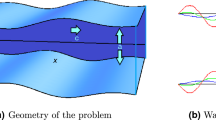
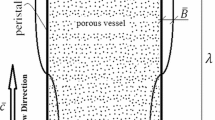
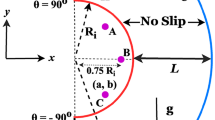
In the present study, a mathematical model for the hydromagnetic non-Newtonian biofluid flow in the non-Darcy porous medium with Joule effect is proposed. A uniform magnetic field acts perpendicularly to the porous surface. The governing nonlinear partial differential equations are transformed into linear ones which are solved numerically by applying the explicit finite difference method. The effects of various parameters, like Reynolds number and hydro-magnetic, Forchheimer, and Darcian parameters, Prandtl, Eckert, and Schmidt numbers, on the velocity, temperature, and concentration are presented graphically. The results of the study can find applications in surgical operations, industrial material processing, and various heat transfer processes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. H. Pennes, Analysis of tissue and arterial blood temperatures in the resting human forearm, J. Appl. Physiol., 1, No. 2, 93–122 (1948).
J. J. W. Lagendijk, The influence of blood flow in large vessels on the temperature distribution in hyperthermia, Phys. Med. Biol., 27, 17–23 (1982).
J. C. Chato, Heat transfer to blood vessels, ASME J. Biomech. Eng., 102, 110–118 (1980).
O. A. Bég and A. Sajid, CFD modeling of axisymmetric hemodynamics and heat transfer using ADINA, in: Technical Report of Biomechanics-III, Bradford University, Science Park, Listerhills, Bradford, UK (2002).
M. C. Kolios, M. D. Sherar, and J. W. Hunt, Large blood vessel cooling in heated tissues: A numerical study, Phys. Med. Biol., 48, 4125–4134 (2003).
S. Chakravarty and S. Sen, Dynamic response of heat and mass transfer in blood flow through stenosed bifurcated arteries, Korean–Austr. J., 17, No. 2, 47–62 (2005).
G. S. Barozzi and A. Dumas, Convective heat transfer coefficients in the circulation, J. Biomech. Eng., 113, 308–313 (1991).
J. W. Baish, Heat transport by countercurrent blood vessels in the presence of an arbitrary pressure gradient, ASME J. Biomech. Eng., 112, 207 (1990).
Z. S. Deng and J. Liu, Blood perfusion-based model for characterizing the temperature fluctuations in living tissue, Physica A: Stat. Mech. Appl., 300, 521–530 (2001).
O. I. Craciiunescu and S. T. Clegg, Pulsatile blood flow effects on temperature distribution and heat transfer in rigid vessels, ASME J. Biomech. Eng., 123, No. 5, 500–505 (2001).
L. Consiglieri, I. Santos, and D. Haemmerich, Theoretical analysis of the heat convection coefficient in large vessels and the significance for thermal ablative therapies, Phys. Med. Biol., 48, 4125–4134 (2003).
R. V. Davalos, B. Rubinsky, and L. M. Mir, Theoretical analysis of the thermal effects during in-vivo tissue electroporation, Bioelectrochem. J., 61, 99–107 (2003).
D. Shrivastava, B. McKay, and R. B. Romer, An analytical study of heat transfer in finite tissue with two blood vessels and uniform Dirichlet boundary conditions, ASME J. Heat Transf., 127, No. 2, 179–188 (2005).
R. Skalak and S. Chien, Rheology of blood cells as soft tissues, Biorheology, 19, 453–461 (1982).
G. R. Cokelet, The rheology of human blood, in: Y. C. Fung (Ed.), Biomechanics – Its Foundations and Objectives, Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1972), pp. 63–104.
T. Takeuchi, T. Mizuno, T. Higashi, A. Yamagishi, and M. Date, Orientation of red blood cells in high magnetic field, J. Magn. Mater., 140, 1462–1463 (1995).
E. E. Tzirtzilakis and G. B. Tanoudis, Numerical study of biomagnetic fluid flow over a stretching sheet with heat transfer, Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow, 13, No. 7, 830– 848 (2003).
V. C. Louckopoulos and E. E. Tzirtzilakis, Biomagnetic channel flow in spatially varying magnetic field, Int. J. Eng. Sci., 42, 571–590 (2004).
A. R. A. Khaled and K. Vafai, The role of porous media in modeling flow and heat transfer in biological tissues, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 26, No. 46, 4989–5003 (2003).
A. Ogulu and E. Amos, Modeling pulsatile blood flow within a homogeneous porous bed in the presence of a uniform magnetic field and time-dependent suction, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer, 34, 989–995 (2007).
I. Pop and D. B. Ingham, Convective Heat Transfer: Mathematical and Numerical Modelling of Viscous Fluids and Porous Media, Pergamon, Oxford (2001).
L. Preziosi and A. Farina, On Darcy’s law for growing porous media, Int. J. Non-Linear Mech., 37, 485–491 (2002).
W. J. Vankan, J. M. Huyghe, J. D. Janssen, A. Huson, W. J. D. Hacking, and W. Schrenner, Finite element analysis of blood flow through biological tissue, Int. J. Eng. Sci., 35, 375–385 (1997).
S. Sorek and S. Sideman, A porous medium approach for modelling heart mechanics, Math. Biosci., 81, 14–32 (1986).
R. Bhargava, S. Rawat, H. S. Takhar, and O. A. Bég, Pulsatile magneto-biofluid flow and mass transfer in a non-Darcian porous medium channel, Meccanica, 42, 247–262 (2007).
R. C. Chaudhary, B. K. Sharma, and A. K. Jha, Radiation effect with simultaneous thermal and mass diffusion in MHD mixed convection flow from a vertical surface with ohmic heating, Rom. J. Phys., 51, No. 7–8, 715–727 (2006).
J. D. Hoffman, Numerical Methods for Engineers and Scientists, McGraw-Hill, New York (1992).
J. C. Chato, Heat transfer to blood vessels, ASME J. Biomech. Eng., 102, 110–118 (1980).
J. W. Valvano, S. Nho, and G. T. Anderson, Analysis of the Weinbaum–Jiji model of blood flow in the canine kidney cortex for self-heated thermistors, ASME J. Biomech. Eng., 116, No. 2, 201–207 (1994).
S. Gabrial, R. W. Lau, and C. Gabrial, The dielectric properties of biological tissues: III. Parametric models for the dielectric spectrum of tissues, Phys. Med. Biol., 41, 2271–2293 (2004).
T. Bég and O. A. Bég, Chemically-decaying drug transport across membranes, in: Technical Report, Bradford University Science Park, Listerhills, Bradford, UK (2003).
A. Sherman and E. W. Sutton, Magnetohydrodynamics, Evanston, IL, USA (1961).
S. Rawat, R. Bhargava, O. Anwar Bég, P. Bhargava, and Ben R. Hughes, Pulsatile dissipative magneto-bio-rheological fluid flow and heat transfer in a non-Darcy porous medium channel: finite element modeling, Emirates J. Eng. Res., 14, No. 2, 77–90 (2009).
A. Dybbs and R. V. Edwards, A new look at porous media fluid mechanics: Darcy to Turbulent, Fundam. Transport Phenom. Porous Media, 82, 201–258 (1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Inzhenerno-Fizicheskii Zhurnal, Vol. 86, No. 3, pp. 717–725, July–August, 2013.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, B.K., Mishra, A. & Gupta, S. Heat and mass transfer in magneto-biofluid flow through a non-Darcian porous medium with Joule effect. J Eng Phys Thermophy 86, 766–774 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-013-0893-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-013-0893-0