Abstract
Purpose
Major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC-II) deficiency is a rare inborn error of immunity (IEI). Impaired antigen presentation to CD4 + T cells results in combined immunodeficiency (CID). Patients typically present with severe respiratory and gastrointestinal tract infections at early ages. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) is the only curative therapy.
Methods
We describe the clinical, immunologic, and genetic features of eighteen unrelated Iranian patients with MHC-II deficiency.
Results
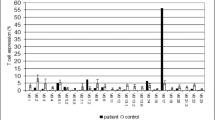
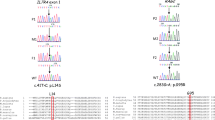
Consanguinity was present in all affected families. The median age at the initial presentation was 5.5 months (range 7 days to 18 years). The main symptoms included failure to thrive, persistent diarrhea, and pneumonia. Autoimmune and neurologic features were also documented in about one-third of the patients, respectively. Thirteen patients carried RFXANK gene mutations, two carried RFX5 gene mutations, and three carried a RFXAP gene mutation. Six patients shared the same RFXANK founder mutation (c.162delG); limited to the Iranian population and dated to approximately 1296 years ago. Four of the patients underwent HSCT; three of them are alive. On the other hand, nine of the fourteen patients who did not undergo HSCT had a poor prognosis and died.
Conclusion
MHC-II deficiency is not rare in Iran, with a high rate of consanguinity. It should be considered in the differential diagnosis of CID at any age. With the limited access to HSCT and its variable results in MHC-II deficiency, implementing genetic counseling and family planning for the affected families are mandatory. We are better determined to study the c.162delG RFXANK heterozygous mutation frequency in the Iranian population.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The NGS data have been submitted to GenBank; the accession numbers are pending.
Abbreviations
- ARD:
-
Ankyrin repeat domain
- APCs:
-
Antigen-presenting cells
- ANCA:
-
Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies
- AIHA:
-
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia
- BCG:
-
Bacillus Calmette–Guerin
- BAL:
-
Bronchoalveolar lavage
- BMSC:
-
Bone marrow stem cells
- CSF:
-
Cerebrospinal fluid
- CADD:
-
Combined annotation-dependent depletion
- CID:
-
Combined immunodeficiency
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- CMV:
-
Cytomegalovirus
- DTH:
-
Delayed-type hypersensitivity
- DBD:
-
DNA-binding domain
- ENT:
-
Ear, nose, and throat
- FTT:
-
Failure to thrive
- HSCT:
-
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
- HSV:
-
Herpes simplex virus
- iVDPV:
-
Immunodeficiency-associated vaccine–derived poliovirus
- IEI:
-
Inborn errors of immunity
- JIA:
-
Juvenile idiopathic arthritis
- MHC-II:
-
Major histocompatibility complex class II
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- MRD:
-
Matched-related donor
- MAF:
-
Minor allele frequency
- MMRD:
-
Mismatched-related donor
- MRCA:
-
Most recent common ancestor
- MSC:
-
Mutation significance cutoff
- NDD:
-
Neurodevelopmental delay
- NLH:
-
Nodular lymphoid hyperplasia
- NTD:
-
N-terminal domain
- NLS:
-
Nuclear localization signal
- OPV:
-
Oral poliovirus vaccine
- PBSC:
-
Peripheral blood stem cells
- PEST:
-
Activation domain rich in acidic amino acids (P, E, S, and T)
- PHA:
-
Phytohemagglutinin
- SCID:
-
Severe combined immunodeficiency
- TCR:
-
T cell receptor
- VAPP:
-
Vaccine-associated paralytic poliomyelitis
- VDPV2:
-
Vaccine-derived poliovirus type 2
References
Viret C, Janeway C Jr. MHC and T cell development. Rev Immunogenet. 1999;1(1):91–104.
Cresswell P. Assembly, transport, and function of MHC class II molecules. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12(1):259–91.
Reith W, Mach B. The bare lymphocyte syndrome and the regulation of MHC expression. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:331.
Villard J, Masternak K, Lisowska-Grospierre B, Fischer A, Reith W. MHC class II deficiency: a disease of gene regulation. Medicine. 2001;80(6):405–18.
Griscelli C, Lisowska-Grospierre B, Le Deist F, Durandy A, Marcadet A, Fischer A, et al. Combined immunodeficiency with abnormal expression of MHC class II genes. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1989;50(1 Pt 2):S140–8.
Griscelli C, Lisowska-Grospierre B, Mach B. Combined immunodeficiency with defective expression in MHC class II genes. Immunodefic Rev. 1989;1(2):135–53.
Reith W, Satola S, Sanchez CH, Amaldi I, Lisowska-Grospierre B, Griscelli C, et al. Congenital immunodeficiency with a regulatory defect in MHC class II gene expression lacks a specific HLA-DR promoter binding protein. RF-X Cell. 1988;53(6):897–906.
Lisowska-Grospierre B, Durandy A, Virelizier JL, Fischer A, Griscelli C. Combined immunodeficiency with defective expression of HLA: modulation of an abnormal HLA synthesis and functional studies. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1983;19(3):87–91.
Ferrua F, Bortolomai I, Fontana E, Di Silvestre D, Rigoni R, Marcovecchio GE, et al. Thymic epithelial cell alterations and defective thymopoiesis lead to central and peripheral tolerance perturbation in MHCII deficiency. Front Immunol. 2021;12:669943.
Waldburger J-M, Masternak K, Muhlethaler-Mottet A, Villard J, Peretti M, Landmann S, et al. Lessons from the bare lymphocyte syndrome: molecular mechanisms regulating MHC class II expression. Immunol Rev. 2000;178:148–65.
Masternak K, Muhlethaler-Mottet A, Villard J, Peretti M, Reith W. Molecular genetics of the bare lymphocyte syndrome. Rev Immunogenet. 2000;2(2):267–82.
Prod’homme T, Dekel B, Barbieri G, Lisowska-Grospierre B, Katz R, Charron D, et al. Splicing defect in RFXANK results in a moderate combined immunodeficiency and long-duration clinical course. Immunogenetics. 2003;55(8):530–9.
Wiszniewski W, Fondaneche M-C, Le Deist F, Kanariou M, Selz F, Brousse N, et al. Mutation in the class II trans-activator leading to a mild immunodeficiency. J Immunol. 2001;167(3):1787–94.
Hanna S, Etzioni A. MHC class I and II deficiencies. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;134(2):269–75.
Ouederni M, Vincent QB, Frange P, Touzot F, Scerra S, Bejaoui M, et al. Major histocompatibility complex class II expression deficiency caused by a RFXANK founder mutation: a survey of 35 patients. Blood J Am Soc Hematol. 2011;118(19):5108–18.
Bejaoui M, Barbouche M, Mellouli F, Largueche B, Dellagi K. Primary immunologic deficiency by deficiency of HLA class II antigens: nine new Tunisian cases. Arch Pediatr: Organe Officiel de la Soc Fr Pediatr. 1998;5(10):1089–93.
Ben-Mustapha I, Ben-Farhat K, Guirat-Dhouib N, Dhemaied E, Larguèche B, Ben-Ali M, et al. Clinical, immunological and genetic findings of a large Tunisian series of major histocompatibility complex class II deficiency patients. J Clin Immunol. 2013;33(4):865–70.
Djidjik R, Messaoudani N, Tahiat A, Meddour Y, Chaib S, Atek A, et al. Clinical, immunological and genetic features in eleven Algerian patients with major histocompatibility complex class II expression deficiency. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2012;8(1):1–5.
El Hawary RE, Mauracher AA, Meshaal SS, Eldash A, AbdElaziz DS, Alkady R, et al. MHC-II deficiency among Egyptians: novel mutations and unique phenotypes. J Allergy Clin Immunol: In Pract. 2019;7(3):856–63.
Wiszniewski W, Fondaneche M-C, Lambert N, Masternak K, Picard C, Notarangelo L, et al. Founder effect for a 26-bp deletion in the RFXANK gene in North African major histocompatibility complex class II-deficient patients belonging to complementation group B. Immunogenetics. 2000;51(4):261–7.
Al-Herz W, Zainal ME, Salama M, Al-Ateeqi W, Husain K, Abdul-Rasoul M, et al. Primary immunodeficiency disorders: survey of pediatricians in Kuwait. J Clin Immunol. 2008;28(4):379–83.
Klein C, Lisowska-Grospierre B, LeDeist F, Fischer A, Griscelli C. Major histocompatibility complex class II deficiency: clinical manifestations, immunologic features, and outcome. J Pediatr. 1993;123(6):921–8.
Saleem M, Arkwright P, Davies E, Cant A, Veys P. Clinical course of patients with major histocompatibility complex class II deficiency. Arch Dis Child. 2000;83(4):356–9.
Wiszniewski W, Fondaneche M-C, Louise-Plence P, Prochnicka-Chalufour A, Selz F, Picard C, et al. Novel mutations in the RFXANK gene: RFX complex containing in-vitro-generated RFXANK mutant binds the promoter without transactivating MHC II. Immunogenetics. 2003;54(11):747–55.
Cai YQ, Zhang H, Wang XZ, Xu C, Chao YQ, Shu Y, et al. A novel RFXANK mutation in a chinese child with MHC II deficiency: case report and literature review. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2020;7(8):ofaa314.
Abolnezhadian F, Dehghani R, Dehnavi S, Khodadadi A, Shohan M. A novel mutation in RFXANK gene and low B cell count in a patient with MHC class II deficiency: a case report. Immunol Res. 2020;68(4):225–31.
Abolnezhadian F, Saeedi-Boroujeni A, Iranparast S. MHC class II deficiency with normal CD4+ T cell counts: a case report. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018;17(6):594–600.
Farrokhi S, Shabani M, Aryan Z, Zoghi S, Krolo A, Boztug K, et al. MHC class II deficiency: report of a novel mutation and special review. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2018;46(3):263–75.
Parvaneh N, Shahmahmoudi S, Tabatabai H, Zahraei M, Mousavi T, Esteghamati AR, et al. Vaccine-associated paralytic poliomyelitis in a patient with MHC class II deficiency. J Clin Virol. 2007;39(2):145–8.
Sheikhbahaei S, Sherkat R, Roos D, Yaran M, Najafi S, Emami A. Gene mutations responsible for primary immunodeficiency disorders: a report from the first primary immunodeficiency biobank in Iran. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2016;12:62.
Hernandez N, Bucciol G, Moens L, Le Pen J, Shahrooei M, Goudouris E, et al. Inherited IFNAR1 deficiency in otherwise healthy patients with adverse reaction to measles and yellow fever live vaccines. J Exp Med. 2019;216(9):2057–70.
Itan Y, Shang L, Boisson B, Ciancanelli MJ, Markle JG, Martinez-Barricarte R, et al. The mutation significance cutoff: gene-level thresholds for variant predictions. Nat Methods. 2016;13(2):109–10.
Krawczyk M, Masternak K, Zufferey M, Barras E, Reith W. New functions of the major histocompatibility complex class II-specific transcription factor RFXANK revealed by a high-resolution mutagenesis study. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25(19):8607–18.
Nekrep N, Geyer M, Jabrane-Ferrat N, Peterlin BM. Analysis of ankyrin repeats reveals how a single point mutation in RFXANK results in bare lymphocyte syndrome. Mol Cell Biol. 2001;21(16):5566–76.
Genin E, Tullio-Pelet A, Begeot F, Lyonnet S, Abel L. Estimating the age of rare disease mutations: the example of triple-A syndrome. J Med Genet. 2004;41(6):445–9.
Wang RJ, Al-Saffar SI, Rogers J, Hahn MW. Human generation times across the past 250,000 years. Sci Adv. 2023;9(1):eabm7047.
Laird KM, Briggs LL, Boss JM, Summers MF, Garvie CW. Solution structure of the heterotrimeric complex between the interaction domains of RFX5 and RFXAP from the RFX gene regulatory complex. J Mol Biol. 2010;403(1):40–51.
Villard J, Peretti M, Masternak K, Barras E, Caretti G, Mantovani R, et al. A functionally essential domain of RFX5 mediates activation of major histocompatibility complex class II promoters by promoting cooperative binding between RFX and NF-Y. Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20(10):3364–76.
Chakraborty M, Sengupta A, Bhattacharya D, Banerjee S, Chakrabarti A. DNA binding domain of RFX5: interactions with X-box DNA and RFXANK. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Protein Proteomics. 2010;1804(10):2016–24.
Naamane H, El Maataoui O, Ailal F, Barakat A, Bennani S, Najib J, et al. The 752delG26 mutation in the RFXANK gene associated with major histocompatibility complex class II deficiency: evidence for a founder effect in the Moroccan population. Eur J Pediatr. 2010;169(9):1069–74.
Klein C, Cavazzana-Calvo M, Le Deist F, Jabado N, Benkerrou M, Blanche S, et al. Bone marrow transplantation in major histocompatibility complex class II deficiency: a single-center study of 19 patients. Blood. 1995;85(2):580–7.
Shaghaghi M, Shahmahmoodi S, Nili A, Abolhassani H, Madani SP, Nejati A, et al. Vaccine-derived poliovirus infection among patients with primary immunodeficiency and effect of patient screening on disease outcomes. Iran Emerg Infect Dis. 2019;25(11):2005–12.
Shahmahmoodi S, Mamishi S, Aghamohammadi A, Aghazadeh N, Tabatabaie H, Gooya MM, et al. Vaccine-associated paralytic poliomyelitis in immunodeficient children, Iran, 1995–2008. Emerg Infect Dis. 2010;16(7):1133–6.
El-Sayed ZA, El-Ghoneimy DH, Ortega-Martell JA, Radwan N, Aldave JC, Al-Herz W, et al. Allergic manifestations of inborn errors of immunity and their impact on the diagnosis: a worldwide study. World Allergy Organ J. 2022;15(6):100657.
Fazlollahi MR, Najmi M, Fallahnezhad M, Sabetkish N, Kazemnejad A, Bidad K, et al. Paediatric asthma prevalence: the first national population-based survey in Iran. Clin Respir J. 2019;13(1):14–22.
Hervé M, Isnardi I, Ng Y-s, Bussel JB, Ochs HD, Cunningham-Rundles C, et al. CD40 ligand and MHC class II expression are essential for human peripheral B cell tolerance. J Exp Med. 2007;204(7):1583–93.
Posovszky C, Sirin M, Jacobsen E, Lorenz M, Schwarz K, Schmidt-Choudhury A, et al. Persisting enteropathy and disturbed adaptive mucosal immunity due to MHC class II deficiency. Clin Immunol. 2019;203:125–33.
Alharby E, Obaid M, Elamin MAO, Almuntashri M, Bakhsh I, Samman M, et al. Progressive ataxia and neurologic regression in RFXANK-associated bare lymphocyte syndrome. Neurol Genet. 2021;7(3):e586.
Lum SH, Anderson C, McNaughton P, Engelhardt KR, MacKenzie B, Watson H, et al. Improved transplant survival and long-term disease outcome in children with MHC class II deficiency. Blood. 2020;135(12):954–73.
Renella R, Picard C, Neven B, Ouachée-Chardin M, Casanova JL, Deist FL, et al. Human leucocyte antigen-identical haematopoietic stem cell transplantation in major histocompatiblity complex class II immunodeficiency: reduced survival correlates with an increased incidence of acute graft-versus-host disease and pre-existing viral infections. Br J Haematol. 2006;134(5):510–6.
Siepermann M, Gudowius S, Beltz K, Strier U, Feyen O, Troeger A, et al. MHC class II deficiency cured by unrelated mismatched umbilical cord blood transplantation: case report and review of 68 cases in the literature. Pediatr Transplant. 2011;15(4):E80–6.
Antoine C, Müller S, Cant A, Cavazzana-Calvo M, Veys P, Vossen J, et al. Long-term survival and transplantation of haemopoietic stem cells for immunodeficiencies: report of the European experience 1968–99. Lancet. 2003;361(9357):553–60.
Bonduel M, Staciuk R, Figueroa C, Oleastro M, Gamba C, Rossi J, et al. Unrelated cord blood transplantation and reduced-intensity conditioning regimen for graft failure in a child with major histocompatibility complex class II deficiency. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2009;43(10):817–8.
Al-Mousa H, Al-Shammari Z, Al-Ghonaium A, Al-Dhekri H, Al-Muhsen S, Al-Saud B, et al. Allogeneic stem cell transplantation using myeloablative and reduced-intensity conditioning in patients with major histocompatibility complex class II deficiency. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2010;16(6):818–23.
Small TN, Qasim W, Friedrich W, Chiesa R, Bleesing JJ, Scurlock A, et al. Alternative donor SCT for the treatment of MHC class II deficiency. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013;48(2):226–32.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Nima Parvaneh. Methodology: Nima Parvaneh, Mohammad Shahrooei, Laurent Abel. Formal analysis and investigation: Mohadese Sadat Mousavi Khorshidi, Yoann Seeleuthner, Zahra Chavoshzadeh, Maryam Behfar, Amir Ali Hamidieh, Hosein Alimadadi, Roya Sherkat, Tooba Momen, Nasrin Behniafard, Shabnam Eskandarzadeh, Mahboubeh Mansouri, Mahdiyeh Behnam, Mohadese Mahdavi, Maryam Heydarazad Zadeh, Mehdi Shokri, Fatemeh Alizadeh, Mahshid Movahedi, Mana Momenilandi, Mohammad Keramatipour, Mohammad Shahrooei, Jean-Laurent Casanova, Aurélie Cobat, Laurent Abel, Nima Parvaneh. Writing — original draft preparation: Mohadese Sadat Mousavi Khorshidi, Yoann Seeleuthner, Nima Parvaneh. Writing — review and editing: Nima Parvaneh, Jean-Laurent Casanova, Laurent Abel, Aurélie Cobat. Supervision: Nima Parvaneh, Mohammad Shahrooei, Jean-Laurent Casanova, Laurent Abel, Aurélie Cobat.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
The Children’s Medical Center Institutional Ethics Committee, affiliated with the Tehran University of Medical Sciences, approved the study.
Consent to Participate/Consent for Publication
Informed consent for participating in the study and publication of data was obtained from the patients or their parents.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mousavi Khorshidi, M.S., Seeleuthner, Y., Chavoshzadeh, Z. et al. Clinical, Immunological, and Genetic Findings in Iranian Patients with MHC-II Deficiency: Confirmation of c.162delG RFXANK Founder Mutation in the Iranian Population. J Clin Immunol 43, 1941–1952 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-023-01562-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-023-01562-z