Abstract
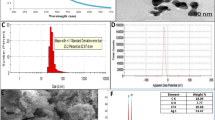
Since green synthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) is a simple, safe, cost-effective and eco-friendly method, AgNPs appear to be promising anti-cancer agents in the medical field. In this study, the biosynthesis of AgNPs was performed using aqueous extract of Satureja rechingeri Jamzad. Their anti-cancer activity was evaluated on the AGS gastric cancer cell line. The characteristics of the AgNPs were evaluated and approved by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), UV–visible spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) and Dynamic light scattering (DLS). The cytotoxic effect of AgNPs on the AGS cell line was evaluated by MTT assay for 24 h. Flow cytometry technique was performed to evaluate apoptosis using AnnexinV-FITC kit as well as cell cycle analysis. The expression of pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic genes was evaluated using Real-Time PCR. The average size of AgNPs was calculated at 62 ± 1 nm. The biosynthesized nanoparticles inhibited AGS cell growth in a time- and dose-dependent manner. Flow cytometry results confirmed apoptotic cell death. Also biosynthesized AgNPs caused up-regulation of pro-apoptotic genes; caspase-3, caspase-9 and Bax and down-regulation of Bcl2 gene and inhibited the expression of cyclin D1 and cyclin E genes. The cell cycle analysis revealed the cancer cells arrest in the G0/G1 phase. It appears that AgNPs synthesized by Satureja rechingeri Jamzad have a high potential for use as an anti-cancer drug for the treatment of gastric cancer.
Graphic Abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Nazir, et al. (2014). Nanomedicine. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2013.07.001.
A. Jemal, et al. (2011). CA Cancer J. Clin. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.20107.
T. Sano, et al. (2004). J. Clin. Oncol.. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2004.10.184.
B. G. Katzung Basic and Clinical Pharmacology (McGraw-Hill Education, New York, 2017).
M. S. Szymanski and R. A. Porter (2013). J. Immunol. Methods. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jim.2012.11.003.
Y. He, et al. (2017). Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2017.08.035.
M. A. Albrecht, C. W. Evans, and C. L. Raston (2006). Green Chem. https://doi.org/10.1039/b517131h.
J. Osuwa and P. Anusionwu (2011). Asian J. Inf. Technol 2011, (10), 96–100.
M. I. Sriram, et al. (2012). Nanosci. Methods. https://doi.org/10.1080/17458080.2010.547878.
B. Zhu, et al. (2016). Nanoscale Res. Lett. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-016-1419-4.
M. A. Malik, P. O’Brien, and N. Revaprasadu (2002). Chem. Mater. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm011154w.
K. N. Thakkar, S. S. Mhatre, and R. Y. Parikh (2010). Nanomedicine. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2009.07.002.
J. Singh, et al. (2018). J. Nanobiotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-018-0408-4.
V. N. Kalpana and V. Devi Rajeswari (2018). Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/3569758.
A. Gour and N. K. Jain (2019). Artif. Cells. Nanomed. Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2019.1577878.
S. E. Fard, F. Tafvizi, and M. B. Torbati (2018). IET Nanobiotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-nbt.2018.5069.
M. A. Rashmezad, et al. (2015). Tehran Univ. Med. J. 72, (12), 799–807.
E. Shirmohammadi, et al. (2014). Int. J. Infect. https://doi.org/10.17795/iji-21944.
S. Salehi, et al. (2016). Int. J. Nanomed. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S99882.
B. Mousavi, F. Tafvizi, and S. Zaker Bostanabad (2018). Artif. Cells. Nanomed. Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2018.1430697.
D. E. Lincoln and J. H. Langenheim (1976). Biochem. Syst. Ecol. https://doi.org/10.1016/0305-1978(76)90046-6.
V. Hajhashemi, et al. (2000). J. Ethnopharmacol. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-8741(99)00209-3.
V. Hajhashemi, B. Zolfaghari, and A. Yousefi (2012). Med. Princ. Pract. https://doi.org/10.1159/000333555.
M. Milos, et al. (2001). Flavour Fragr J. https://doi.org/10.1002/ffj.965.
J. Góra, A. Lis, and A. Lewandowski (1996). J. Essent Oil Res. https://doi.org/10.1080/10412905.1996.9700656.
Teimori, M., Essential oil analysis and antibacterial activity of Satureja Bachtiarica Bunge. In Ardebile Province. (2009)
Z. F. Baher, et al. (2002). Flavour Fragr. J. https://doi.org/10.1002/ffj.1097.
I. Rasaee, M. Ghannadnia, and S. Baghshahi (2018). Microporous Mesoporous Mater 264, 240–247.
P. Afshar and S. Sedaghat (2016). Curr. Nanosci 12, (1), 90–93.
S. Aslany, F. Tafvizi, and V. Naseh (2020). Mater. Today Commun 24, 101011.
C. Y. Loo, et al. (2016). J. Agric. Food Chem. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.5b04559.
Y. He, et al. (2016). Int. J. Nanomed. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S103695.
P. Jegadeeswaran, R. Shivaraj, and R. Venckatesh (2012). Digest J. Nanomater. Biostruct 7, (3), 991–998.
K. Kalishwaralal, et al. (2010). Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2010.02.007.
S. Roy and T. K. Das (2015). Int. J. Plant Biol. Res 7, 991–998.
K. S. Siddiqi, A. Husen, and R. A. K. Rao (2018). J. Nanobiotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-018-0334-5.
S. Pirtarighat, M. Ghannadnia, and S. Baghshahi (2018). J. Nanostruct. Chem. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40097-018-0291-4.
U. Kreibig and M. Vollmer Optical Properties of Metal Clusters (Springer, Berlin, 1995).
A. G. Al-Nuairi, et al. (2020). Biol. Trace Elem. Res.. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-019-01791-7.
K. Kokila, N. Elavarasan, and V. Sujatha (2017). Smart Sci 5, (3), 140–149.
S. Soman and J. Ray (2016). J. Photochem. Photobiol. B: Biol 163, 391–402.
A. Panáček, et al. (2006). J. Phys. Chem. B 110, (33), 16248–16253.
H. Erjaee, H. Rajaian, and S. Nazifi (2017). Adv. Nat. Sci 8, 025004.
J. Baharara, et al. (2015). Molecules 20, (2), 2693–2706.
R. Mukhopadhyay, J. Kazi, and M. C. Debnath (2018). Biomed. Pharmacother. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.10.167.
L. Pecorino Molecular biology of cancer: mechanisms, targets, and therapeutics (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2012).
S. Firoozi, M. Jamzad, and M. Yari (2016). J. Nanostruct. Chem 6, (4), 357–364.
F. Narchin, et al. (2018). Adv. Pharm. Bull.. https://doi.org/10.15171/apb.2018.028.
X.-J. Huang, et al. (2006). Sensors 6, 756–782.
Ranjbar, A., et al. (2014), Effects of silver nanoparticle (Ag NP) on oxidative stress biomarkers in rat. Nanomed. J
D. Raghunandan, et al. (2011). Cancer Nanotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12645-011-0014-8.
P. V. Asharani, M. P. Hande, and S. Valiyaveettil (2009). BMC Cell Biol. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2121-10-65.
C. Greulich, et al. (2011). Acta Biomater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2010.08.003.
S. Kim, et al. (2009). Toxicol In Vitro. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2009.06.001.
H. Rosas-Hernandez, et al. (2009). Toxicol. Lett. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2009.09.014.
Y. H. Hsin, et al. (2008). Toxicol. Lett. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2008.04.015.
P. Sanpui, A. Chattopadhyay, and S. S. Ghosh (2011). ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. https://doi.org/10.1021/am100840c.
M. Ahamed, et al. (2008). Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2008.09.015.
R. Sukirtha, et al. (2012). Process Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2011.11.003.
D. Philip (2010). Physica E Low-dimensional Syst. Nanostruct. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physe.2009.11.081.
M. I. Sriram, et al. (2010). Int. J. Nanomed. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S11727.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Laboratory of PIAU.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shiripoure Ganjineh Ketab, R., Tafvizi, F. & Khodarahmi, P. Biosynthesis and Chemical Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles Using Satureja Rechingeri Jamzad and Their Apoptotic Effects on AGS Gastric Cancer Cells. J Clust Sci 32, 1389–1399 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-020-01903-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-020-01903-7