Abstract
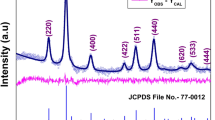
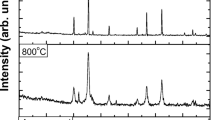
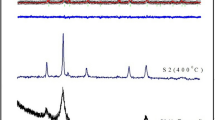
Ni0.6Zn0.4Fe2−xCrxO4 (x = 0–0.5) ferrite nanoparticles were prepared using reverse micelle process. X-ray diffraction patterns demonstrated that single phase of spinel ferrites are obtained. TEM micrographs demonstrate the formation of well dispersed nanoparticle with almost spherical morphologies. The EDS analysis proved that the chemical composition has almost uniform distribution in the whole series of samples. Magnetic dynamics of the samples was studied by the measurement of AC magnetic susceptibility versus temperature at different frequencies. The phenomenological Néel–Brown and Vogel–Fulcher models were employed to distinguish between the interacting or non-interacting system. Results exhibited that there is strong interaction between fine particles. The results obtained from vibrating sample magnetometer confirmed that with an increase in chromium content, the saturation magnetization increases. SQUID results at 2 K displayed the ferromagnetic state in nanoparticle and it was found that with an increase in substitution contents, the coercivity decreased.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. P. Herrera, L. Polo-Corrales, E. Chavez, J. Cabarcas-Bolivar, O. N. C. Uwakweh, and C. Rinaldi (2013). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 328, 41.
M. Sajjia, K. Y. Benyounis, and A. G. Olabi (2012). Powder Technol. 222, 143.
M. Sajjia, M. Oubaha, M. Hasanuzzaman, and A. G. Olabi (2014). Ceram. Int. 40, 1147.
M. Houshiar, F. Zebhi, Z. Jafari Razi, A. Alidoust, and Z. Askari (2014). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 371, 43.
K. O. Abdulwahab, M. A. Malik, P. O’Brien, and G. A. Timco (2014). Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 27, 303.
V. G. Andreev, S. B. Menshova, A. N. Klimov, R. M. Vergazov, S. B. Bibikov, and M. V. Prokofiev (2015). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 394, 1.
V. G. Andreev, S. B. Menshova, A. N. Klimov, and R. M. Vergazov (2015). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 393, 569.
M. A. Gabal, Y. M. Al Angari, and F. A. Al-Agel (2015). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 391, 108.
M. A. Gabal, W. A. Bayoumy, A. Saeed, and Y. M. Al Angari (2015). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1097, 45.
Z. Zheng, H. Zhang, Q. Yang, and L. Jia (2015). J. Alloys Compd. 648, 160.
Y. Köseoğlu (2015). Ceram. Int. 41, 6417.
Ch. Srinivas, B. V. Tirupanyam, A. Satish, V. Seshubai, D. L. Sastry, and O. F. Caltun (2015). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 382, 15.
A. Ghasemi, V. Šepelák, X. X. Liu, and A. Morisako (2013). J. Appl. Phys. 113, 17B524.
A. Ghasemi, V. Šepelák, X. X. Liu, and A. Morisako (2010). J. Appl. Phys. 107, 09A743.
A. Ghasemi, V. Šepelák, X. Liu, and A. Morisako (2009). IEEE Trans. Magn. 45, 2456.
A. Ghasemi, X. Liu, and A. Morisako (2009). IEEE Trans. Magn. 45, 4420.
A. Ghasemi and A. Morisako (2008). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 320, 1167.
W. A. Johnson and R. F. Mehl (1939). Trans. Am. Inst. Min. (Metall.) Eng. 135, 416.
M. P. Pileni (1997). Langmuir 13, 3266.
H. Althues and S. Kaskel (2002). Langmuir 18, 7428.
P. K. Roy and J. Bera (2008). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 197, 279.
S. A. Ghodake, U. R. Ghodake, S. R. Sawant, S. S. Suryavanshi, and P. P. Bakare (2006). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 305, 110.
W.-C. Hsu, S. C. Chen, P. C. Kuo, C. T. Lie, and W. S. Tsai (2004). Mater. Sci. Eng. B 111, 142.
I. Yaacob, A. Nunes, A. Bose, and D. Shah (1994). J. Colloid Interface Sci. 168, 289.
J. L. Dormann, D. Fiorani, and D. Tronc (1999). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 202, 251.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghasemi, A. Real and Imaginary Parts of Magnetic Susceptibility of Fine Dispersed Nanoparticles Synthesized by Reverse Micelle: From Superparamagnetic Trend to Ferrimagnetic State. J Clust Sci 27, 979–992 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-016-0978-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-016-0978-y