Abstract
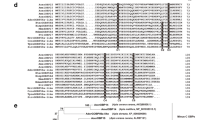
An odorant-binding protein cDNA (Acer-ASP2) was cloned and characterized from antennae of adult workers of an Asian honey bee, Apis cerana cerana F. (Hymenoptera: Apidae). The full-length open reading frame of Acer-ASP2 cDNA was 429 bp, encoding 142 amino acids. Protein signature analyses revealed that it contained six conserved cysteines with an N-terminal signal sequence of 19 amino acids. The deduced protein sequence shares high homology with Amel-ASP2 from the honey bee, Apis mellifera L., and low similarity with odorant-binding proteins from other species of insects. Immunocytochemical localization showed that Acer-ASP2 was concentrated in the lymph of olfactory sensilla, such as sensilla placodea and sensilla trichodea A. Real-time polymerase chain reaction of Acer-ASP2 transcripts showed that Acer-ASP2 was expressed on antennae but not in other general anatomical regions of the body. Temporally, Acer-ASP2 was expressed at a relatively high level in adults during two periods (9 and 27 vs. 1, 15, and 30 days). This timing is correlated with the production of beeswax and searching behavior for nectar/pollen, respectively. Thus, Acer-ASP2 is a species-specific gene that we propose to be involved in the acquisition of odorant molecules from nectar, pollen, and other general odorant sources.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ågren, L. 1977. Flagellar sensilla of some Colletidae (Hymenoptera: Apoidae). Int. J. Insect Morphol. Embryol. 6:137–146.
Ågren, L. 1978. Flagellar sensilla of two species of Andrena (Hymenoptera: Andrenidae). Int. J. Insect Morphol. Embryol. 7:73–79.
Ban, L., Scaloni, A., D'ambrosio, C., Zhang, L., Yahn, Y., and Pelosi, P. 2003. Biochemical characterization and bacterial expression of an odorant-binding protein from Locusta migratoria. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 60:390–400.
Bendtsen, J. D., Nielsen, H., Von Heijne, G., and Brunak, S. 2004. Improved prediction of signal peptides: SignalP 3.0. J. Mol. Biol. 340:783–795.
Biessmann, H., Walter, M. F., Dimitratos, S., and Woods, D. 2002. Isolation of cDNA clones encoding putative odourant binding proteins from the antennae of the malaria-transmitting mosquito, Anopheles gambiae. Insect Mol. Biol. 11:123–132.
Briand, L., Nespoulous, C., Huet, J. C., Takahashi, M., and Pernollet, J. C. 2001. Ligand binding and physico-chemical properties of ASP2, a recombinant odorant-binding protein from honeybee (Apis mellifera L.). Eur. J. Biochem. 268:752–760.
Calvello, M., Guerra, N., Brandazza, A., D'ambrosio, C., Scaloni, A., Dani, F. R., Turillazzi, S., and Pelosi, P. 2003. Soluble proteins of chemical communication in the social wasp Polistes dominulus. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 60:1933–1943.
Calvello, M., Brandazza, A., Navarrini, A., Dani, F. R., Turillazzi, S., Felicioli, A., and Pelosi, P. 2005. Expression of odorant-binding proteins and chemosensory proteins in some Hymenoptera. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 35:297–307.
Chen, S. L. 2001. The Apiculture Science in China. pp. 123–131. Agricultural Publishing House of China, Beijing, China(in Chinese).
Danty, E., Michard-Vanhee, C., Huet, J. C., Genecque, E., Pernollet, J. C., and Masson, C. 1997. Biochemical characterization, molecular cloning and localization of a putative odorant-binding protein in the honey bee Apis mellifera L. (Hymenoptera: Apidea). FEBS Lett. 414:595–598.
Danty, E., Arnold, G., Huet, J. C., Huet, D., Masson, C., and Pernollet, J. C. 1998. Separation, characterization and sexual heterogeneity of multiple putative odorant-binding proteins in the honeybee Apis mellifera L. (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Chem. Senses 23:83–91.
Danty, E., Briand, L., Michard-Vanhee, C., Perez, V., Arnold, G., Gaudemer, O., Huet, D., Huet, J. C., Ouali, C., and Masson, C. 1999. 7468–7475. Cloning and expression of a queen pheromone-binding protein in the honeybee: an olfactory-specific, developmentally regulated protein. J. Neurosci. 19:7468–7475.
Dickens, D. J., Callahan, W. P., Wergin, W. P., and Erbe, E. F. 1995. Olfaction in a hemimetabolous insect: antennal-specific proteins in adult Lygus lineolaris (Heteroptera: Miridae). J. Insect Physiol. 41:857–867.
Esslen, J., and Kaissling, K. -E. 1976. Number and distribution of the sensilla on the antennal flagullum of the honeybee (Apis mellifera L.). Zoomorphologie 83:227–251.
Forêt, S., and Maleszka, R. 2006. Function and evolution of a gene family encoding odorant binding-like proteins in a social insect, the honey bee (Apis mellifera). Genome Res. 16:1404–1413.
Gasteiger, E., Gattiker, A., Hoogland, C., Ivanyi, I., Appel, R. D., and Bairoch, A. 2003. ExPASy: The proteomics server for in-depth protein knowledge and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 31:3784–3788.
Graham, L. A., Brewer, D., Lajoie, G., and Davies, P. L. 2003. Characterization of a subfamily of beetle odorant-binding proteins found in hemolymph. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2:541–549.
Hekmat-Scafe, D. S., Steinbrecht, R. A., and Carlson, J. R. 1997. Coexpression of two odorant-binding protein homologs in Drosophila: implications for olfactory coding. J. Neurosci. 17:1616–1624.
Ishida, Y., Cornel, A. J., and Leal, W. S. 2002a. Identification and cloning of a female antenna-specific odorant-binding protein in the mosquito Culex quinquefasciatus. J. Chem. Ecol. 28:867–871.
Ishida, Y., Chiang, V. P., Haverty, M. I., and Leal, W. S. 2002b. Odorant-binding proteins from a primitive termite. J. Chem. Ecol. 28:1887–1893.
Ishida, Y., Chen, A. M., Tsuruda, J. M., Cornel, A. J., Debboun, M., and Leal, W. S. 2004. Intriguing olfactory proteins from the yellow fever mosquito, Aedes aegypti. Naturwissenschaften 91:426–431.
Jin, X., Brandazza, A., Navarrini, A., Ban, L., Zhang, S., Steinbrecht, R. A., Zhang, L., and Pelosi, P. 2005. Expression and immunolocalisation of odorant-binding and chemosensory proteins in locusts. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 62:1156–1166.
Leal, W. S., Nikonova, L., and Peng, G. 1999. Disulfide structure of the pheromone binding protein from the silkworm moth, Bombyx mori. FEBS Lett. 464:85–90.
Livak, K. J., and Schmittgen, T. D. 2001. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25:402–408.
Lu, D., Li, X., Liu, X., and Zhang, Q. 2007. Identification and molecular cloning of putative odorant-binding proteins and chemosensory protein from the bethylid wasp, Scleroderma guani Xiao et Wu. J. Chem. Ecol. 33:1359–1375.
Maida, R., Mameli, M., Muller, B., Krieger, J., and Steinbrecht, R. A. 2005. The expression pattern of four odorant-binding proteins in male and female silk moths, Bombyx mori. J. Neurocytol. 34:149–163.
Maleszka, R., and Stange, G. 1997. Molecular cloning, by a novel approach, of a cDNA encoding a putative olfactory protein in the labial palps of the moth Cactoblastis cactorum. Gene 202:39–43.
Michelette, E. R. F., and Soares, A. E. E. 1993. Characterization of preimaginal developmental stages in Africanized honey bee workers (Apis mellifera L.). Apidologie 24:431–440.
Nagnan-Le Meillour, P., Francois, M. C., and Jacquin-Joly, E. 2004. Identification and molecular cloning of putative odorant-binding proteins from the American palm weevil, Rhynchophorus palmarum L. J. Chem. Ecol. 30:1213–1223.
Ozaki, M., Morisaki, K., Idei, W., Ozaki, K., and Tokunaga, F. 1995. A putative lipophilic stimulant carrier protein commonly found in the taste and olfactory systems. A unique member of the pheromone-binding protein superfamily. Eur. J. Biochem. 230:298–308.
Pelosi, P. 1996. Perireceptor events in olfaction. J. Neurobiol. 30:3–19.
Pelosi, P., and Maida, R. 1995. Odorant-binding proteins in insects. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 111:503–514.
Pelosi, P., Zhou, J. J., Ban, L. P., and Calvello, M. 2006. Soluble proteins in insect chemical communication. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 63:1658–1676.
Peng, Y. S., Fang, Y. Z., Xu, S. Y., and Ge, L. S. 1987. The resistance mechanism of the Asian honey bee Apis cerana Fabr., to an ectoparasitic mite, Varroa jacobsoni Oudemans. J. Inverteb. Pathol. 49:54–60.
Rachinsky, A., Strambi, C., Strambi, A., and Hartfelder, K. 1990. Caste and metamorphosis: hemolymph titers of juvenile hormone and ecdysteroids in last instar honeybee larvae. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 79:31–38.
Scaloni, A., Monti, M., Angeli, S., and Pelosi, P. 1999. Structural analysis and disulfide-bridge pairing of two odorant-binding proteins from Bombyx mori. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 266:386–391.
Steinbrecht, R. A. 1998. Odorant-binding proteins: expression and function. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 855:323–332.
Steinbrecht, R. A., Ozaki, M., and Ziegelberger, G. 1992. Immunocytochemical localization of pheromone-binding protein in moth antennae. Cell Tissue Res. 270:287–302.
Steinbrecht, R. A., Laue, M., and Ziegelberger, G. 1995. Immunolocalization of pheromone-binding protein and general odorant-binding protein in olfactory sensilla of the silk moths Antheraea and Bombyx. Cell Tissue Res. 282:203–217.
Tan, X. M. 2006. Wild resources of Apis cerana cerana are reducing rapidly. J. Bee (in Chinese) 4:16.
The Honeybee Genome Sequencing Consortium 2006. Insights into social insects from the genome of the honeybee Apis mellifera. Nature 443:931–949.
Vogt, R. G., and Riddiford, L. M. 1981. Pheromone binding and inactivation by moth antennae. Nature 293:161–163.
Vogt, R. G., and Lerner, M. R. 1989. Two groups of odorant binding proteins in insects suggest specific and general olfactory pathways. Neurosci. Abstr. 15:1290–1296.
Vogt, R. G., Prestwich, G. D., and Lerner, M. R. 1991a. Odorant-binding-protein subfamilies associate with distinct classes of olfactory receptor neurons in insects. J. Neurobiol. 22:74–84.
Vogt, R. G., Rybczynski, R., and Lerner, M. R. 1991b. Molecular cloning and sequencing of general odorant-binding proteins GOBP1 and GOBP2 from the tobacco hawk moth Manduca sexta: comparisons with other insect OBPs and their signal peptides. J. Neurosci. 11:2972–2984.
Wang, G. R., Wu, K. M., and Guo, Y. Y. 2003. Cloning, expression and immunocytochemical localization of a general odorant-binding protein gene from Helicoverpa armigera (Hubner). Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 33:115–124.
Xiu, W. M., and Dong, S. L. 2007. Molecular characterization of two pheromone binding proteins and quantitative analysis of their expression in the beet armyworm, Spodoptera exigua Hübner. J. Chem. Ecol. 33:947–961.
Xu, P. X., Zwiebel, L. J., and Smith, D. P. 2003. Identification of a distinct family of genes encoding atypical odorant-binding proteins in the malaria vector mosquito, Anopheles gambiae. Insect Mol. Biol. 12:549–560.
Yang, C. H. 1998. The development and lives of male and worker bees of Apis cerana cerana. J. Bee (in Chinese) 8:16.
Zhang, S., Maida, R., and Steinbrecht, R. A. 2001. Immunolocalization of odorant-binding proteins in noctuid moths (Insecta, Lepidoptera). Chem. Senses 26:885–896.
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30270896) to Gao Qi-Kang and (30471127) to Lou Bing-Gan and by a grant from the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang (Y307597) to Li Hong-Liang.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, HL., Zhang, YL., Gao, QK. et al. Molecular Identification of cDNA, Immunolocalization, and Expression of a Putative Odorant-Binding Protein from an Asian Honey Bee, Apis cerana cerana . J Chem Ecol 34, 1593–1601 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-008-9559-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-008-9559-3