Abstract
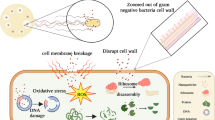
An easy mechanochemical and eco-friendly method was employed to obtain nanocrystals with an average size of about 9 nm of zinc ferrite (ZnFe2O4) and copper ferrite (CuFe2O4). Their corresponding X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns reveal a cubic crystal structure for ZnFe2O4, whereas in CuFe2O4 the tetragonal and cubic crystal phases coexist, the latter being the majority phase. The transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images of these nano ferrites corroborate the formation of nanocrystals with dimensions consistent with those obtained from the XRD patterns. Furthermore, their corresponding Raman spectra confirm the structure and composition of nano ferrites. In addition, both nano ferrites show an electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectrum with a wide band with g ~ 2.0, characteristic of ferromagnetic oxides. Besides, the antibacterial effect of ZnFe2O4 and CuFe2O4 nanocrystals against two opportunistic pathogens, Staphylococcus epidermidis (ATCC 14,990) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (ATCC 43,636), was tested. The minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) results showed that ZnFe2O4 was more effective against S. epidermidis, while CuFe2O4 was for P. aeruginosa. On the other hand, when 27 mg/mL of nano ferrites were dispersed in the agar plates, the growth of S. epidermidis was 100% inhibited, whereas ZnFe2O4 and CuFe2O4 inhibited 67% and 78% of P. aeruginosa growth, respectively.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. K. Kefeni and B. B. Mamba (2020). Sustain Mater Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susmat.2019.e00140.
M. L. Baynosa, A. H. Mady, V. Q. Nguyen, D. R. Kumar, M. S. Sayed, D. Tuma, and J. J. Shim (2020). J Colloid Interface Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.11.018.
Y. Fu and X. Wang (2011). Ind Eng Chem Res. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie200162a.
Y. Zhang, Q. Shi, J. Schliesser, B. F. Woodfield, and Z. Nan (2014). Inorg Chem. https://doi.org/10.1021/ic501487c.
J. Haetge, C. Suchomski, and T. Brezesinski (2010). Inorg Chem. https://doi.org/10.1021/ic102052r.
C. Yao, Q. Zeng, G. F. Goya, T. Torres, J. Liu, and H. J. Wu (2007). Phys Chem C. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0732763.
M. R. Anantharaman, S. Jagatheesan, K. A. Malini, S. Sindhu, A. Narayanasamy, C. N. Chinnasamy, J. P. Jacobs, S. Reijne, K. Seshan, R. H. H. Smits, H. H., Brongersma, J. Magn. Magn. (1998) https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(98)00171-1
M. Gharibshahian, O. Mirzaee, and M. S. Nourbakhsh (2017). J Magn Magn Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.10.116.
F. Liu, X. Li, Q. Zhao, Y. Hou, X. Quan, and G. Chen (2009). Acta Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2009.02.022.
Z. H. Yuan and L. D. Zhang (1998). Mater Res Bull. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2009.02.022.
C. Nordhei, K. Mathisen, I. Bezverkhyy, and D. Nicholson (2008). J Phys Chem C. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp7112158.
M. Sivakumar, T. Takami, H. Ikuta, A. Towata, K. Yasui, T. Tuziuti, T. Kozuka, D. Bhattacharya, and Y. Iida (2006). J Phys Chem B. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp055024c.
S. H. Yu, T. Fujino, and M. Yoshimura (2003). J Magn Magn Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(02)00977-0.
N. Wakiya, K. Muraoka, T. Kadowaki, T. Kiguchi, N. Mizutani, H. Suzuki, and K. Shinozaki (2007). J Magn Magn Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2006.11.145.
R. Zhang, J. Huang, J. Zhao, Z. Sun, and Y. Wang (2007). Energy Fuels. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef070064w.
A. R. Vazquez-Olmos, M. Abatal, R. Sato-Berru, G. K. Pedraza-Basulto, V. Garcia-Vazquez, A. Sainz-Vidal, R. Perez-Bañuelos, and A. Quiroz (2016). J Nanomater. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/9182024.
M. Balasubramanian and K. R. Murali (2020). Ferroelectrics. https://doi.org/10.1080/00150193.2019.1691381.
E. Manova, T. Tsoncheva, D. Paneva, M. Popova, N. Velinov, B. Kunev, K. Tenchev, and I. Mitov (2011). J Solid State Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2011.03.035.
N. Masunga, O.K. Mmelesi, K.K., Kefeni, B.B. Mamba, J. of Environ. Chem. Eng. (2019) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103179
A.T. Dhiwahar, M. Sundararajan, P. Sakthivel, C.S. Dash, S. Yuvaraj, J. of Physics and Chemistry of Solids (2020) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2019.109257
V. N. Nikolić, M. Vasić, and M. M. Milić (2018). Ceramics Int. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.08.157.
A. Subha, M.G. Shalini, B. Sahu, S.C. Sahoo, J. of Materials Science: Materials in electronics (2018) https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-0221-8
Z. Ye, Z. Deng, L. Zhang, J. Chen, G. Wang, and Z. Wu (2020). Mater Res Express. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab778b.
V. A. Zhuravlev, R. V. Minin, V. I. Itin, and I. Y. Lilenko (2017). J of Alloys and Compounds. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.09.069.
W. Lv, B. Liu, Z. Luo, X. Ren, and P. Zhang (2008). J of Alloys and Compounds. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2007.10.049.
K. Muthukumar, D. S. Lakshmi, S. D. Acharya, S. Natarajan, A. Mukherjee, and H. C. Bajaj (2018). Mater Chem and Phys. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2018.02.004.
P. Chand (2008). Hyperfine Interact. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-008-9789-3.
M.A. Ansari, A. Baykal, S. Asiri, S. Rehman, J. of Inorganic and Organometallic Polymers and Materials (2018) https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-018-0889-5
S. J. Stewart, M. J. Tueros, G. Cernicchiaro, and R. B. Scorzelli (2004). Solid State Communications. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssc.2003.11.010.
M. M. Rashad, S. Soltan, A. A. Ramadan, M. F. Bekheet, and D. A. Rayan (2015). Ceramics Int. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.06.046.
T. F. Marinca, I. Chicinas, and O. Isnard (2013). Ceramics Int. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2012.10.274.
G. F. Goya and H. R. Rechenberg (1998). J of Appl Phys. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.368109.
K. K. Kefeni, T. A. M. Msagati, T. T. Nkambule, and B. B. Mamba (2020). Mater Sci Eng C. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.110314.
M. M. Rashad, R. M. Mohamed, M. A. Ibrahim, L. F. M. Ismail, and E. A. Abdel-Aal (2012). Adv Powder Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2011.04.005.
V. N. Nikolić, M. M. Vasić, and D. Kisić (2019). J of Solid State Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2019.04.007.
I. Khan, K. Saeed, and I. Khan (2019). Arab J Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2017.05.011.
K. Kaviyarasu, C.M. Magdalane, D. Jayakumar, Y. Samson, A.K.H. Bashir, M. Maaza, D. Letsholathebe, A. Hossam Mahmoud, J. Kennedy, Journal of King Saud University – Science (2020) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2019.12.006.
G. Kaupp (2009). Cryst Eng Comm. https://doi.org/10.1039/B810822F.
J. L. Do, T. Friščić, and A. C. S. Cent (2017). Sci. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscentsci.6b00277.
A.R. Vázquez-Olmos, M.E. Sánchez-Vergara, A.L. Fernández-Osorio, A. Hernández-García, R.Y. Sato-Berrú, J.R. Alvarez-Bada, J. Clust. Sci. (2018)
K. Becker, C. Heilmann, and G. Peters (2014). Clin Microbiol Rev. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00109-13.
D. Chessa, G. Ganau, and M. Mazzarello (2015). J Infect Dev Ctries. https://doi.org/10.3855/jidc.6923.
M. Moradali, S. Ghods, and B. H. A. Rehm (2017). Front Cell Infect Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2017.00039.
L. B. Zakiyah, E. Saion, N. M. Al-Hada, E. Gharibshahi, A. Salem, N. Soltani, and S. Gene (2015). Mater Sci Semicond Process. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2015.07.027.
L. Wang, C. Hu, and L. Shao (2017). Int J Nanomedicine. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S121956.
J. P. Singh, R. C. Srivastava, H. M. Agrawat, and R. Kumar (2010). J of Raman Spectrosc. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrs.2902.
Z. Wanga, D. Schiferla, Y. Zhao, H.St.C. O’Neill, J. Phys. Chem. Solids. (2003) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2003.08.005
M. Bibhas, K. Mousumi, M. Siba, S. Rajat, R. Ujjal Kanti, R. Anirban, D. Dipankar, ACS Omega (2019) https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b01477.
K. K. Chattopadhyay, B. K. Chatterjee, K. Bhattacharyya, A. Dey, and C. K. Ghosh (2014). Dalton Trans. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4DT00093E.
N. Pathak, S. K. Gupta, K. Sanyal, M. Kumar, R. M. Kadam, and V. Natarajan (2014). Dalton Trans. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4DT00741G.
M. I. Nemufulwi, H. C. Swart, W. B. Mdlalose, and G. H. Mhlongo (2020). Appl Surf Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.144863.
X. Tang, A. Manthiram, and J. B. Goodenough (1989). J of Solid State Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-4596(89)90272-7.
F. Gunkel, D. V. Christensen, Y. Z. Chen, and N. Pryds (2020). Appl Phys Lett. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5143309.
M.A. Ansari, A. Baykal, S. Asiri, S. Rehman, J. of Inorganic and Organometallic Polymers and Materials (2018) https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-018-0889-5.
Acknowledgements
América Vázquez-Olmos gratefully acknowledges the support for this research to the UNAM-PAPIIT IN108616 grant. Argelia Almaguer-Flores acknowledges the support of the UNAM-PAPIIT # IT200319 grant. Blanca Paz-Díaz gratefully thanks CONACyT for the doctoral scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paz-Díaz, B., Vázquez-Olmos, A.R., Almaguer-Flores, A. et al. ZnFe2O4 and CuFe2O4 Nanocrystals: Synthesis, Characterization, and Bactericidal Application. J Clust Sci 34, 111–119 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-021-02203-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-021-02203-4