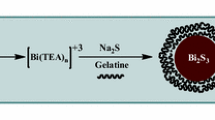
Abstract
Nanoparticles are gaining a new impetus in the field of medicine because of their potential to overcome core problems of drug efficacy. Amongst inorganic nanoparticles, barium sulphate in nano form is achieving wide attention due to its valuable applications. Despite the several advantages of barium sulphate nanoparticles, there is a major difficulty in their preparation and stability in the medium, as they belong to poorly soluble particles group. Hence, bearing in mind the synthesis barriers associated with these nanoparticles, a modified methodology has been designed for the synthesis of nanoparticles by capping them with gelatin. In addition, to enhance their physico-chemical properties and antimicrobial efficacy, BaSO4 nanoparticles were doped with four different metals. The synthesized nanoparticles were characterized through UV–Visible spectra, X-Ray Diffraction patterns, Dynamic Light Scattering, Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy analysis. Their antimicrobial potential and cytotoxicity through mitogenic response was also evaluated. These doped nanoparticles have shown enhanced properties in their structure (size reduction from micro to nano, dispersibility in the medium, non-aggregation etc.) and antimicrobial efficiency than its bulk counterparts. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report on antimicrobial potential of synthesized metal-doped barium sulphate nanoparticles stabilized with gelatin.
Graphic Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data
All available data has been presented in the paper.
Abbreviations
- BaSO4 :
-
Barium Sulphate
- CFU/ml:
-
Colony Forming Units/milliliter
- Co:
-
Cobalt
- Cu:
-
Copper
- DLS:
-
Dynamic Light Scattering
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl Sulfoxide
- FE-SEM:
-
Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy
- Mn:
-
Manganese
- MTCC:
-
Microbial Type Culture Collection and Gene Bank
- MTT:
-
(3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide)
- ppm:
-
Parts Per Million
- XRD:
-
X-Ray Diffraction
- Zn:
-
Zinc
References
D. Botequim, J. Maia, M.M.F, Lino, L.M.F. Lopes, P.N. Simões, L.M. Ilharco, and L. Ferreira (2012). Langmuir 28(20), 7646–7656. https://doi.org/10.1021/la300948n.
C. Jingjing, Z. Yu, L. Yong, T. Shuang, Z. Chunxiong, L. Chenhui, Y. Zhai, A. Yingli, J. B. Henk, S. Linqi, and L. Yang (2019). ACS Macro Lett 8, 651–657. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsmacrolett.9b00142.
P. D. Sruthi, C. S. Sahithya, C. Justin, C. S. Priya, K. S. Bhavya, P. Senthilkumar, and A. V. Samrot (2019). J. Clust. Sci 30, 11–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-018-1454-7.
B. Pannerselvam, T. S. Alagumuthu, S. K. Cinnaiyan, N. A. Al-Dhabi, K. Ponmurugan, M. Saravanan, S. V. Kanth, and K. P. Thangavelu (2020). J. Clust. Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-020-01759-x.
H. J. Kim, H. W. Park, and S. W. Seo (2017). Nano Convergence 4, (33), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40580-017-0126-x.
S. Chandna, N.S. Thakur, Y.N. Reddy, R. Kaur, and J. Bhaumik (2019). ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng 5(7), 3212–3227. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.9b00233.
H. Meng-Hsuan, M. Qingxin, R. S. Zachary, F. Chen, and Z. Miqin (2015). ACS Macro Lett 4, 403–407. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsmacrolett.5b00091.
T. Angelo, A. D. F. Yuri, A. Elvio, C. Lucia, D. Giacomo, G. Pietro, N. Vittorio, P. Piersandro, P. Luca, and P. Maddalena (2012). Langmuir 28, (21), 8140–8148. https://doi.org/10.1021/la3003838.
A. Viswadevarayalu, P.V. Ramana, G.S. Kumar, L.R. sylvia, J. Sumalatha, and S.A. Reddy (2015). J. Clust. Sci 27(1), 155-168. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-015-0917-3.
K. Lavanya, D. Kalaimurugan, M. S. Shivakumar, and S. Venkatesan (2020). J. Clust. Sci 31, 265–275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-019-01644-2.
R. Rekha, S. Mahboob, A. K. Ramya, S. Kerthekeyan, M. Govindarajan, K. A. Al-Ghanim, F. Al-Misned, Z. Ahmed, and B. Vaseeharan (2020). J. Clust. Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-020-01849-w.
V. Ramaswamy, G. Suresh, V. Meenakshisundaram, and V. Ponnusamy (2011). J. Ceramic Process Res 12, 184–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2010.07.020.
B. A. Sifontes, E. Canizales, J. Toro-Mendoza, E. Avila, P. Hernandez, A. B. Delgado, B. G. Gutierrez, Y. Diaz, and E. Cruz-Barrios (2015). J. Nanomater 2015, 1–9.
J. S. Hanor (2000). Rev. Mineral. Geochem 40, 193–275. https://doi.org/10.2138/rmg.2000.40.4.
F. Ibarra, C. Meyer, S. Haubold, and T. Heidelberg, US Patent No. 7288239, 30 October 2007.
S. Singh, A. Vij, S. P. Lochab, R. Kumar, and N. Singh (2010). Materials Research Bulletin 45, (5), 523–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2010.02.007.
A. Maynard and E. D. Kuempel (2007). J. Nanopart. Res 9, 1–3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-006-9164-8.
G. Oberdorster (2002). Inhalation Toxicol 14, 29–56. https://doi.org/10.1080/089583701753338631.
C. L. Tran, D. Buchanan, R. T. Cullen, A. Searl, A. D. Jones, and K. Donaldson (2008). Inhalation Toxicol 12, 1113–1126. https://doi.org/10.1080/08958370050166796.
Y. Shen, C. Li, X. Zhu, A. Xie, L. Qiu, and J. Zhu (2007). J. Chem. Sci 119, (4), 319–324.
E. G. Aninwene, D. Stout, Z. Yang, and J. T. Webster (2013). Int. J. Nanomed 8, 1197–1205.
S. Sivakumar, P. Soundhirarajan, A. Venkatesan, and P. C. Khatiwada (2015). Spectrochim. Acta, Part A 151, 895–907. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2015.07.048.
N. Padmavathy and R. Vijayaraghavan (2008). Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 9, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1088/1468-6996/9/3/035004.
T. Mosmann (1983). J. Immunol Methods. 65, 55–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4.
D. Zhang, and H. Yang (2013). Physica B 415, 44–48.
S. Sivakumar, P. Soundhirarajan, A. Venkatesan, and P. C. Khatiwad (2015). Spectrochim. Acta, Part A 137, 137–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2014.08.080.
N. Sharma, S. Jandaik, S. Kumar, M. Chitkara, and I. S. Sandhu (2016). J. Exp. Nanosci 11, 54–71. https://doi.org/10.1080/17458080.2015.1025302.
A. K. Chatterjee, R. Chakraborty, and T. Basu (2014). Nanotechnol. 25, 11360–11370. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/25/13/135101.
M. Sivera, L. Kvitek, J. Soukupova, A. Panacek, R. Prucek, R. Vecerova, and R. Zboril (2014). PLoS ONE 9, (8), e103675. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0103675.
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Department of Biotechnology, Punjabi University, Patiala for providing the basic necessary facility to conduct the experimental work. Authors are also grateful to Sophisticated Analytical Instrumentation Facility (SAIF) Centre at Punjab University, Chandigarh for providing the facilities for characterization of nanoparticles.
Funding
The authors declare that they had received no funding from any agency for the execution of the present research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BSS has conceived and conceptualized the study, and designed all experiments. BSS, MK and MS have performed the experiments. BSS and MK have drafted and refined the manuscript with equal contribution.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interest or conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sooch, B.S., Mann, M.K. & Sharma, M. Metal-Doped Barium Sulphate Nanoparticles Decorated with Gelatin as Antibacterial Agents. J Clust Sci 32, 1141–1154 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-020-01878-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-020-01878-5