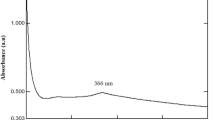
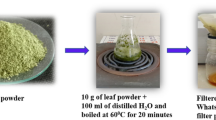
Abstract
Zinc-oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) synthesized from plant extracts are considered to possess superior biological activities compared to chemically synthesized nanoparticles and are of immediate interest to pharmaceutical and agriculture industries. The current study reports the green synthesis of ZnO-NPs from the aqueous leaf extract of Simarouba glauca for the first time. The physico-chemical characterization revealed hexagonal shaped nanoparticles with a size of ~ 17 to 37 nm calculated by Scherrer’s formula with a purity of 98.51%. The FT-IR results confirmed that functional groups present in the plant extract had coagulated well to form a metal oxide during the synthesis process. The antioxidant potential of green synthesized ZnO-NPs evaluated by different methods revealed significant (p ≤ 0.05) radical scavenging activity (5% to 59%) with IC50 value falling between 400 and 500 µg mL−1 among the test methods. The green synthesized nanoparticles also inhibited the mitotic cell division up to 17.46% with increase in concentration. Further, the haemolytic assay by spectroscopic analysis affirmed the biocompatible nature of the nanoparticles which was also evidenced through SEM studies. The present findings indicate that the green synthesized ZnO-NPs from S. glauca possess antioxidant and antimitotic properties apart from possessing biocompatible nature to RBCs thereby warranting in vivo studies.
Graphic Abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Fakruddin, Z. Hossain, and H. Afroz (2012). J. Nanobiotechnol.10, 31.
M. Murali, C. Mahendra, Nagabhushan, N. Rajashekar, M. S. Sudarshana, K. A. Raveesha and K. N. Amruthesh (2017). Spectrochim Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc.15, 104.
P. Mohanpuria, N. K. Rana, and S. K. Yadav (2008). J. Nanoparticles Res.10, 507.
X. Li, H. Xu, Z. Chen, and G. Chen (2011). J. Nanomaterials, 2011, 270974.
D. Suresh, R. M. Shobharani, P. C. Nethravathi, M. A. Pavan-Kumar, H. Nagabhushana, and S. C. Sharma (2015). Spectrochim Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc.141, 128.
S. Gunalan, R. Sivaraj, and V. Rajendran (2012). Prog Nat Sci Mater Int.22, 693.
M. Stan, A. Popa, D. Toloman, T. D. Silipas, and D. C. Vodnar (2016). Acta. Metal. Sin.29, 228.
D. Sharma, M. I. Sabela, S. Kanchi, P. S. Mdluli, G. Singh, T. A. Stenstrom, and K. Bisetty (2016). J. Photochem. Photobiol. B: Biol. B.162, 199.
K. Nithya and S. Kalyanasundharam (2019). OpenNano.1, 100024.
A. Happy, M. Soumya, S. V. Kumar, S. Rajeshkumar, R. D. Sheba, T. Lakshmi, and V. D. Nallaswamy (2019). Biochem. Biophy. Rep.1, 208.
S. Fakhari, M. Jamzad, and H. Kabiri Fard (2019). Green Chem. Lett. Rev.2, 19.
P. S. Mansi and D. K. Gaikwad (2011). J. Pharm. Sci. Res.3, 1195.
K. Ashwani, T. Gaurav, S. Sunayana, V. Kumar, and R. Pundir (2014). Int. J. Pharmacognosy1, 735.
J. S. Gamble Flora of the Presidency of Madras, vol. 3 (BSI, Calcutta, 1935).
A. Serpen, E. Capuano, V. Fogliano, and V. Gokmen (2007). J. Agri. Food Chem.55, 7676.
E. A. Shalaby and S. M. M. Shanab (2013). Indian J. Geo-Mar Sci.42, 556.
R. J. Ruch, S. J. Cheng, and E. Klaunig (1989). Carcinogenesis10, 1003.
M. Nishikimi, N. A. Rao, and K. Yagi (1972). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.46, 849.
G. Fiskesjo (1985). Hereditas102, 99.
T. V. Surendra, S. M. Roopan, N. A. Al-Dhabi, M. V. Arasu, G. Sarkar, and K. Suthindhiran (2016). Nanoscale Res. Lett.11, 546.
S. Kalita, R. Kandimalla, B. Devi, B. Kalita, K. Kalita, M. Deka, A. C. Kataki, A. Sharma, and J. Kotoky (2017). RSC Adv.7, 1749.
S. Passi, O. De Pita, P. Puddu, and G. P. Littarru (2002). Free Radic. Res.36, 477.
B. Auffray (2007). Int. J. Cosmet. Sci.29, 29.
L. Medina-Ramirez, S. Bashir, Z. Luo, and J. L. Liu (2009). Colloids Surf. B.73, 185.
A. K. Jha and K. Prasad (2010). Int. J. Green Nanotechnol. Phys. Chem.1, 110.
R. Yuvakkumar, J. Suresh, A. J. Nathanael, M. Sundrarajan, and S. I. Hong (2014). Mater. Lett.1, 170.
T. Karnanm and S. A. Selvakumar (2016). J. Mol. Struct.5, 358.
S. Jafarirad, M. Mehrabi, B. Divband, and M. Kosari-Nasab (2016). Mater. Sci. Eng. C.59, 296.
Y. H. Ni, X. W. Wei, J. M. Hong, and Y. Ye (2005). Mater. Sci. Eng. B.151, 42.
R. Seshadri, in: Rao A CNR, Muller AK Cheetham (eds.), The Chemistry of Nanomaterials, vol 1, (Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH, Weinheim 2004), p. 94.
A. Sirelkhatim, S. Mahmud, A. Seeni, N. H. M. Kaus, L. C. Ann, S. K. M. Bakhori, H. Hasan, and D. Mohamed (2015). Nano-Micro Lett.7, 219.
T. R. Lakshmeesha, M. K. Sateesh, B. D. Prasad, S. C. Sharma, D. Kavyashree, M. Chandrashekar, and H. Nagabushana (2014). Cryst. Growth Des.14, 4068.
C. Mahendra, M. Murali, G. Manasa, P. Ponnamma, M. R. Abhilash, T. R. Lakshmeesha, A. Satish, K. N. Amruthesh, and M. S. Sudarshana (2017). Microbial Pathogenesis.110, 620.
H. Sawada, R. Wang, and A. W. Sleight (1996). J. Solid. State Chem.122, 150.
S. R. Senthilkumar and T. Sivakumar (2015). Int. J. Pharm. Sci.6, 461.
V. Lobo, A. Patil, A. Phatak, and N. Chandra (2010). Pharmacognosy Rev.4, 118.
A. Thenmozhi, A. Nagalakshmi, and U. Mahadeva Rao (2011). Int. J. Sci. Technol1, 26–47.
N. H. Kumar, J. D. Andia, S. Manjunatha, M. Murali, K. N. Amruthesh, and S. Jagannath (2018). Biocatal. Agricult. Biotechnol.1, 101024.
S. Ananda Soubhagya (2014). Am. Chem. Sci. J.4, 616.
T. C. Taranath, B. N. Patil, T. U. Santosh, and B. S. Sharath (2015). Env. Sci. Pol. Res.22, 8611.
D. Pan, O. Vargas-Morales, B. Zern, A. C. Anselmo, V. Gupta, M. Zakrewsky, S. Mitragotri, and V. Muzykantov (2016). PloS ONE11, 0152074.
J. Autian in R. Kronenthal (ed.), Polymers in Medicine and Surgery, vol. 8 (Springer, New York, 1975), pp. 181–203.
E. P. Babu, A. Subastri, A. Suyavaran, K. Premkumar, V. Sujatha, B. Aristatile, G. M. Alshammari, V. Dharuman, and C. Thirunavukkarasu (2017). Sci. Rep.7, 4203.
D. Das, B. C. Nath, P. Phukon, and S. K. Dolui (2013). Colloids Surf. B.111, 556–560.
G. K. Prashanth, P. A. Prashanth, B. M. Nagabhushana, S. Ananda, H. G. Nagendra, and C. Rajendra Singh (2016). Adv. Sci. Eng. Med.8, 306–313.
M. A. Dobrovolskaia, J. D. Clogston, B. W. Neun, J. B. Hall, A. K. Patri, and S. E. McNeil (2008). Nano Lett.8, 2180.
Acknowledgements
The author M. Murali would like to acknowledge the University Grants Commission (UGC)- New Delhi, India for providing the financial support under UGC Post-Doctoral Fellowship (No. F/PDFSS-2015-17-KAR-11846). The authors are also thankful to University with Potential for Excellence (UPE) Project authorities and Department of Studies in Botany, University of Mysore for providing facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hemanth Kumar, N.K., Murali, M., Satish, A. et al. Bioactive and Biocompatible Nature of Green Synthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles from Simarouba glauca DC.: An Endemic Plant to Western Ghats, India. J Clust Sci 31, 523–534 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-019-01669-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-019-01669-7