doi:10.1021/j100204a036
Draxler S, Lippitsch ME (1993) Excited-state acid-base kinetics and equilibria in norharman. J. Phys. Chem. 99(44):11493–11496. doi:10.1021/j100146a024
Varela AP, Dias A, Miguel MG, Becker RS, Maçanita AL (1995) Comment on excited-state acid-base kinetics and equilibria in Norharmane. J. Phys. Chem. 99(7):2239–2240. doi:10.1021/j100007a065
Draxler S, Lippitsch ME (1995) Reply to “Comment on excited-state acid-base kinetics and equilibria in Norharmane”. J. Phys. Chem. 99(7):2241. doi:10.1021/j100007a066
Dias A, Varela AP, Miguel MG, Becker RS, Burrows HD, Maçanita AL (1996) β-carbolines. 2. Rate constants of proton transfer from multiexponential decays in the lowest singlet excited state of harmine in water as a function of pH. J. Phys. Chem. 100:17970–17977. doi:10.1021/jp961406u
Reyman D, Pardo A, Poyato JML (1994) Phototautomerism of betacarbolines. J. Phys. Chem. 98(41):10408–104110. doi:10.1021/j100092a004
Reyman D, Viñas MH, Poyato JML, Pardo A (1997) Proton transfer dynamics of norharmane in organic solvents. J. Phys. Chem. A 101(5):768–775. doi:10.1021/jp961742a
Reyman D, Viñas MH (1999) Temperature effect on excited-state proton transfer reactions of β-carboline in different acetic-acid mixtures. Chem. Phys. Lett. 301(5–6):551–558. doi:10.1016/S0009-2614(99)00060-3
Chou P-T, Liu YI, Wu GR, Shiabo MY, Yu WS (2001) Proton-transfer tautomerim of β-carbolines mediated by hydrogen-bonded complexes. J. Phys. Chem. B 105(43):10674–10683. doi:10.1021/jp011031z
Sánchez-Coronilla A, Carmona C, Muñoz MA, Balón M (2006) Ground state isomerism and dual emission of the β-carboline anhydrobase (N2-methyl-)H-pyrido[3, 4-b]indole) in aprotic solvents. Chem. Phys. 327(1):70–76. doi:10.1016/j.chemphys.2006.03.032
Sánchez-Coronilla A, Balón M, Muñoz MA, Carmona C (2008) Influence of hydrogen bonding in the ground and the excited states of the isomers of the β-carboline anhydrobase (N2-methyl-9H-pyrido[3.4-b]indole) in aprotic solvents. Chem. Phys. 344(1):72–78. doi:10.1016/j.chemphys.2007.11.011
Sánchez-Coronilla A, Balón M, Muñoz MA, Hidalgo J, Carmona C (2008) Ground state isomerism in betacarboline hydrogen bond complexes: the charge transfer nature of its large Stokes shifted emission. Chem. Phys. 351(1):27–32. doi:10.1016/j.chemphys.2008.03.025
Balón M, Carmona C, Guardado P, Muñoz MA (1998) Hydrogen-bonding and proton transfer interactions between Harmane and trifluoroethanol in the ground and excited singlet states. Photochem. Photobiol. 67(4):414–419. doi:10.1111/j.1751-1097.1998.tb05220.x
Carmona C, Galán M, Angulo G, Muñoz MA, Guardado P, Balón M (2000) Ground and singlet excited states hydrogen bonding interactions of betacarbolines. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2(22):5076–5083. doi:10.1039/b005455k
Carmona C, Balón M, Galán M, Angulo G, Guardado P, Muñoz MA (2001) Kinetic study of hydrogen bonded exciplex formation of N9-methyl harmane. J. Phys. Chem. A 105(45):10334–10338. doi:10.1021/jp0104942
Carmona C, Balón M, Galán M, Guardado P, Muñoz MA (2002) Dynamic study of excited state hydrogen-bonded complexes of harmane in cyclohexane-toluene mixtures. Photochem. Photobiol. 76(3):239–246. doi:10.1562/0031-8655(2002)076<0239:DSOESH>2.0.CO;2
Carmona C, Balón M, Sánchez Coronilla A, Muñoz MA (2004) New insights on the excited-state proton-transfer reactions of betacarbolines: Cationic exciplex formation. J. Phys. Chem. A 108:1910–1918. doi:10.1021/jp030829a
Doig, G.G., Loudon, J.D., Mac Closkey, P.J.: The chemistry of the Mitragyna Genus. Part IV: Derivatives of Harman. J. Chem. Soc. 3912–3916 (1952) doi:10.1039/jr9520003912
Frank HS, Wen WY (1957) Structural aspects of ion-solvent interaction in aqueous solutions: a suggested picture of water structure. Discuss. Faraday Soc. 24:133–140. doi:10.1039/df9572400133
Gutmann V (1973) Redox properties: changes effected by coordination. Struct Bonding 15:141–166. doi:10.1007/BFb0036785
Lee J, Robinson GW, Webb SP, Philips LA, Clark JH (1986) Hydration dynamics of protons from photon initiated acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 108(21):6538–6542. doi:10.1021/ja00281a016
Robinson GW, Thidthethwhite PJ, Lee J (1986) Molecular aspects of ionic hydration reactions. J. Phys. Chem. 90(18):4224–4233. doi:10.1021/j100409a003
Lee J, Griffin RD, Robinson GW (1985) 2-Naphthol: A simple example of proton transfer affected by water structure. J. Chem. Phys. 82(11):4920–4925. doi:10.1063/1.448665
Solntsev KM, Huppert D, Agmon N, Tolbert LM (2000) Photochemistry of “super” photoacids. 2. Excited-state proton transfer in methanol/water mixtures. J. Phys. Chem. A 104(19):4658–4669. doi:10.1021/jp994454y
Agmon N (2005) Elementary steps in excited-state proton transfer. J. Phys. Chem. A 109(1):13–35. doi:10.1021/jp047465m
Mohammed OF, Pines D, Dreyer J, Pines E, Nibbering ETJ (2005) Sequential proton transfer through water bridges in acid-base reactions. Science 310:83–86. doi:10.1126/science.1117756
Siwick BJ, Bakker HJ (2007) On the role of water in intermolecular proton-transfer reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129(44):13412–13420. doi:10.1021/ja069265p
de Grotthuss CJT (1806) Sur la décomposition de l’eau et des corps qu’elle tient en dissolution à l’aide de l’électricité galvanique. Ann Chim 58:54–73
Sicilia MC, Muñoz-Caro C, Niño A (2005) Theoretical analysis of pyridine protonation in water clusters of increasing size. ChemPhysChem 6(1):139–147. doi:10.1002/cphc.200400344
Sicilia MC, Niño A, Muñoz-Caro M (2005) Mechanism of pyridine protonation in water clusters of increasing size. J. Phys. Chem. A 109(37):8341–8347. doi:10.1021/jp050530n
Marcus Y (1993) The properties of organic liquids that are relevant to their use as solvating solvents. Chem. Soc. Rev. 22:409–416. doi:10.1039/cs9932200409
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge financial support from the Dirección General Científica y Técnica MEC, CTQ2006-13539 and Junta de Andalucía, 2005/FQM-368, 2007/FQM-106.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coronilla, A.S., Carmona, C., Muñoz, M.A. et al. Ground and Singlet Excited State Pyridinic Protonation of N9-Methylbetacarboline in Water-N,N-Dimethylformamide Mixtures. J Fluoresc 19, 1025–1035 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-009-0502-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-009-0502-y