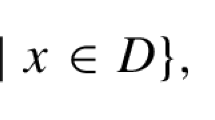Abstract
In recent years, the general binary quadratic programming (BQP) model has been widely applied to solve a number of combinatorial optimization problems. In this paper, we recast the maximum vertex weight clique problem (MVWCP) into this model which is then solved by a probabilistic tabu search algorithm designed for the BQP. Experimental results on 80 challenging DIMACS-W and 40 BHOSLIB-W benchmark instances demonstrate that this general approach is viable for solving the MVWCP problem.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alidaee B, Glover F, Kochenberger GA, Wang H (2007) Solving the maximum edge weight clique problem via unconstrained quadratic programming. Eur J Oper Res 181:592–597
Alidaee B, Kochenberger GA, Lewis K, Lewis M, Wang H (2008) A new approach for modeling and solving set packing problem. Eur J Oper Res 86(2):504–512
Babel L (1994) A fast algorithm for the maximum weight clique problem. Computing 52(1):31–38
Ballard D, Brown C (1983) Computer vision. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Benlic U, Hao JK (2013) Breakout local search for maximum clique problems. Comput Oper Res 40(1):192–206
Bomze IM, Pelillo M, Stix V (2000) Approximating the maximum weight clique using replicator dynamics. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 11:1228–1241
Busygin S (2006) A new trust region technique for the maximum weight clique problem. Discret Appl Math 154:2080–2096
Carraghan R, Pardalos PM (1990) An exact algorithm for the maximum clique problem. Oper Res Lett 9(6):375–382
Dorigo M (1997) Ant colony system: a cooperative learning approach to the traveling salesman problem. IEEE Trans Evolut Comput 1(1):53–66
Garey MR, Johnson DS (1979) Computers and intractability: a guide to the theory of NP-Completeness. Freeman, San Francisco
Glover F (1989) Tabu search—Part I. ORSA J Comput 1(3):190–206
Glover F, Hao JK (2010) Efficient evaluation for solving 0–1 unconstrained quadratic optimization problems. Int J Metaheuristics 1(1):3–10
Glover F, Hao JK (2010) Fast 2-flip move evaluations for binary unconstrained quadratic optimization problems. Int J Metaheuristics 1(2):100–107
Glover F, Laguna M (1997) Tabu search. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Norwell
Hansen P, Mladenović N (2001) Variable neighborhood search: principles and applications. Eur J Oper Res 130(3):449–467
He K, Huang W (2010) A quasi-human algorithm for solving the three-dimensional rectangular packing problem. Sci China Inf Sci 53(12):2389–2398
Horst R, Pardalos PM, Thoai NV (1995) Introduction to global optimization, nonconvex optimization and its applications, vol 3. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Norwell
Kochenberger GA, Glover F, Alidaee B, Rego C (2004) A unified modeling and solution framework for combinatorial optimization problems. OR Spectr 26:237–250
Kochenberger G, Alidaee B, Glover F, Wang HB (2007) An effective modeling and solution approach for the generalized independent set problem. Optim Lett 1:111–117
Kochenberger G, Hao JK, Lü Z, Wang H, Glover F (2013) Solving large scale max cut problems via tabu search. J Heuristics 19(4):565–571
Kochenberger G, Hao JK, Glover F, Lewis M, Lü Z, Wang H, Wang Y (2014) The unconstrained binary quadratic programming problem: a survey. J Comb Optim 28(1):58–81
Konc J, Janĕzic̆ D (2007) An improved branch and bound algorithm for the maximum clique problem. MATCH Commun Math Comput Chem 58:569–590
Li C, Quan Z (2010) An efficient branch-and-bound algorithm based on MAXSAT for the maximum clique problem. In: Proceedings of the 24th AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, pp 128–133
Lewis M, Kochenberger G, Alidaee B (2008) A new modeling and solution approach for the set-partitioning problem. Comput Oper Res 2008:807–813
Macreesh C, Prosser P (2013) Multi-threading a state-of-the-art maximum clique algorithm. Algorithms 6(4):618–635
Manninno C, Stefanutti E (1999) An augmentation algorithm for the maximum weighted stable set problem. Comput Optim Appl 14:367–381
Östergård PRJ (2001) A new algorithm for the maximum weight clique problem. Nordic J Comput 8(4):424–436
Östergård PRJ (2002) A fast algorithm for the maximum clique problem. Discret Appl Math 120(1):197–207
Pajouh FM, Balasumdaram B, Prokopyev O (2013) On characterization of maximal independent sets via quadratic optimization. J Heuristics 19(4):629–644
Pardalos PM, Rodgers GP (1992) A branch and bound algorithm for the maximum clique problem. Comput Oper Res 19(5):363–375
Pullan W (2008) Approximating the maximum vertex/edge weighted clique using local search. J Heuristics 14:117–134
Rebennack S, Oswald M, Theis D, Seitz H, Reinelt G, Pardalos PM (2011) A branch and cut solver for the maximum stable set problem. J Comb Optim 21(4):434–457
Rebennack S, Reinelt G, Pardalos PM (2012) A tutorial on branch and cut algorithms for the maximum stable set problem. Int Trans Oper Res 19(1–2):161–199
Segundo PS, Rodríguez-Losada D, Jiménez A (2011) An exact bitparallel algorithm for the maximum clique problem. Comput Oper Res 38(2):571–581
Sengor NS, Cakir Y, Guzelis C, Pekergin F, Morgul O (1999) An analysis of maximum clique formulations and saturated linear dynamical network. ARI 51:268–276
Tomita E, Kameda T (2007) An efficient branch-and-bound algorithm for finding a maximum clique with computational experiments. J Glob Optim 37(1):95–111
Wang Y, Lü Z, Glover F, Hao JK (2013) Probabilistic GRASP-tabu search algorithms for the UBQP problem. Comput Oper Res 40(12):3100–3107
Warren JS, Hicks IV (2006) Combinatorial branch-and-bound for the maximum weight independent set problem. Technical Report, Texas A&M University
Wu Q, Hao JK (2015) A review on algorithms for maximum clique problems. Eur J Oper Res 242:693–709
Wu Q, Hao JK, Glover F (2012) Multi-neighborhood tabu search for the maximum weight clique problem. Ann Oper Res 196(1):611–634
Wu Y, Huang W, Lau S, Wong CK, Young GH (2002) An effective quasi-human based heuristic for solving the rectangle packing problem. Eur J Oper Res 141(2):341–358
Xu JF, Chiu SY, Glover F (1996) Probabilistic tabu search for telecommunications network design. Comb Optim Theory Pract 1(1):69–94
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the reviewers and the editors for their comments which help us to improve the paper. This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 71501157, 71172124), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2015M580873) and Northwestern Polytechnical University (Grant No. 3102015RW007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
In memory of Professor Wenqi Huang for his pioneer work on nature-inspired optimization methods.
Appendix
Appendix
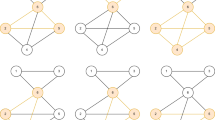
To illustrate the transformation from the MVWCP to the BQP, we consider the following graph (see Fig. 1):
Its linear formulation according to Eq. (1) is:
Choosing the scalar penalty \(P=-15\), we obtain the following BQP model:
which can be re-written as:
Solving this BQP problem yields \(x_3=x_4=1\) (all other variables equal zero) and the optimal objective function value is 9.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Hao, JK., Glover, F. et al. Solving the maximum vertex weight clique problem via binary quadratic programming. J Comb Optim 32, 531–549 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10878-016-9990-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10878-016-9990-2