Abstract
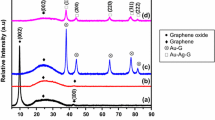
Graphene oxide (GO) was decorated with gold–aryl (Au–C) nanoparticles of AuNPs–COOH by sodium borohydride reduction of aryldiazonium tetrachloroaurate(III) salt at room temperature in aqueous solutions. Morphology of AuNPs–COOH/GO nanocomposite (NC) was probed using atomic force microscopy (AFM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM), showing NC surface roughness and wrinkling. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) results suggest the clear reductive reaction of tetrachloroaurate anion into metallic gold in AuNPs–COOH/GO along with detailed interpretations of the nature of the functional groups. Brunauer–Emmett–Teller measurements supported GO anchoring by AuNPs modified with COOH; surface area dropped significantly. Molecular dynamics calculations endowed support of favorable wrinkling at the edges and carboxyl intercalation to GO surface of types π–π, hydrogen bonding, and hydrophobic interactions. Solvent accessible surface area calculations of GO showed a decrease in total surface area.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
X. Li, F. Chen, C. Lian, et al. (2016). J. Clust. Sci. 27, 1877–1892.
C. Chung, Y. K. Kim, D. Shin, S. R. Ryoo, B. H. Hong, and D. H. Min (2013). Acc. Chem. Res. 46, 2211–2224.
T. Zhou, Y. Cheng, H. Zhang, et al. (2019). J. Clust. Sci. 30, 985–994.
Y. Luo, F. Y. Kong, C. Li, J. J. Shi, W. X. Lv, and W. Wang (2016). Sens. Actuators 234, 625–632.
W. L. Fu, S. J. Zhen, and C. Z. Huang (2013). Analyst 138, 3075.
D. Hernández-Sánchez, G. Villabona-Leal, I. Saucedo-Orozco, V. Bracamonte, E. Pérez, C. Bittencourt, et al. (2018). Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 20, 1685–1692.
D. Li, M. B. Müller, S. Gilje, R. B. Kaner, and G. G. Wallace (2008). Nat. Nanotechnol. 3, 101–105.
S. Pei, J. Zhao, J. Du, W. Ren, and H. M. Cheng (2010). Carbon 48, 4466–4474.
S. H. Jiang, J. Ding, R. H. Wang, F. Y. Chen, J. Sun, Y. X. Deng, and X. L. Li, Rare Met. (2021) 1–11.
Z. H. Duan, Q. N. Zhao, C. Z. Li, S. Wang, Y. D. Jiang, Y. J. Zhang, B. H. Liu, and H. L. Tai (2021). Rare Met. 40, 1762–1767.
M. Quintana, E. Vazquez, and M. Prato (2012). Acc. Chem. Res. 46, 138–148.
N. Bugárová, Z. Špitálsky, M. Mičušík, M. Bodík, P. Šiffalovič, M. Koneracká, et al. (2019). Cancers 11, 753. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11060753.
H. He and C. Gao (2011). Sci. China Chem. 54, 397–404.
H. Yang, J. Jiang, W. Zhou, L. Lai, L. Xi, Y. Lam, et al. (2011). Nanoscale Res. Lett. 6, 531.
Y. Tao, A. Dandapat, L. Chen, Y. Huang, Y. Sasson, Z. Lin, et al. (2016). Langmuir 32, 8557–8564.
S. He, K. K. Liu, S. Su, J. Yan, X. Mao, D. Wang, et al. (2012). Anal. Chem. 84, 4622–4627.
N. T. Khoa, S. W. Kim, D. H. Yoo, E. J. Kim, and S. H. Hahn (2014). Appl. Catal. A 469, 159–164.
T. A. Pham, B. C. Choi, K. T. Lim, and Y. T. Jeong (2011). Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 3350–3357.
A. A. L. Ahmad, S. Panicker, M. M. Chehimi, M. Monge, J. M. Lopez-De-Luzuriaga, A. A. Mohamed, et al. (2019). Catal. Sci. Technol. 9, 6059–6071.
W. S. Hummers and R. E. Offeman (1958). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 80, 1339–1339.
M. J. Abraham, M. D. Van der Spoel, B. Lindahl, B. Hess and the GROMACS development team, GROMACS User Manual version (2019) 4, http://www.gromacs.org.
N. Schmid, A. P. Eichenberger, A. Choutko, S. Riniker, M. Winger, A. E. Mark, et al. (2011). Eur. Biophys. J. 40, 843–856.
A. Lerf, H. He, M. Forster, and J. Klinowski (1998). J. Phys. Chem. B 102, 4477–4482.
M. Stroet, B. Caron, K. M. Visscher, D. P. Geerke, A. K. Malde, and A. E. Mark (2018). J. Chem. Theory Comput. 14, 5834–5845.
H. J. C. Berendsen, J. P. M. Postma, W. F. V. Gunsteren, and J. Hermans (1981) The Jerusalem Symposia on Quantum Chemistry and Biochemistry Intermolecular Forces, 331–342.
T. Darden, D. York, and L. Pedersen (1993). J. Chem. Phys. 98, 10089–10092.
S. Link and M. A. El-Sayed (1999). J. Phys. Chem. B 103, 4212–4217.
L. Laurentius, S. R. Stoyanov, S. Gusarov, A. Kovalenko, R. Du, G. P. Lopinski, et al. (2011). ACS Nano 5, 4219–4227.
S. Almheiri, A. A. L. Ahmad, B. L. Droumaguet, R. Pires, A. A. Mohamed, and M. M. Chehimi (2019). Langmuir 36, 74–83.
http://sites.cardiff.ac.uk/xpsaccess/reference/gold/Last. Accessed 9 Nov 2020
M. Davies, High resolution XPS of organic polymers: The Scienta ESCA300 database G. Beamson and D. Briggs John Wiley, Chichester, UK 1992, Biomaterials 15 (1994) 318–318.
A. Saad, M. Abderrabba, and M. M. Chehimi (2016). Surf. Interface Anal. 49, 340–344.
W. M. Skinner, C. A. Prestidge, and R. S. C. Smart (1996). Surf. Interface Anal. 24, 620–626.
M. M. Chehimi, Aryl Diazonium Salts: New Coupling Agents in Polymer and Surface Science (Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2012).
A. Mesnage, X. Lefèvre, P. Jégou, G. Deniau, and S. Palacin (2012). Langmuir 28, 11767–11778.
M. Thommes, K. Kaneko, A. V. Neimark, J. P. Olivier, F. R. Reinoso, J. Rouquerol, et al. (2015). Pure Appl. Chem. 87, 1051–1069.
K. W. Song, M. H. Park, T. H. Kim, S. H. Lim, and C. W. Yang (2014). J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 14, 8766–8770.
H. Tang, Y. Zhao, S. Shan, X. Yang, D. Liu, F. Cui, et al. (2018). Environ. Sci. Technol. 52, 7689–7697.
W. Zhan, J. Wang, H. Wang, J. Zhang, X. Liu, P. Zhang, et al. (2017). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139, 8846–8854.
H. Tang, Y. Zhao, S. Shan, X. Yang, D. Liu, F. Cui, et al. (2018). Environ. Sci. Nano. 5, 2357–2367.
Acknowledgements
MO acknowledges VEGA 02/0010/18 (Slovakia) for financial support. AAM acknowledges the University of Sharjah support of SEED grant (VC-GRC-SR-83-2015), competitive grants (160-2142-029-P and 150-2142-017-P), Organometallic Research Group grant (RISE-046-2016), and Functionalized Nanomaterials Synthesis Lab grant (151-0039). CH acknowledges the support of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (No. 2021R1A4A1032746) and (No. 2021R1A2C1093183).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Research Involving Human Participants and/or Animals
This research does not involve human participants and/or animals.
Informed Consent
There is no need for informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parambath, J.B.M., Arooj, M., Omastova, M. et al. Immobilization of Gold–Aryl Nanoparticles Over Graphene Oxide Platforms: Experimental and Molecular Dynamics Calculations Study. J Clust Sci 34, 577–586 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-022-02247-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-022-02247-0