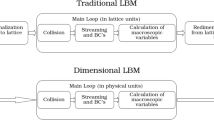
A hybrid mathematical model has been developed in which the flow field of a viscous incompressible medium is calculated by the method of lattice Boltzmann equations using the Bhatnagar–Gross–Krook approximation and a two-dimensional nine-velocity scheme, and free convective heat transfer is calculated by the finite difference method. The formulated approach to solving thermogravitational-convection problems has been verified on numerical and experimental data of other researchers. From a comparative analysis, it has been established that the computational efficiency of the hybrid mathematical model is 50 times higher than that of the traditional approach, which is based on the finite difference method and transformed "vorticity–stream function" variables.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Sheikhi, M. Najafi , and V. Enjilela, Solving natural convection heat transfer in turbulent flow by extending the meshless local Petrov–Galerkin method, Eng. Anal. Boundary Elem., 93, 29–43 (2018).
O. Hireche, I. Ramadan, C. Weisman, H. Bailliet, Ya. Fraigneau, D. Baltean-Carlès, and V. Daru, Experimental and numerical investigation of natural convection flows in two horizontal thermoacoustic cavities, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf., 149, 1–17 (2020).
C. Peng, N. Geneva, Z. Guo, and L.-P. Wang, Direct numerical simulation of turbulent pipe flow using the lattice Boltzmann method, J. Comput. Phys., 357, 16–42 (2018).
M. Sheikholeslami, Lattice Boltzmann method simulation for MHD non-Darcy nanofluid free convection, Physica B, 516, 55–71 (2017).
Y. Zhao, B. Shi, Z. Chai, and L. Wang, Lattice Boltzmann simulation of melting in a cubical cavity with a local heat-flux source, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf., 127, 497–506 (2018).
Y. Hu, Z. Zhang, H. Gao, and Y. He, Forced convective heat transfer of solar salt-based Al2O3 nanofluids using lattice Boltzmann method, Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog., 8, 2–9 (2018).
C. Xie, J. Zhang, V. Bertola, and M. Wang, Lattice Boltzmann modeling for multiphase viscoplastic fluid flow, J. Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech., 234, 118–128 (2016).
P. Pavlo, G. Vahala, L. Vahala, and M. Soe, Linear stability analysis of thermo-lattice Boltzmann models, J. Comput. Phys., 139, 79–91 (1998).
A. Mezrhab, M. A. Moussaoui, M. Jami, H. Naji, and M. Bouzidi, Double MRT thermal lattice Boltzmann method for simulating convective flows, Phys. Lett. A, 374, 3499–3507 (2010).
P. Lallemand and L.-S. Lou, Hybrid finite-difference thermal lattice Boltzmann equation, Int. J. Mod. Phys. B, 17, 41–47 (2003).
S. Bettaibi, F. Kuznik, and E. Sediki, Hybrid lattice Boltzmann finite difference simulation of mixed convection flows in a lid-driven square cavity, Phys. Lett. A, 378, 2429–2435 (2014).
S. Bettaibi, F. Kuznik, and E. Sediki, Hybrid LBM-MRT model coupled with finite difference method for doublediffusive mixed convection in rectangular enclosure with insulated moving lid, Physica A, 444, 311–326 (2016).
A. A. Mohamad, Lattice Boltzmann Method, Springer-Verlag, London (2011).
G. V. Kuznetsov, T. A. Nagornova, and A. É. Ni, Computational modeling of conjugate heat transfer in a closed rectangular domain under the conditions of radiant heat supply to the horizontal and vertical surfaces of enclosure structures, J. Eng. Phys. Thermophys., 88, No. 1, 168–177 (2015).
S. Jani, M. Mahmoodi, M. Amini, and J. E. Jam, Numerical investigation of natural convection heat transfer in a symmetrically cooled square cavity with a thin fin on its bottom wall, Therm. Sci., 18, 1119–1132 (2014).
H. N. Dixit and V. Babu, Simulation of high Rayleigh number natural convection in a square cavity using the lattice Boltzmann method, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf., 49, 727–739 (2006).
S. M. Bajorek and J. R. Lloyd, Experimental investigation of natural convection in partitioned enclosures, J. Heat Transf., 104, 527–532 (1982).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Inzhenerno-Fizicheskii Zhurnal, Vol. 94, No. 2, pp. 431–438, March–April, 2021.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ni, A.É. Hybrid Method of Lattice Boltzmann Equations to Model Thermogravitational Flows. J Eng Phys Thermophy 94, 415–422 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-021-02326-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-021-02326-5