Summary
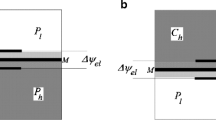
By means of a laser-interferometrical method diffusion layers at the interface of a noncharged cellulose membrane are studied. These layers are induced by a concentration difference between the NaCl solutions separated by the membrane. The temporal and local shift of the NaCl concentration in the diffusion layers were measured. A steady-state concentration profile could be obtained for times of 121 sec≦t 0≦484 sec. The concentration profiles at any time (t 0≦900) are not a linear function of the membrane surface, but could be fitted to a quadratic function. The thickness of the diffusion layers is also a function of time and its stationary value in this system is (575±49)×10−6 m. The role of concentration polarization for the determination of phenomenological thermodynamic coefficients of membranes is discussed and a new method is suggested, which excludes the difficulties of the concentration polarization in the diffusion layers at the membrane.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barry, P.H., Hope, A.B. 1969a. Electroosmosis in membranes: Effects of unstirred layers and transport numbers. I. Theory.Biophys. J. 9:700
Barry, P.H., Hope, A.B. 1969b. Electroosmosis in membranes: Effects of unstirred layers and transport numbers. II. Experimental.Biophys. J. 9:279
Borisova, M.P., Ermishkin, L.N., Liberman, E.A., Silberstein, A.Y., Trofimov, E.M. 1974. Mechanism of conductivity of bimolecular lipid membranes in the presence of tetrachlorotrifluoromethylbenzimidazole.J. Membrane Biol. 18:243
Bressler, E.H., Wendt, R.P., Mason, E.A. 1971. Steady-state sieving across membranes.Science 172:858
Bruner, L., Tolloczko, St. 1900. Über die Auflösegeschwindigkeit fester Körper.Z. Phys. Chem. 35:283
Brunner, E. 1904. Reaktionsgeschwindigkeit in heterogenen Systemen.Z. Phys. Chem. 47:56
Correns, E., Purz, H. J., Schwarz, H. H., Hagen, I. 1971. Verfahren zur Herstellung von Membranen und Flächengebilden aus Bakteriencellulose. GDR-patent, co 8b/157624, Sept. 2, 1971.
Dainty, J. 1963a. Water relations of plant cells.Adv. Bot. Res. 1:279
Dainty, J. 1963b. The polar permeability of plant cell membranes to water.Protoplasma 57:220
Dainty, J., House, C.R. 1966. “Unstirred layers” in frog skin.J. Physiol. (Lond.) 182:66
Dewhurst, D.J. 1960. Concentration polarization in plane membrane-solution systems.Trans. Faraday Soc. 56:599
Everitt, C.T., Haydon, D.A. 1969. Influence of diffusion during osmotic flow across bimolecular lipid membranes.J. Theoret. Biol. 22:9
Gingras, G., Samson, J.P. 1970. The Haxo and Blinks electrode — a mathematical model.Biophys. J. 10:1189
Gitelson, I.I., Fish, A.M. 1969. O “konzentrazionnych jamach” w raspredelenii westschestw w okolokletotschnom prostranstwe.Dokl. Akad. Nauk. SSSR 184:713
Green, K., Otori, T. 1970. Direct measurements of membrane unstirred layers.J. Physiol. (Lond.) 207:93
Grigoryev, P.A., Ermishkin, L.N. 1970. Unstationary voltage current characteristics with negative resistance on artificial membranes.Biofizika 15:1129
Ibl, N. 1962. Applications of mass transfer theory: The formation of powdered metal deposits.In: Advances in electrochemistry and electrochemical engineering. C.W. Tobias, editor. p. 49. Interscience Publishers, New York, London
Kruis, A. 1936. Die Äquivalenzdispersion von starken Elektrolyten in Lösungen.Z. Phys. Chem. 34b:13
Lerche, D. 1974. Untersuchungen zum zeitlichen Verhalten des Konzentrationsprofils in Diffusionsschichten an Membranen. Ph. D. Dissertation, Humboldt-Universität, Berlin
Lerche, D. 1975. Quantitative characterisation of current-induced diffusion layers at cation exchange membranes.J. Bioelectrochem. Bioenerget 2:304
Lerche, D. Becker, R., Falk, M., Fürst, W. 1976. Arzneimittelpermeation durch künstliche Lipoidmembranen. 6. Mitteilung: Untersuchungen zum Auftreten von Diffusionsschichten in Abhängigkeit von der Membranzusammensetzung und den permeierenden Arzneimitteln.Die Pharmazie 2:304
Lerche, D., Kott, M. 1973. Der direkte Nachweis strominduzierter Diffusionsschichten an Epithelgeweben mit Hilfe der Laserinterferometrie.Stud. Biophys. 38:73
Lerche, D., Wolf, H. 1971. Laserinterferometrische Bestimmung der Diffusionsschicht an Ionenaustauschmembranen.Stud. Biophys. 27:189
Lerche, D., Wolf, H. 1974. Direkte quantitative Bestimmung des Konzentrationsverlaufs in Diffusionsschichten an Membranen mit Hilfe der Laserinterferometrie.Z. Phys. Chem. 255:126
Levich, V.G. 1952. Fiziko-chimitscheskaja gidrodinamika. Izdatelstwo Akad. Nauk SSSR, Moskwa
Liberman, E.A., Topaly, V.R., Silberstein, A.Y., Oklobistin, O.Yu. 1971. Mobile carriers and negative membrane resistance. I. Uncouplers of oxidative phosphorylation-proton carriers.Biofizika 16:615
Markin, V.S., Grigoryev, P.A., Ermishkin, L.N. 1971. Direct passage of ions through lipid membranes. I. Mathematical model.Biofizika 16:1011
Miller, D.M. 1972. The effect of unstirred layers on the measurement of transport rates in individual cells.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 266:85
Nernst, W. 1904. Theorie der Reaktionsgeschwindigkeit in heterogenen Systemen.Z. Phys. Chem. 47:52
Schlögl, R. 1971. Selektiver Transport durch biologische und künstliche Membranen.Umschau 71:470
Sonin, A.A., Grossman, G. 1972. Ion transport through layered ion exchange membranes.J. Phys. Chem. 76:3996
Stehle, R.G., Higuchi, W.I. 1972. In vitro model for transport of solutes in three-phase system. II. Experimental considerations.J. Pharm. Sci. 61:1922
van Os, C.M., Slegers, J.F.G. 1973. Path of osmotic water flow through rabbit gall bladder epithelium.Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 291:197
Vetter, K.J. 1961. Elektrochemische Kinetik. Springer-Verlag, Berlin-Göttingen-Heidelberg
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lerche, D. Temporal and local concentration changes in diffusion layers at cellulose membranes due to concentration differences between the solutions on both sides of the membrane. J. Membrain Biol. 27, 193–205 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01869136
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01869136