Abstract
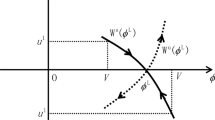
On the basis of the classic formula of the concentration Rayleigh number and the Kedem–Katchalsky equation for diffusive membrane transport, we derived the equations of sixteenth order which show the dependence of the thicknesses of the concentration boundary layers on the difference of the solution concentrations, the concentration Rayleigh number, the solute permeability coefficient of the membrane and the diffusion coefficients in the solution, the kinematic viscosity of the solution, the density of solutions, the temperature and gravitational acceleration. The obtained equation has numerical solutions in the first, third and fourth quadrant of a co-ordinate system. However, only two solutions from the first quadrant of the co-ordinate system have physical meaning. Confining ourselves to the set of solutions with physical meaning only, the thicknesses of concentration boundary layers for different parameters occurring in the obtained equation were calculated numerically.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Katchalsky, A., Curran, P.F.: Nonequilibrium Thermodynamics in Biophysics. Harvard University Press, Cambridge (1965)
Barry, P.H., Diamond, J.M.: Effects of unstirred layers on membrane phenomena. Physiol. Rev. 64, 763–872 (1984)
Cogoli, A., Gründer, F.K.: Gravity effects on single cells: techniques, findings and theory. Adv. Space Biol. Med. 1, 183–248 (1991)
Rubinstein, I., Zaltzman, B.: Electro-osmotically induced convection at a permselective membrane. Phys. Rev. E 62, 2238–2251 (2000)
Rubinstein, I., Staude, E., Kedem, O.: Role of the membrane surface in concentration polarization at ion-exchange membrane. Desalination 69, 101–114 (1988)
Rubinstein, I., Zaltzman, B., Kedem, O.: Electric fields in and around ion-exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 125, 17–21 (1997)
Sistat, P., Pourelly, G.: Chronopotentiometric response of an ion exchange membrane in the underlimiting current range. Transport phenomena within the diffusion layers. J. Membr. Sci. 123, 121–131 (1997)
Rösler, H.W., Maletzki, F., Staude, E.: Ion transfer across electrodialysis membranes in the overlimiting current-range. Chronopotentiometric studies. J. Membr. Sci. 72, 171–179 (1992)
Krol, J.J., Wessling, M., Strathmann, H.: Chronopotentiometry and overlimiting ion transport through monopolar ion exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 162, 155–164 (1999)
Murhy, W.D., Manzanares, J.A., Mafe, S., Reiss, H.: A numerical study on the equilibrium and nonequilibrium diffuse double layer in electrochemical cells. J. Phys. Chem. 96, 9983–9991 (1992)
Gnusin, N.P., Berezina, N.P., Kononenko, N.A., Dyomina, O.A.: Transport structural parameters to characterize ion exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 243, 301–310 (2004)
Ślęzak, A., Ślęzak, I.H., Ślęzak, K.: Influence of the concentration boundary layers on membrane potential in a single-membrane system. Desalination 184, 113–123 (2005)
Dworecki, K., Ślęzak, A., Wasik, S.: Temporal and spatial structure of the concentration boundary layers in membrane system. Physica A 326, 360–369 (2003)
Ginzburg, B.Z., Katchalsky, A.: The frictional coefficients of the flows of nonelectrolytes through artificial membranes. J. Gen. Physiol. 47, 403–418 (1963)
Ślęzak, A., Dworecki, K., Ślęzak, I.H., Wasik, S.: Permeability coefficient model equations of the complex: membrane-concentration boundary layers for ternary nonelectrolyte solutions. J. Membr. Sci. 267, 50–57 (2005)
Dworecki, K., Ślęzak, A., Ornal-Wasik, B., Wasik, S.: Effect of hydrodynamic instabilities on solute transport in a membrane system. J. Membr. Sci. 265, 94–100 (2005)
Holtz, R., Finkelstein, A.: The water and nonelectrolyte permeability induced in thin lipid membranes by the polyene antibiotics nystatin and amphotericin B. J. Gen. Physiol. 56, 125–145 (1970)
Fischbarg, J., Li, J., Kuang, K., Echevarria, M., Iserovich, P.: Determination of volume and water permeability of platea cells from measurements of light scattering. Am. J. Physiol. 265, C1412–C1423 (1993)
Cotton, C.U., Reuss, L.: Measurement of the effective thickness of the mucosal unstirred layer in Necturus gallbladder epithelium. J. Gen. Physiol. 93, 631–647 (1989)
Pohl, P., Saparov, S.M., Antonenko, Y.N.: The size of the unstirred layer as a function of the solute diffusion coefficient. Biophys. J. 75, 1403–1409 (1998)
Lerche, D.: Temporal and local concentration changes in diffusion layers at cellulose membranes due to concentration difference between the solutions on both sides of the membrane. J. Membr. Biol. 27, 193–205 (1976)
Fernandez-Sempere, J., Ruiz-Bevia, F., Salcedo-Diaz, R.: Measurements by holographic interferometry of concentration profiles in dead-end ultrafiltration of polyethylene glycol solutions. J. Membr. Sci. 229, 187–197 (2004)
Ślęzak, A., Dworecki, K., Anderson, J.E.: Gravitational effects on transmembrane flux: the Rayleigh–Taylor convective instability. J. Membr. Sci. 23, 71–81 (1985)
Pedley, T.J.: Calculation of unstirred layers thickness in membrane transport experiments: a survey. Q. Rev. Biophys. 16, 115–150 (1983)
McLaughin, S.G.A., Dilger, J.P.: Transport of protons across membranes by weak acids. Physiol. Rev. 60, 825–863 (1980)
Winne, D.: Unstirred layer, source of biased Michaelis constant in membrane transport. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 298, 27–31 (1973)
Lewitt, M.D., Strocchi, A., Lewitt, D.G.: Human jejunum unstirred layer: evidence for extremely efficient luminal stirring. Am. J. Physiol. 262, 593–595 (1992)
Pappenheimer, J.R.: Role of pre-epitheial “unstirred” layers in a absorption of nutrients from the human jejunum. J. Membr. Biol. 179, 185–204 (2001)
Schatz, A., Linke-Hommes, A.: Gravity and the membrane-solution interface: theoretical investigations. Adv. Space Res. 9, 61–64 (1989)
Kondepudi, D.K., Prigogine, I.: Sensitivity of non-equilibrium chemical systems to gravitational field. Adv. Space Res. 3, 171–176 (1983)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ślęzak, A., Bryll, A. & Grzegorczyn, S. A Numerical Study of the Hydrodynamic Stable Concentration Boundary Layers in a Membrane System Under Microgravitational Conditions. J Biol Phys 32, 553–562 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10867-007-9037-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10867-007-9037-0