Abstract
Social insects maintain colony cohesion by recognizing and, if necessary, discriminating against conspecifics that are not part of the colony. This recognition ability is encoded by a complex mixture of cuticular hydrocarbons (CHCs), although it is largely unclear how social insects interpret such a multifaceted signal. CHC profiles often contain several series of homologous hydrocarbons, possessing the same methyl branch position but differing in chain length (e.g., 15-methyl-pentatriacontane, 15-methyl-heptatriacontane, 15-methyl-nonatriacontane). Recent studies have revealed that within species these homologs can occur in correlated concentrations. In such cases, single compounds may convey the same information as the homologs. In this study, we used behavioral bioassays to explore how social insects perceive and interpret different hydrocarbons. We tested the aggressive response of Argentine ants, Linepithema humile, toward nest-mate CHC profiles that were augmented with one of eight synthetic hydrocarbons that differed in branch position, chain length, or both. We found that Argentine ants showed similar levels of aggression toward nest-mate CHC profiles augmented with compounds that had the same branch position but differed in chain length. Conversely, Argentine ants displayed different levels of aggression toward nest-mate CHC profiles augmented with compounds that had different branch positions but the same chain length. While this was true in almost all cases, one CHC we tested elicited a greater aggressive response than its homologs. Interestingly, this was the only compound that did not occur naturally in correlated concentrations with its homologs in CHC profiles. Combined, these data suggest that CHCs of a homologous series elicit the same aggressive response because they convey the same information, rather than Argentine ants being unable to discriminate between different homologs. This study contributes to our understanding of the chemical basis of nestmate recognition by showing that, similar to spoken language, the chemical language of social insects contains “synonyms,” chemicals that differ in structure, but not meaning.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Recognition of group members is considered a key innovation in the evolution of sociality, as the direct and indirect fitness benefits of social living can be gained only if altruistic behaviors are directed toward the appropriate recipients. Some of the fundamental contributions to our understanding of social evolution, and the underlying social recognition systems, have come from research on social insects. Social insects have evolved a highly sophisticated recognition system that allows individuals to identify a non-colony mate among large numbers of colony mates. These insects are able to achieve such precise discrimination with a single sweep of the antenna across the cuticle of another individual. The cues used for nest-mate recognition are typically hydrocarbons on the exoskeleton of workers (Thomas et al. 1999; Wagner et al. 2000; Torres et al. 2007). These cuticular hydrocarbons (CHCs) usually are a complex mixture of alkanes, alkenes, and methyl-branched alkanes (Martin and Drijfhout 2009b). The number of CHCs that have been recorded for an ant species ranges from as few as 8, in Formica exsecta (Martin and Drijfhout 2009b), to as many as 110, in Myrmica incompleta (Elmes et al. 2002). In total, almost 1,000 different CHCs have been described for ants (Martin and Drijfhout 2009b). CHC profiles usually are colony specific, with colonies having different relative concentrations of compounds (Nielsen et al. 1999; Tentschert et al. 2002; van Wilgenburg et al. 2006; Foitzik et al. 2007; Martin et al. 2008a; Brandt et al. 2009). Studies have shown that there is a positive relationship between the level of aggression among colonies and their differences in CHC profiles (Suarez et al. 2002; Zweden et al. 2009). Moreover, behavioral studies have shown that workers often act aggressively toward dummies or workers that have been treated with CHCs of non-colony mates (Thomas et al. 1999; Wagner et al. 2000; Akino et al. 2004; Ozaki et al. 2005; Torres et al. 2007; Martin et al. 2008a). However, little is known about the mechanisms that allow individual social insects to discriminate between the complex cocktails of chemicals emitted by members of their own colony versus those of other colonies.
The primary function of CHCs is to prevent water loss, with not all CHCs functioning for recognition (Hadley 1984; Singer 1998). For example, it appears that methyl-branched alkanes and alkenes, but not n-alkanes, are used as nest-mate recognition cues (Bonavita-Cougourdan et al. 1987; Dani et al. 2005; Lucas et al. 2005; Martin et al. 2008b; but see Greene and Gordon 2007). Additionally, some cues may be used for intra-colony recognition. Workers performing different tasks may have different CHC profiles (Kaib et al. 2000; Wagner et al. 2001; Martin and Drijfhout 2009c), and can detect and respond to these intra-colony differences (Greene and Gordon 2003). Finally, not all compounds within a profile may function independently as recognition cues. A recent study of Formica ants and Vespa hornets has shown that CHC profiles are a mixture of correlated and non-correlated compounds (Martin et al. 2008a; Martin and Drijfhout 2009b). Within a CHC profile, many of the hydrocarbons are structurally related, being part of a homologous series, in which all members possess the same methyl group or double bond, with a backbone that varies in length by two carbons [e.g., 15-methyl-pentatriacontane (15-MeC35), 15-methyl-heptatriacontane (15-MeC37), 15-methyl-nonatriacontane (15-MeC39)]. The relative amounts of compounds within a homologous series often are constant, both within colonies (Martin et al. 2008a; Martin and Drijfhout 2009b) and species (Martin and Drijfhout 2009b). Consequently, a single compound may provide the same information as its homologs.
It also is possible that social insects may not be able to distinguish between structurally related chemicals. Several studies of honey bees have shown that workers are able to discriminate compounds that differ in functional group better than those that differ in carbon chain length, especially when the latter differ by only a few carbons (Vareschi 1971; Getz and Smith 1990; Chaline et al. 2005; Guerrieri et al. 2005). Taken together, these finding suggest that the chemical basis of nest-mate recognition may be simpler than it appears, and that specific features of a few key hydrocarbons may allow social insects to identify colony mates. If so, we would predict that homologous CHCs that are correlated in abundance, and thus contain redundant information, should elicit similar behavioral responses.
The aim of this study was to investigate the aggressive response to homologous CHCs by using the Argentine ant, Linepithema humile, as a model species. The Argentine ant, native to South America, is an introduced and invasive species in many temperate regions of the world (Suarez et al. 2001; Tsutsui and Case 2001). Although native populations display intraspecific (inter-colonial) aggression across spatial scales, ranging from tens to hundreds of meters (Suarez et al. 1999; Tsutsui et al. 2000; Pedersen et al. 2006), introduced populations are characterized by the formation of much larger supercolonies, up to several thousand kilometers long (Suarez et al. 1999; Tsutsui et al. 2000; Giraud et al. 2002; Corin et al. 2007; Bjorkman-Chiswell et al. 2008; Sunamura et al. 2009). This unicolonial structure is one of the keys to the success of introduced populations (Holway et al. 1998).
We showed previously that Argentine ants can perceive and respond aggressively to colony mates treated with a single hydrocarbon, and the intensity of the response varies from colony to colony (Brandt et al. 2009). We also showed that Argentine ants show a higher aggressive response when several different hydrocarbons are applied simultaneously. In this study, we tested whether compounds within a homologous series elicit correlated nest-mate recognition responses. For this, we conducted a series of field-based bioassays, in which we compared the behavioral response of workers to hydrocarbon extracts augmented with one each of eight synthetic hydrocarbons that were either homologs or non-homologs of each other. In addition, we investigated the relationships among these compounds in CHC profiles within and among 14 Argentine ant colonies.
Methods and Materials
For the behavioral assays, we used Argentine ants from three supercolonies in California: Berkeley (B), Lake Hodges (LH), and Cottonwood (CW). These supercolonies are behaviorally and genetically distinct from each other (Tsutsui et al. 2000, 2003). To test whether the hydrocarbons of a homologous series triggered similar responses, we tested the behavior of workers to filter papers treated with hydrocarbon extracts of colony mates, augmented with one of eight synthetic HCs (see hydrocarbon synthesis and behavioral assays below). We tested two homologous pairs of methyl-branched alkanes [15-MeC35 and 15-MeC37; 17-methyl-pentatriacontane (17-MeC35) and 17-methyl-heptatriacontane (17-MeC37)], and one methyl-branched alkane with a different methyl branch position [19-methyl-heptatriacontane (19-MeC37]. We also tested three homologous tri-methyl alkanes [5,3,17-trimethyl-tritriacontane (5,13,17-triMeC33), 5,13,17-trimethyl-pentatriacontane (5,13,17-triMeC35), and 5,13,17-trimethyl-heptatriacontane (5,13,17-triMeC37)]. All behavioral assays were conducted in the field. For controls, we tested the behavioral response of Argentine ant workers to filter papers treated with CHCs of their own colony mates (negative control) or of workers from a foreign colony (positive control).
Synthesis of Monomethyl Hydrocarbon Nestmate Recognition Cues
We synthesized the mono-methyl hydrocarbons 1–5 [15-MeC35 (1), 17-MeC35 (2), 15-MeC37 (3), 17-MeC37 (4), and 19-MeC37 (5)] according to the schemes in Figs. 1 and 2 (see Table 1 for yields). 2-Ketone precursors 6a–b were reacted with α-Grignard reagents 7a–c of desired length to produce 3° alcohols 8a–d, which were separated from hydrocarbon byproducts by silica column chromatography. Dehydration of 8a–d with catalytic TsOH created mixtures of isomers of alkenes 9a–d, which were purified by a second silica column. The alkenes 9a–d were subsequently hydrogenated with catalytic Pd/C under hydrogen (1 atm) to yield the desired mono-methyl hydrocarbons 1–4.
We began synthesis of the symmetrical hydrocarbon 5 by the double addition of an α-C18-Grignard reagent 7a to ethyl acetate (10) to form 3° alcohol 8e. Dehydration of 8e with catalytic TsOH produced a mixture of isomers 9e. Both products 8e and 9e were purified by silica gel chromatography from hydrocarbon byproducts. The alkene 9e was hydrogenated with catalytic Pd/C under hydrogen to yield hydrocarbon 5.
Products (and purity) were characterized by NMR and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). NMR was not particularly useful to confirm the exact structures, since there were so many similar carbons and protons in the compounds. The alcohol products 8a–e appeared as a single peak on GC, and the diagnostic ion as M+-H2O in the mass spectrum. The alkene products 9a–e appeared as two peaks on GC, with the M+ ion diagnostic in the mass spectrum and a 1H NMR multiplet at ∼5 ppm corresponding to the expected alkene protons. We observed the final products 1–5 as single peaks in the GC with (M-Me)+ as one of the main fragments in the mass spectrum. A (M-Me)+ peak is a common fragment of saturated linear hydrocarbons. Other main diagnostic mass spectral fragments arose from fragmentation at the tertiary carbon. The 1H NMR spectrum, although not diagnostic, supported the structure of the final products.
Synthesis of Tri-methyl Hydrocarbon Nestmate Recognition Cues
We synthesized the tri-methyl compounds 11, 12, and 13 [5,13,17-triMeC33 (11), 5,13,17-triMeC35 (12), and 5,13,17-triMeC37 (13)] by sequential Grignard reactions (Figs. 3, 4). Treatment of 8-bromooctanoic acid (14) with two equivalents of methyl lithium provided methyl ketone 15, which was converted to ketal 16 with TsOH and ethylene glycol. Grignard reagent, derived from bromo ketal 16, was added to 2-hexanone (17) to produce tertiary alcohol 18. Alcohol 18 was dehydrated with TsOH and, following a H2O work up, gave the deprotected methyl ketone 19. Addition of the Grignard reagent, derived from protected ketal 20 to ketone 19, produced alcohol 21. The 5,13,17-trimethyl core 22 was produced following dehydration, and subsequent deprotection of alcohol 21. To eliminate the possibility of cyclization, the intermediate 22 was reacted with Wittig reagent 23a–c to form triene 24a–c. The hydrogenation of 24a–c, with Pd/C H2 at elevated pressure, produced the saturated alkanes 11–13. The structures of hydrocarbons 11–13 were confirmed by the fragmentation patterns of the mass spectra. The tri-methyl compounds produced were a mixture of the chiral forms.
Preparation of Filter Paper
To prepare the treatment solution for the filter papers used in the behavioral assays, we extracted the CHCs of ca 8000 frozen, field-collected workers by immersing the ants in n-hexane for 10 min. Hydrocarbons were separated from polar surface lipids by running samples through a Pasteur pipette filled with silica gel. The eluate was divided into 10 aliquots, the solvent evaporated, and the extract reconstituted in 267 μl hexane. To each of the vials we added either 218 μl of a synthetic hydrocarbon (1 mg/ml hexane) or 218 μl of hexane (control). The amount of synthetic hydrocarbon solution used was a 2–7-fold increase of that in the CHC profile (Brandt et al, unpublished data). Next, we added 9 μl of treatment (about 15 ant equivalents) or control solution to each filter paper (6 x 4 mm, with three slits). We allowed the hexane to evaporate, and stored the filter papers in the freezer (−20°C) until used in the behavioral assays.
Behavioral Assays
Seven Argentine ant workers were collected from a foraging trail, and their responses to a filter paper treatment recorded for 3 min. in a 35 mm, Fluon-coated Petri dish. We scored behavioral assays as either aggressive (flaring of mandibles, biting or grabbing of the filter paper) or non-aggressive. We repeated this 45 times for each treatment, and tested 10 treatments, for colonies LH and LP, and nine treatments for colony CW (a total of 1,305 trials). All behavioral assays were conducted blind with regard to the treatment.
Statistical analyses were carried out using Genstat (version 6). We used generalized linear mixed models (GLMM), with the presence or absence of aggression as the response variable and colony identity as a random factor, to accommodate repeated measures of each colony.
Chemical Analysis
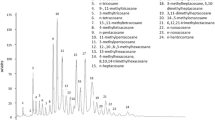
Cuticular lipids, from at least 12 workers from each colony, were extracted by immersing an individual ant in 45 μl of hexane for 10 min, and the individual’s CHC profile analyzed by GC–MS. For quantification, 1 μl of each sample was injected splitless (temperature 250°C) into an Agilent 7890 GC equipped with an HP5-MS capillary column (30 m × 250 mm × 0.25 μm, Agilent Technologies). Helium, at 1 ml.min−1, was the carrier gas, and the column oven was programmed at 80°C, for 2 min., then to 270°C at 20°C.min−1, then to 310°C at 3°C.min−1. Electron impact mass spectra were obtained with an ionization voltage of 70 eV and a source temperature set to 250°C. Chromatograms were integrated using the program ACD SpecManager (version 10.0, Advanced Chemistry Development), and relative proportions of each peak area, to that of the total sample, were calculated. Selected ion monitoring was used to record m/z 99, 113, and 127. Full mass spectra of all the peaks in the cuticular extracts from a pool of 50 ants of each colony also were recorded, enabling characterization of the compounds based on diagnostic ions and Kovat’s indices.
Inter- and intra-colony ratios (relative amounts) of the compounds used in the behavioral assays were based on quantitative analyses of individuals of 14 colonies, three of which were used in our study and the others published in Brandt et al (2009). To avoid pseudo-replication we included colonies only that are chemically and genetically distinct from each other. Data were analysed using SPSS 12.0.
Methyl-branched hydrocarbons with the same carbon-chain backbone often co-elute on a non-polar column as a single peak. While others have determined the ratios of the different hydrocarbons within a given peak by the ratios of the respective diagnostic ions (Martin et al. 2008a), this method failed to provide consistent results in our study. Therefore, we correlated relative amounts of whole peaks (i.e., all the co-eluting compounds) with other whole peaks.
Results
Synthetic Hydrocarbon Experiment
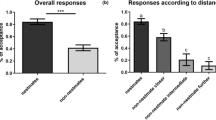
In general, workers frequently were more aggressive (F 1,1164 = 14.68, P < 0.001) to filter papers augmented with a single synthetic hydrocarbon than to filter papers treated only with nest mate hydrocarbons (negative control), but were less frequently aggressive (F 1,1164 = 5.76, P = 0.017) to filter papers augmented with synthetic hydrocarbons than to filter papers treated with non-colony mate hydrocarbons (i.e., positive control; Fig. 5). Workers showed similar frequencies of aggression to each of the compounds in the respective pairs of homologous monomethyl hydrocarbons (i.e., to 15-MeC35 and 15-MeC37, and to 17-MeC35 and 17-MeC37). The location of the methyl branch of a monomethyl alkane had an effect on the frequency of aggression of workers, but carbon chain did not (Fig. 5; branch position, F 2,621 = 11.60, P < 0.001, chain length F 1,621 = 1.49, P = 0.222). In contrast, workers showed different frequencies of aggression to filter papers treated with the three homologous trimethyl hydrocarbons; workers were more often aggressive to filter papers treated with 5,13,17-triMeC33 than to those treated with 5,13,17-triMeC35 or 5,13,17-triMeC37. For these compounds, there was an effect of chain length (F 2,402 = 4.18, P = 0.016).
Mean frequencies of aggression (±SE) exhibited by Linepithema humile workers across colonies to filter papers treated with cuticular hydrocarbons of the same colony augmented with a synthetic hydrocarbon (grey bars) and filter paper controls (black = cuticular hydrocarbons of a foreign colony only, and white = cuticular hydrocarbons of the same colony only). 13-methyl-pentatriacontane (13-MeC35), 15-methyl-pentatriacontane (15-MeC35), 17-methyl-pentatriacontane (17-MeC35), 13-methyl-heptatriacontane (13-MeC37), 15-methyl-heptatriacontane (15-MeC37), 17-methyl-heptatriacontane (17-MeC37), 5,3,17-trimethyl-tritriacontane (5,13,17-triMeC33), 5,13,17-trimethyl-pentatriacontane (5,13,17-triMeC35), and 5,13,17-trimethyl-heptatriacontane (5,13,17-triMeC37)
Relationship Among Compounds
Monomethyl C35 and C37 peaks were correlated both across and within colonies (Fig. 6, Table 2). Similarly, 5,13,17-triMeC35 was highly correlated with 5,13,17-triMeC37 across, but to a lesser extent within, colonies (Fig. 6, Table 2). There was a weaker correlation between the 5,13,17-triMeC33 and the 5,13,17-triMeC35 peaks both across and within colonies. The 5,13,17-triMeC33 and the 5,13,17-triMeC37 peaks were not correlated across or within colonies (Fig. 6, Table 2).
Correlations between relative proportions of hydrocarbon peaks (consisting of co-eluting compounds) within cuticular hydrocarbon profiles of Linepithema humile. Distinct supercolonies are encoded for individuals within the same supercolony. Sampling locations and abbreviations for supercolonies are described in the methods and in Brandt et al. (2009). 13-,15-,17-MeC35 = total of 13-methyl-pentatriacontane, 15-methyl-pentatriacontane, and 17-methyl-pentatriacontane; 13-,15-,17-MeC37 = total of 13-methyl-heptatriacontane, 15-methyl-heptatriacontane, and 17-methyl-heptatriacontane; 5,13,17-triMeC33 = 5,3,17-trimethyl-tritriacontane; 5,13,17-triMeC35 = 5,13,17-trimethyl-pentatriacontane; 5,13,17-triMeC37 = 5,13,17-trimethyl-heptatriacontane
Discussion
The recognition code of social insects generally is embedded in a complex mixture of chemicals. This study provides a significant step forward in the understanding of the chemical basis of nest mate recognition by suggesting that, similar to spoken language, the chemical language of social insects contains “synonyms”: chemicals that differ in structure, but are interpreted as being equivalent.
In general, Argentine ants showed similar levels of aggression to nest-mate CHC profiles augmented with compounds that differed in chain length but with the same methyl-branch position. There are at least two possible explanations for this. First, ants may not be able to discriminate among roughly similar homologs. It has been shown that honey bees often generalize odors with the same functional group, and that the ability to discriminate among compounds decreases with decreasing differences in chain length and increasing chain length (Vareschi 1971; Guerrieri et al. 2005). We tested compounds of very long carbon-chain length (33, 35, and 37), differing only by two or four carbons. Thus, it is possible that Argentine ants respond similarly to these homologs because they perceive them as the same compound. Alternatively, homologous CHCs may elicit the same aggressive response because they convey the same information. The data from our and other studies (Martin et al. 2008a; Martin and Drijfhout 2009b) show that homologs often occur in concentrations correlated within the CHC profile; colonies or individuals that produce relatively high or low concentrations of one compound also produce relatively high or low concentrations of a homolog. Increasing the concentration of one compound within the CHC profile may thus change the profile to a degree similar to increasing the concentration of the homolog. Although the exact biosynthetic mechanisms that regulate the number and position of methyl branches are unknown (Howard and Blomquist 2005), it has been suggested that amounts of homologous CHCs are correlated because they share a biosynthetic pathway (Martin and Drijfhout 2009b). However, we found that the relative amount of one of the compounds did not correlate with the amounts of its homologs; the amount of 5,13,17-triMeC33 was only weakly correlated with homologous 5,13,17-triMeC35, and not at all with 5,13,17-triMeC37. Interestingly, this lack of correlation was matched by responses to these compounds; workers were more frequently aggressive to nest-mate CHC profiles augmented with 5,13,17-triMeC33 than to those augmented with 5,13,17-triMeC35 or 5,13,17-triMeC37. Thus, it appears that the amounts of some homologous CHCs are not strictly related biosynthetically, and that Argentine ants are able to distinguish between certain homologs of similar carbon length.
In spite of this, our data show that individual compounds within a profile do not necessarily function as independent recognition cues, but rather that groups of homologs may do so. Consequently, the diversity of recognition cues likely may be far smaller than the number of CHCs in a profile. Studies on colony-cue recognition by social insects typically perform statistical tests, such as discriminate and principal component analysis, using all the CHCs in a profile as variables (Nielsen et al. 1999; Tentschert et al. 2002; van Wilgenburg et al. 2006; Foitzik et al. 2007). Our findings, as well as those of other studies (Martin and Drijfhout 2009a), indicate that it may be more appropriate to treat highly correlated compounds as a single variable. Moreover, when testing the function of individual CHCs in colony recognition, specificity of response may be elucidated more readily by testing non-homologous CHCs.
The evolution of complex signals, such as CHC profiles, can be driven by the value of providing additional and more reliable information. However, signal evolution is expected to be constrained by the interaction of physiological factors and the chemoreception system. Ants may not have evolved additional pathways that allow for variation in concentration among homologous CHCs because they either cannot detect or generate this type of variation.
References
AKINO, T., YAMAMURA, K., WAKAMURA, S., and YAMAOKA, R. 2004. Direct behavioral evidence for hydrocarbons as nestmate recognition cues in Formica japonica (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 39:381–387.
BJORKMAN-CHISWELL, B. T., VAN WILGENBURG, E., THOMAS, M. L., SWEARER, S. E., and ELGAR, M. A. 2008. Absence of aggression but not nestmate recognition in an Australian population of the Argentine ant Linepithema humile. Insect. Soc. 55:207–212.
BONAVITA-COUGOURDAN, A., CLÉMENT, J. L., and LANGE, C. 1987. Nestmate recognition: The role of cuticular hydrocarbons in the ant Camponotus vagus. J. Entomol. Sci. 22:1–10.
BRANDT, M., VAN WILGENBURG, E., and TSUTSUI, N. D. 2009. Global-Scale analyses of chemical ecology and population genetics in the Argentine ant. Mol. Ecol. 18:997–1005.
CHALINE, N., SANDOZ, J. C., MARTIN, S. J., RATNIEKS, F. L. W., and JONES, G. R. 2005. Learning and discrimination of individual cuticular hydrocarbons by honeybees (Apis mellifera). Chem. Senses 30:327–335.
CORIN, S. E., ABBOTT, K. L., RITCHIE, P. A., and LESTER, P. J. 2007. Large scale unicoloniality: the population and colony structure of the invasive Argentine ant (Linepithema humile) in New Zealand. Insect. Soc. 54:275–282.
DANI, F. R., JONES, G. R., CORSI, S., BEARD, R., PRADELLA, D., and TURILLAZZI, S. 2005. Nestmate recognition cues in the honey bee: Differential importance of cuticular alkanes and alkenes. Chem. Senses 30:477–489.
ELMES, G. W., AKINO, T., THOMAS, J. A., CLARKE, R. T., and KNAPP, J. J. 2002. Interspecific differences in cuticular hydrocarbon profiles of Myrmica ants are sufficiently consistent to explain host specificity by Maculinea (large blue) butterflies. Oecologia 130:525–535.
FOITZIK, S., STURM, H., PUSCH, K., D’ETTORRE, P., and HEINZE, J. 2007. Nestmate recognition and intraspecific chemical and genetic variation in Temnothorax ants. Anim. Behav. 73:999–1007.
GETZ, W. M., and SMITH, K. B. 1990. Odorant moiety and odor mixture perception in free-flying honey bees (Apis melifera). Chem. Senses 15:111–128.
GIRAUD, T., PEDERSEN, J. S., and KELLER, L. 2002. Evolution of supercolonies: The Argentine ants of southern Europe. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 99:6075–6079.
GREENE, M. J., and GORDON, D. M. 2003. Cuticular hydrocarbons inform task decisions. Nature 423:32.
GREENE, M. J., and GORDON, D. M. 2007. Structural complexity of chemical recognition cues affects the perception of group membership in the ants Linephithema humile and Aphaenogaster cockerelli. J. Exp. Biol. 210:897–905.
GUERRIERI, F., SCHUBERT, M., SANDOZ, J. C., and GIURFA, M. 2005. Perceptual and neural olfactory similarity in honeybees. Plos Biol. 3:718–732.
HADLEY, M. F. 1984. Cuticle: Ecological significance. pp 685–702 in: J. B-H, Matoltsy AG, Richards KS, editors. Biology of the integument. Berlin: Spring-Verlag.
HOLWAY, D. A., SUAREZ, A. V., and CASE, T. J. 1998. Loss of intraspecific aggression in the success of a widespread invasive social insect. Science 282:949–952.
HOWARD, R. W., and BLOMQUIST, G. J. 2005. Ecological, behavioral, and biochemical aspects of insect hydrocarbons. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 50:371–393.
KAIB, M., EISERMANN, B., SCHOETERS, E., BILLEN, J., FRANKE, S., and FRANCKE, W. 2000. Task-related variation of postpharyngeal and cuticular hydrocarbon composition in the ant Myrmucaria eumenoides. J. Comp. Physiol. A 186:939–948.
LUCAS, C., PHO, D. B., FRESNEAU, D., and JALLON, J. M. 2005. Role of cuticular hydrocarbons in the chemical recognition between ant species in the Pachycondyla villosa species complex. J. Insect Physiol. 51:1148–1157.
MARTIN, S. J., and DRIJFHOUT, F. P. 2009a. How reliable is the analysis of complex cuticular hydrocarbon profiles by multivariate statistical methods? J. Chem. Ecol. 35:375–382.
MARTIN, S., and DRIJFHOUT, F. 2009b. A review of ant cuticular hydrocarbons. J. Chem. Ecol. 35:1151–1161.
MARTIN, S. J., and DRIJFHOUT, F. P. 2009c. Nestmate and Task Cues are Influenced and Encoded Differently within Ant Cuticular Hydrocarbon Profiles. J. Chem. Ecol. 35:368–374.
MARTIN, S. J., HELANTERA, H., and DRIJFHOUT, F. P. 2008a. Colony-specific hydrocarbons identify nest mates in two species of Formica ant. J. Chem. Ecol. 34:1072–1080.
MARTIN, S. J., VITIKAINEN, E., HELANTERA, H., and DRIJFHOUT, F. P. 2008b. Chemical basis of nest-mate discrimination in the ant Formica exsecta. Proc. Roy. Soc. B. 275(1640):1271–1278.
NIELSEN, J., BOOMSMA, J. J., OLDHAM, N. J., PETERSEN, H. C., and MORGAN, E. D. 1999. Colony-level and season-specific variation in cuticular hydrocarbon profiles of individual workers in the ant Formica truncorum. Insect. Soc. 46:58–65.
OZAKI, M., WADA-KATSUMATA, A., FUJIKAWA, K., IWASAKI, M., YOKOHARI, F., SATOJI, Y., NISIMURA, T., and YAMAOKA, R. 2005. Ant nestmate and non-nestmate discrimination by a chemosensory sensillum. Science 309:311–314.
PEDERSEN, J. S., KRIEGER, M. J. B., VOGEL, V., GIRAUD, T., and KELLER, L. 2006. Native supercolonies of unrelated individuals in the invasive Argentine ant. Evolution 60:782–791.
SINGER, T. L. 1998. Roles of hydrocarbons in the recognition systems of insects. Am. Zool. 38:394–405.
SUAREZ, A. V., TSUTSUI, N. D. T., HOLWAY, D. A., and CASE, T. J. 1999. Behavioral and genetic differentiation between native and introduced populations of the Argentine ant. Biol. Invasions 1:43–53.
SUAREZ, A. V., HOLWAY, D. A., and CASE, T. J. 2001. Patterns of spread in biological invasions dominated by long-distance jump dispersal: insights from Argentine ants. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 98:1095–1100.
SUAREZ, A. V., HOLWAY, D. A., LIANG, D. S., TSUTSUI, N. D., and CASE, T. J. 2002. Spatiotemporal patterns of intraspecific aggression in the invasive Argentine ant. Anim. Behav. 64:697–708.
SUNAMURA, E., HATSUMI, S., KARINO, S., NISHISUE, K., TERAYAMA, M., KITADE, O., and TATSUKI, S. 2009. Four mutually incompatible Argentine ant supercolonies in Japan: inferring invasion history of introduced Argentine ants from their social structure. Biol. Invasions 11:2329–2339.
TENTSCHERT, J., BESTMANN, H. J., and HEINZE, J. 2002. Cuticular compounds of workers and queens in two Leptothorax ant species—a comparison of results obtained by solvent extraction, solid sampling, and SPME. Chemoecology 12:15–21.
THOMAS, M. L., PARRY, L. J., ALLAN, R. A., and ELGAR, M. A. 1999. Geographic affinity, cuticular hydrocarbons and colony recognition in the Australian meat ant Iridomyrmex purpureus. Naturwissenschaften 86:87–92.
TORRES, C. W., BRANDT, M., and TSUTSUI, N. D. 2007. The role of cuticular hydrocarbons as chemical cues for nestmate recognition in the invasive Argentine ant (Linepithema humile). Insect. Soc. 54:363–373.
TSUTSUI, N. D., and CASE, T. J. 2001. Population genetics and colony structure of the Argentine ant (Linepithema humile) in its native and introduced ranges. Evolution 55:976–985.
TSUTSUI, N. D., SUAREZ, A. V., HOLWAY, D. A., and CASE, T. J. 2000. Reduced genetic variation and the success of an invasive species. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97:5948–5953.
TSUTSUI, N. D., SUAREZ, A. V., and GROSBERG, R. K. 2003. Genetic diversity, asymmetrical aggression, and recognition in a widespread invasive species. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100:1078–1083.
VAN WILGENBURG, E., RYAN, D., MORRISON, P., MARRIOTT, P. J., and ELGAR, M. A. 2006. Nest- and colony-mate recognition in polydomous colonies of meat ants (Iridomyrmex purpureus). Naturwissenschaften 93:309–314.
VAN ZWEDEN, J. S., DREIER, S., and D’ETTORRE, P. 2009. Disentangling environmental and heritable nestmate recognition cues in a carpenter ant. J. Insect Physiol. 55:158–163.
VARESCHI, E. 1971. Dufunterscheidung bei der Honigbiene—Einzelzell-Ableitungen und Verhaltensreaktionen. Z. Vgl. Physiol. 75:143–173.
WAGNER, D., TISSOT, M., CUEVAS, W., and GORDON, D. M. 2000. Harvester ants utilize cuticular hydrocarbons in nestmate recognition. J. Chem. Ecol. 26:2245–2257.
WAGNER, D., TISSOT, M., and GORDON, D. M. 2001. Task-related environment alsters the cuticular hydrocarbon composition of harvester ants. J. Chem. Ecol. 27:1805–1819.
Acknowledgements
We thank Miriam Brandt for providing GC-MS data. This work was supported by grants from the United States Department of Agriculture, the California Structural Pest Control Board, the Defining Wisdom Program (a project of the Arete Initiative of the University of Chicago), and the Australian Research Council.
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/2.0), which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
About this article
Cite this article
van Wilgenburg, E., Sulc, R., Shea, K.J. et al. Deciphering the Chemical Basis of Nestmate Recognition. J Chem Ecol 36, 751–758 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-010-9812-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-010-9812-4