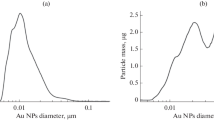
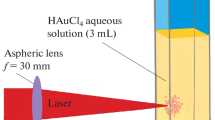
The average temperature of a gas cloud formed in an aqueous solution of a gold salt under the action of a nanosecond laser-radiation pulse with a wavelength of 532 nm was calculated. It is shown that the average temperature of such a cloud reaches thousands of degrees for several nanoseconds, and the collisions of molecules in it cause the dissociation of all the chemical compounds in the cloud. As the cloud is cooled, the gold vapor is supersaturated, and solid gold clusters nucleate and grow in it. The repeated laser pulses heat not only the solution but also the gold nanoparticles formed in it, with the result that relatively large nanoparticles are evaporated, and the temperature of the particles with a radius of about 5 nm reaches only the melting point.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. P. Fisenko, Yu. A. Khodyko, V. I. Saverchenko, and O. G. Penyazkov, Nanoparticles formation via low pressure spray pyrolysis –– physical fundamentals and puzzles, in: Z. Bartul and J. Trenor (Eds.), Advances in Nanotechnology, Nova Science, New York (2015), Ch. 6, pp. 163–184.
V. S. Gerasimov, A. E. Ershov, S. V. Karpov, A. P. Gavrilyuk, V. I. Zakomirnyi, I. L. Rasskazov, Hans Ågren, and S. P. Polyutov, Thermal effects in systems of colloidal plasmonic nanoparticles in high-intensity pulsed laser fields, Opt. Mater. Express, 7, No. 2, 555–568 (2017).
C. F. Bohren and D. R. Huffman, Absorption and Scattering of Light by Small Particles, John Wiley & Sons, New York (1998).
P. B. Johnson and R. W. Christy, Optical constants of the noble metals, Phys. Rev. B, 6, No. 12, 4370–4379 (1972).
I. S. Grigor’ev and E. Z. Meilikhov (Eds.), Physical Quantities, Reference Book [in Russian], Énergoatomizdat, Moscow (1991).
N. V. Tarasenko, A. V. Butsen, E. A. Nevar, and N. A. Savastenko, Synthesis of nanosized particles during laser ablation of gold in water, Appl. Surf. Sci., 252, 4439–4444 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Inzhenerno-Fizicheskii Zhurnal, Vol. 92, No. 2, pp. 385–390, March–April, 2019.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bobb, J.A., Fisenko, S.P., Rodrigues, C.J. et al. Mechanisms of Formation of Nanoparticles in Aqueous Salt Solutions Under the Action of a High-Power Periodic Laser Radiation. J Eng Phys Thermophy 92, 369–375 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-019-01940-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-019-01940-8