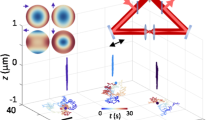
A 3D single-particle-tracking (SPT) system was developed based on two-photon excitation fluorescence microscopy that can track the motion of particles in three dimensions over a range of 100 μm and with a bandwidth up to 30 Hz. We have implemented two different techniques employing feedback control. The first technique scans a small volume around a particle to build up a volumetric image that is then used to determine the particle's position. The second technique scans only a single plane but utilizes optical aberrations that have been introduced into the optical system that break the axial symmetry of the point spread function and serve as an indicator of the particle's axial position. We verified the performance of the instrument by tracking particles in well-characterized models systems. We then studied the 3D viscoelastic mechanical response of 293 kidney cells using the techniques. Force was applied to the cells, by using a magnetic manipulator, onto the paramagnetic spheres attached to the cell via cellular integrin receptors. The deformation of the cytoskeleton was monitored by following the motion of nearby attached fluorescent polystyrene spheres. We showed that planar stress produces strain in all three dimensions, demonstrating that the 3D motion of the cell is required to fully model cellular mechanical responses.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
L. S. Barak and W. W. Webb (1981). Fluorescent low-density lipoprotein for observation of dynamics of individual receptor complexes on cultured human-fibroblasts. J. Cell Biol. 90(3), 595–604.
M. Debrander, G. Geuens, R. Nuydens, M. Moeremans, and J. Demey (1985). Probing microtubule-dependent intracellular motility with nanometer particle video ultramicroscopy (nanovid ultramicroscopy). Cytobios. 43(174), 273–283.
T. Fujiwara, K. Ritchie, H. Murakoshi, K. Jacobson, and A. Kusumi (2002). Phospholipids undergo hop diffusion in compartmentalized cell membrane. J. Cell Biol. 157(6), 1071–1081.
K. Murase, T. Fujiwara, Y. Umemura, K. Suzuki, R. Iino, H. Yamashita, M. Saito, H. Murakoshi, K. Ritchie, and A. Kusumi (2004). Ultrafine membrane compartments for molecular diffusion as revealed by single molecule techniques. Biophys. J. 86(6), 4075–4093.
K. Kis-Petikova and E. Gratton (2004). Distance measurement by circular scanning of the excitation beam in the two-photon microscope. Microsc. Res. Tech. 63(1), 34–49.
A. Yildiz, J. N. Forkey, S. A. McKinney, T. Ha, Y. E. Goldman, and P. R. Selvin (2003). Myosin V walks hand-over-hand: Single fluorophore imaging with 1.5-nm localization. Science 300(5628), 2061–2065.
H. Bornfleth, P. Edelmann, D. Zink, T. Cremer, and C. Cremer (1999). Quantitative motion analysis of subchromosomal foci in living cells using four-dimensional microscopy. Biophys. J. 77(5), 2871–2886.
D. D. Li, J. Xiong, A. L. Qu, and T. Xu (2004). Three-dimensional tracking of single secretory granules in live PC12 cells. Biophys. J. 87(3), 1991–2001.
W. F. Marshall, A. Straight, J. F. Marko, J. Swedlow, A. Dernburg, A. Belmont, A. W. Murray, D. A. Agard, and J. W. Sedat (1997). Interphase chromosomes undergo constrained diffusional motion in living cells. Curr. Biol. 7(12), 930–939.
D. Thomann, D. R. Rines, P. K. Sorger, and G. Danuser (2002). Automatic fluorescent tag detection in 3D with super-resolution: Application to the analysis of chromosome movement. J. Microsc. Oxf. 208, 49–64.
R. M. Dickson, D. J. Norris, Y. L. Tzeng, and W. E. Moerner (1996). Three-dimensional imaging of single molecules solvated in pores of poly(acrylamide) gels. Science 274(5289), 966–969.
I. M. Peters, Y. van Kooyk, S. J. van Vliet, B. G. de Grooth, C. G. Figdor, and J. Greve (1999). 3D single-particle tracking and optical trap measurements on adhesion proteins. Cytometry 36(3), 189–194.
M. Speidel, A. Jonas, and E. L. Florin (2003). Three-dimensional tracking of fluorescent nanoparticles with subnanometer precision by use of off-focus imaging. Opt. Lett. 28(2), 69–71.
H. P. Kao, A. S. Verkman. (1994). Tracking of Single Fluorescent Particles in 3 Dimensions - Use of Cylindrical Optics to Encode Particle Position. Biophys. J. 67(3), 1291–1300.
H. Huang, C. Y. Dong, H.-S. Kwon, J. D. Sutin, R. D. Kamm, and P. T. C. So (2002). Three-dimensional cellular deformation analysis with a two-photon magnetic manipulator workstation. Biophys. J. 82(4), 2211–2223.
A. R. Bausch, W. Moller, and E. Sackmann (1999). Measurement of local viscoelasticity and forces in living cells by magnetic tweezers. Biophys. J. 76(1 Pt 1), 573–579.
A. Bausch, F. Ziemann, A. Boulbitch, K. Jacobson, and E. Sackmann (1998). Local measurements of viscoelastic parameters of adherent cell surfaces by magnetic bead microrheometry. Biophys. J. 75, 2038–2049.
H. Huang, R. D. Kamm, PTC So, and R. T. Lee (2001). Receptor-based differences in human aortic smooth muscle cell membrane stiffness. Hypertension 38(5), 1158–1161.
B. P. Helmke, A. B. Rosen, and P. F. Davies (2003). Mapping mechanical strain of an endogenous cytoskeletal network in living endothelial cells. Biophys. J. 84(4), 2691–2699.
B. P. Helmke, D. B. Thakker, R. D. Goldman, and P. F. Davies (2001). Spatiotemporal analysis of flow-induced intermediate filament displacement in living endothelial cells. Biophys. J. 80(1), 184–194.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ragan, T., Huang, H., So, P. et al. 3D Particle Tracking on a Two-Photon Microscope. J Fluoresc 16, 325–336 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-005-0040-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-005-0040-1