Abstract
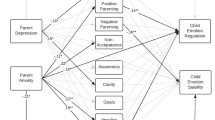
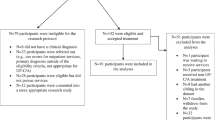
The current multimethod longitudinal study examines how parents’ distress reactions to adolescents’ negative emotions may shape youths’ own perceptions of negative life events and subsequent increases in depressive symptomology. Ninety adolescents (41 girls, 49 boys, average age = 16.5 years old) and their parents were assessed over three timepoints. We found that greater parent-reported distress reactions to adolescents’ emotions predicted subsequent increase in youths’ own self-reported negative reactions to stressful experiences over a two-week period, which in turn predicted steeper increases in youth-reported depressive symptoms across this same two-week period. Moreover, youths’ negative reactions mediated the relation between parent emotion socialization and increases in adolescent depressive symptoms. These findings support the use of interventions that simultaneously target parent and child distress to prevent the onset of adolescent depression.


Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
As adolescent participants and their parents/guardians were specifically asked to report their sex, the term “sex” (which refers to a biological construct) is used throughout the manuscript rather than “gender” (which refers to the social roles associated with sex).
References
Airagnes, G., Lemogne, C., Hoertel, N., Goldberg, M., Limosin, F., & Zins, M. (2016). Childhood adversity and depressive symptoms following retirement in the Gazel cohort. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2016.07.015
Avenevoli, S., Swendsen, J., He, J., Burstein, M., & Merikangas, K. R. (2015). Major depression in the national comorbidity survey–adolescent supplement: Prevalence, correlates, and treatment. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 54(1), 37–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaac.2014.10.010
Bentler, P. M. (1990). Comparative fit indexes in structural models. Psychological Bulletin, 107(2), 238–246. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.107.2.238
Brand, A. E., & Klimes-Dougan, B. (2010). Emotion socialization in adolescence: The roles of mothers and fathers. In A. K. Root & S. A. Denham (Eds.), Focus on gender: Parent and child contributions to the socialization of emotional competence, 2010(128), 85–100. Jossey-Bass.
Brown, C. H., Brincks, A., Huang, S., Perrino, T., Cruden, G., Pantin, H., Howe, G., Young, J. F., Beardslee, W., Montag, S., & Sandler, I. (2018). Two-year impact of prevention programs on adolescent depression: An integrative data analysis approach. Prevention Science, 19(Suppl 1), 74–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-016-0737-1
Browne, M. W., & Cudeck, R. (1993). Alternative ways of assessing model fit. In K. A. Bollen & J. S. Long (Eds.), Testing structural equation models (pp. 136–162). Sage.
Buckholdt, K. E., Parra, G. R., & Jobe-Shields, L. (2014). Intergenerational transmission of emotion dysregulation through parental invalidation of emotions: Implications for adolescent internalizing and externalizing behaviors. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 23(2), 324–332. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-013-9768-4
Calvete, E., Fernández-Gonzalez, L., Orue, I., Echezarraga, A., Royuela-Colomer, E., Cortazar, N., Muga, J., Longa, M., & Yeager, D. S. (2019). The effect of an intervention teaching adolescents that people can change on depressive symptoms, cognitive schemas, and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis hormones. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 47(9), 1533–1546. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-019-00538-1
Chan, M. H., Feng, X., Inboden, K., Hooper, E. G., & Gerhardt, M. (2021). Dynamic, bidirectional influences of children’s emotions and maternal regulatory strategies. Emotion. https://doi.org/10.1037/emo0001005
Chorpita, B. F., Moffitt, C. E., & Gray, J. (2005). Psychometric properties of the Revised Child Anxiety and Depression Scale in a clinical sample. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 43(3), 309–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brat.2004.02.004
Chorpita, B. F., Yim, L., Moffitt, C., Umemoto, L. A., & Francis, S. E. (2000). Assessment of symptoms of DSM-IV anxiety and depression in children: A revised child anxiety and depression scale. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 38(8), 835–855. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0005-7967(99)00130-8
Chronis-Tuscano, A., Bui, H., & Lorenzo, N. E. (2021). Transdiagnostic Implications of Parental Socialization of Child and Adolescent Emotional Development: Commentary and Future Directions. Research on child and adolescent psychopathology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-021-00872-3. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-021-00872-3
Chronis-Tuscano, A., Clarke, T. L., O’Brien, K. A., Raggi, V. L., Diaz, Y., Mintz, A. D., & Seeley, J. (2013). Development and preliminary evaluation of an integrated treatment targeting parenting and depressive symptoms in mothers of children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 81(5), 918.
Cole, D. A., Ciesla, J. A., & Steiger, J. H. (2007). The insidious effects of failing to include design-driven correlated residuals in latent-variable covariance structure analysis. Psychological Methods, 12(4), 381.
Compas, B. E., Davis, G. E., Forsythe, C. J., & Wagner, B. M. (1987). Assessment of major and daily stressful events during adolescence: The Adolescent Perceived Events Scale. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 55(4), 534–541. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-006X.55.4.534
Compas, B. E., Howell, D. C., Phares, V., Williams, R. A., & Giunta, C. T. (1989). Risk factors for emotional/behavioral problems in young adolescents: A prospective analysis of adolescent and parental stress and symptoms. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 57(6), 732–740. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-006X.57.6.732
Costello, E. J., Erkanli, A., & Angold, A. (2006). Is there an epidemic of child or adolescent depression? Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 47(12), 1263–1271.
Cummings, E. M., George, M. R. W., Koss, K. J., & Davies, P. T. (2013). Parental depressive symptoms and adolescent adjustment: Responses to children’s distress and representations of attachment as explanatory mechanisms. Parenting: Science and Practice, 13(4), 213–232. https://doi.org/10.1080/15295192.2013.832568
Daughters, S. B., Gorka, S. M., Rutherford, H. J. V., & Mayes, L. C. (2014). Maternal and adolescent distress tolerance: The moderating role of gender. Emotion, 14(2), 416–424. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0034991
Deal, S. L., & Williams, J. E. (1988). Cognitive distortions as mediators between life stress and depression in adolescents. Adolescence, 23(90), 477–490.
Desjardins, T. L., & Leadbeater, B. J. (2011). Relational victimization and depressive symptoms in adolescence: Moderating effects of mother, father, and peer emotional support. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 40(5), 531–544. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-010-9562-1
Ehrlich, K. B., Cassidy, J., Lejuez, C. W., & Daughters, S. (2014). Discrepancies about adolescent relationships as a function of informant attachment and depressive symptoms. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 24, 654–666. https://doi.org/10.1111/jora.12057
Eisenberg, N., Cumberland, A., & Spinrad, T. L. (1998). Parental socialization of emotion. Psychological Inquiry, 9(4), 241–273. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15327965pli0904_1
Eisenberg, N., Fabes, R. A., Shepard, S. A., Guthrie, I. K., Murphy, B. C., & Reiser, M. (1999). Parental reactions to children’s negative emotions: Longitudinal relations to quality of children’s social functioning. Child Development, 70(2), 513–534. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8624.00037
Fabes, R. A., Eisenberg, N., & Bernzweig, J. (1990). Coping with Children’s Negative Emotions Scale (CCNES): Description and scoring. Arizona State University.
Fabes, R. A., Poulin, R. E., Eisenberg, N., & Madden-Derdich, D. A. (2002). The Coping with Children’s Negative Emotions Scale (CCNES): Psychometric properties and relations with children’s emotional competence. Marriage & Family Review, 34(3–4), 285–310. https://doi.org/10.1300/J002v34n03_05
Faro, A. L., McKee, L. G., Garcia, R. L., & O’Leary, J. L. (2019). Emotion socialization, social connectedness and internalizing symptoms in emerging adults. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appdev.2019.101051
Feiring, C., Taska, L., & Lewis, M. (1999). Age and gender differences in children’s and adolescents’ adaptation to sexual abuse. Child Abuse & Neglect, 23(2), 115–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0145-2134(98)00116-1
Felton, J. W., Collado, A., Havewala, M., Shadur, J. M., MacPherson, L., & Lejuez, C. W. (2019). Distress tolerance interacts with negative life events to predict depressive symptoms across adolescence. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 48(4), 633–642. https://doi.org/10.1080/15374416.2017.1405354
Felton, J. W., Kofler, M. J., Lopez, C. M., Saunders, B. E., & Kilpatrick, D. G. (2015). The emergence of cooccurring adolescent drug use and depressive symptoms: A latent growth modeling approach. Development and Psychopathology, 27(4 Pt 1), 1367–1383. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954579414001473
Felton, J. W., Schwartz, K., Oddo, L. E., Lejuez, C. W., & Chronis-Tuscano, A. (2021). Transactional patterns of depressive symptoms between mothers and adolescents: The role of emotion regulation. Depression and anxiety. https://doi.org/10.1002/da.23225. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1002/da.23225
Fox, A. R., Aldrich, J. T., Ahles, J. J., & Mezulis, A. H. (2019). Stress and parenting predict changes in adolescent respiratory sinus arrhythmia. Developmental Psychobiology, 61(8), 1214–1224. https://doi.org/10.1002/dev.21863
Goodman, S. H. (2020). Intergenerational transmission of depression. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 16.
Halberstadt, A. G. (1991). Toward an ecology of expressiveness: Family socialization in particular and a model in general. In R. S. Feldman & B. Rimé (Eds.), Studies in emotion & social interaction. Fundamentals of nonverbal behavior (p. 106–160). Cambridge University Press; Editions de la Maison des Sciences de l'Homme.
Hankin, B. L., & Abramson, L. Y. (2001). Development of gender differences in depression: An elaborated cognitive vulnerability–transactional stress theory. Psychological Bulletin, 127(6), 773–796. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.127.6.773
Hastings, P. D., Klimes-Dougan, B., Kendziora, K. T., Brand, A., & Zahn-Waxler, C. (2014). Regulating sadness and fear from outside and within: Mothers’ emotion socialization and adolescents’ parasympathetic regulation predict the development of internalizing difficulties. Development and Psychopathology, 26(4, Pt 2), 1369–1384. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954579414001084
Havighurst, S. S., Wilson, K. R., Harley, A. E., & Prior, M. R. (2009). Tuning in to kids: An emotion-focused parenting program—initial findings from a community trial. Journal of Community Psychology, 37(8), 1008–1023. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcop.20345
Hilt, L., & Nolen-Hoeksema, S. (2009). The emergence of gender differences in depression in adolescence. Em L. Hilt, & S. Nolen-Hoeksema, Handbook of Depression in Adolescents (pp. 111–126). New York: Routledge.
Ho, T. C. (2019). Stress and neurodevelopment in adolescent depression. Biological Psychiatry, 86(10), e33–e35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2019.09.012
Hu, L.-T., & Bentler, P. M. (1999). Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Structural Equation Modeling, 6(1), 1–55. https://doi.org/10.1080/10705519909540118
Johnson, J. G., Cohen, P., & Kasen, S. (2009). Minor depression during adolescence and mental health outcomes during adulthood. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 195(3), 264–265. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.bp.108.054239
Katz, L. F., Shortt, J. W., Allen, N. B., Davis, B., Hunter, E., Leve, C., & Sheeber, L. (2014). Parental emotion socialization in clinically depressed adolescents: Enhancing and dampening positive affect. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 42(2), 205–215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-013-9784-2
Kerns, C. E., Pincus, D. B., McLaughlin, K. A., & Comer, J. S. (2017). Maternal emotion regulation during child distress, child anxiety accommodation, and links between maternal and child anxiety. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 50, 52–59.
Klimes-Dougan, B., Brand, A. E., Zahn-Waxler, C., Usher, B., Hastings, P. D., Kendziora, K., & Garside, R. B. (2007). Parental emotion socialization in adolescence: Differences in sex, age and problem status. Social Development, 16(2), 326–342. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9507.2007.00387.x
Lewinsohn, P. M., Seeley, J. R., Roberts, R. E., & Allen, N. B. (1997). Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CES-D) as a screening instrument for depression among community-residing older adults. Psychology and Aging, 12(2), 277–287. https://doi.org/10.1037/0882-7974.12.2.277
Little, R. J., & Rubin, D. B. (1987). Statistical analysis with missing data. John Wiley and Sons.
Maccoby, E. E., & Martin, J. A. (1983). Socialization in the context of the family: Parent-child interaction. In P. H. Mussen (Ed.), Handbook of child psychology, 4 (pp. 1–101). Wiley.
Martin, C. G., Kim, H. K., & Freyd, J. J. (2018). In the spirit of full disclosure: Maternal distress, emotion validation, and adolescent disclosure of distressing experiences. Emotion, 18(3), 400–411. https://doi.org/10.1037/emo0000363. (Supplemental).
Mason, W. A., Chmelka, M. B., Trudeau, L., & Spoth, R. L. (2017). Gender moderation of the intergenerational transmission and stability of depressive symptoms from early adolescence to early adulthood. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 46(1), 248–260.
Matta, J., Hoertel, N., Kesse-Guyot, E., Plesz, M., Wiernik, E., Carette, C., Czernichow, S., Limosin, F., Goldberg, M., Zins, M., & Lemogne, C. (2019). Diet and physical activity in the association between depression and metabolic syndrome: Constances study. Journal of Affective Disorders, 244, 25–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2018.09.072
Maxwell, S. E., Lau, M. Y., & Howard, G. S. (2015). Is psychology suffering from a replication crisis? What does “failure to replicate” really mean? American Psychologist, 70(6), 487.
McMahon, S. D., Grant, K. E., Compas, B. E., Thurm, A. E., & Ey, S. (2003). Stress and psychopathology in children and adolescents: Is there evidence of specificity? Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines, 44, 107–133.
Monroe, S. M., & Simons, A. D. (1991). Diathesis-stress theories in the context of life stress research: Implications for the depressive disorders. Psychological Bulletin, 110(3), 406–425. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.110.3.406
Morris, A. S., Criss, M. M., Silk, J. S., & Houltberg, B. J. (2017). The impact of parenting on emotion regulation during childhood and adolescence. Child Development Perspectives, 11(4), 233–238.
Morris, A. S., Silk, J. S., Steinberg, L., Myers, S. S., & Robinson, L. R. (2007). The role of the family context in the development of emotion regulation. Social Development, 16(2), 361–388. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9507.2007.00389.x
Muthén, L. K., & Muthén, B. O. (2010). Mplus User’s Guide (6th ed.). Muthén & Muthén.
Newcomb, M. D., & Harlow, L. L. (1986). Life events and substance use among adolescents: Mediating effects of perceived loss of control and meaninglessness in life. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 51(3), 564–577. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.51.3.564
Park, S.-Y., Trommsdorff, G., & Lee, E. G. (2012). Korean mothers’ intuitive theories regarding emotion socialization of their children. International Journal of Human Ecology, 13, 39–56. https://doi.org/10.6115/ijhe.2012.13.1.39
Powers, A., & Casey, B. J. (2015). The adolescent brain and the emergence and peak of psychopathology. Journal of Infant, Child & Adolescent Psychotherapy, 14(1), 3–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/15289168.2015.1004889
Preacher, K. J., & Hayes, A. F. (2008). Asymptotic and resampling strategies for assessing and comparing indirect effects in multiple mediator models. Behavior Research Methods, 40(3), 879–891. https://doi.org/10.3758/BRM.40.3.879
Radloff, L. S. (1977). The CES-D scale: A self report depression scale for research in the general population. Applied Psychological Measurement, 1, 385–401.
Remmes, C. S., & Ehrenreich-May, J. (2014). Parental emotion regulation strategy use and responses to youth negative affect. Journal of Cognitive Psychotherapy, 28(1), 34–47. https://doi.org/10.1891/0889-8391.28.1.34
Schleider, J. L., Chorpita, B. F., & Weisz, J. R. (2014). Relation between parent psychiatric symptoms and youth problems: Moderation through family structure and youth gender. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 42(2), 195–204.
Schwartz, O. S., Sheeber, L. B., Dudgeon, P., & Allen, N. B. (2012). Emotion socialization within the family environment and adolescent depression. Clinical Psychology Review, 32(6), 447–453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2012.05.002
Schwartz, O. S., Simmons, J. G., Whittle, S., Byrne, M. L., Yap, M. B. H., Sheeber, L. B., & Allen, N. B. (2017). Affective parenting behaviors, adolescent depression, and brain development: A review of findings from the orygen adolescent development study. Child Development Perspectives, 11(2), 90–96. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdep.12215
Shadur, J. M., & Hussong, A. M. (2019). Conceptualization and measurement of parent emotion socialization among mothers in substance abuse treatment. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 28(2), 325–342. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-018-1269-z
Shadur, J., & Lejuez, C. W. (2015). Adolescent substance use and comorbid psychopathology: Emotion regulation deficits as a transdiagnostic risk factor. Current Addiction Reports (topical Collection on Transgenerational Considerations in Addictions), 2(4), 354–363. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40429-015-0070-y
Shaffer, A., Suveg, C., Thomassin, K., & Bradbury, L. L. (2012). Emotion socialization in the context of family risks: Links to child emotion regulation. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 21(6), 917–924. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-011-9551-3
Shirk, S. R., Crisostomo, P. S., Jungbluth, N., & Gudmundsen, G. R. (2013). Cognitive mechanisms of change in CBT for adolescent depression: Associations among client involvement, cognitive distortions, and treatment outcome. International Journal of Cognitive Therapy, 6(4), 311–324. https://doi.org/10.1521/ijct.2013.6.4.311
Shore, L., Toumbourou, J. W., Lewis, A. J., & Kremer, P. (2018). Longitudinal trajectories of child and adolescent depressive symptoms and their predictors–a systematic review and meta-analysis. Child and Adolescent Mental Health, 23(2), 107–120.
Shortt, A. L., & Spence, S. H. (2006). Risk and Protective Factors for Depression in Youth. Behaviour Change, 23(1), 1–30. https://doi.org/10.1375/bech.23.1.1
Silk, J. S. (2019). Context and dynamics: The new frontier for developmental research on emotion regulation. Developmental Psychology, 55(9), 2009–2014. https://doi.org/10.1037/dev0000768
Silk, J. S., Shaw, D. S., Prout, J. T., O’Rourke, F., Lane, T. J., & Kovacs, M. (2011). Socialization of emotion and offspring internalizing symptoms in mothers with childhood-onset depression. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 32(3), 127–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appdev.2011.02.001
Slavich, G. M., Stewart, J. G., Esposito, E. C., Shields, G. S., & Auerbach, R. P. (2019). The stress and Adversity Inventory for Adolescents (Adolescent STRAIN): Associations with mental and physical health, risky behaviors, and psychiatric diagnoses in youth seeking treatment. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 60(9), 998–1009.
Steiger, J. H. (1990). Structural model evaluation and modification: An interval estimation approach. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 25, 173–180.
Suveg, C., Shaffer, A., Morelen, D., & Thomassin, K. (2011). Links between maternal and child psychopathology symptoms: Mediation through child emotion regulation and moderation through maternal behavior. Child Psychiatry and Human Development, 42(5), 507–520. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-011-0223-8
Tucker, L. R., & Lewis, C. (1973). A reliability coefficient for maximum likelihood factor analysis. Psychometrika, 38(1), 1–10
Weersing, V. R., Jeffreys, M., Do, M.-C.T., Schwartz, K. T. G., & Bolano, C. (2017). Evidence base update of psychosocial treatments for child and adolescent depression. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 46(1), 11–43. https://doi.org/10.1080/15374416.2016.1220310
Wild, L. G., Flisher, A. J., & Lombard, C. (2004). Suicidal ideation and attempts in adolescents: Associations with depression and six domains of self-esteem. Journal of Adolescence, 27(6), 611–624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adolescence.2004.03.001
Zeman, J., Cassano, M., & Adrian, M. (2013). Socialization influences on children’s and adolescent’s emotional self-regulation processes: A developmental psychopathology perspective. In K. C. Barrett, N. A. Fox, G. A. Morgan, D. J. Fidler, & L. A. Daunhauer (Eds.), Handbook of self-regulatory processes in development: New directions and international perspectives (pp. 79–106). Psychology Press.
Funding
This project was supported in part by a grant from the National Institute on Drug Abuse (R01 DA18647) awarded to Carl W. Lejuez and by a Dean’s Research Initiative grant through the College of Behavioral & Social Sciences at the University of Maryland award to Julia W. Felton.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in the study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments.
Conflict of Interest
Julia W. Felton, Julia M. Shadur, Mazneen Havewala, Jude Cassidy, Carl W. Lejuez and Andrea Chronis-Tuscano declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Informed Consent
Informed consent and assent was obtained from all participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Felton, J.W., Shadur, J.M., Havewala, M. et al. Specific Pathways from Parental Distress Reactions to Adolescent Depressive Symptoms: The Mediating Role of Youths’ Reactions to Negative Life Events. J Psychopathol Behav Assess 44, 750–762 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10862-022-09954-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10862-022-09954-y