Abstract
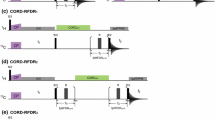
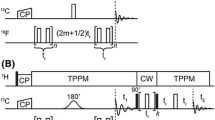
Magic angle spinning (MAS) solid-state NMR (ssNMR) spectroscopy is a major technique for the characterization of the structural dynamics of biopolymers at atomic resolution. However, the intrinsic low sensitivity of this technique poses significant limitations to its routine application in structural biology. Here we achieve substantial savings in experimental time using a new subclass of Polarization Optimized Experiments (POEs) that concatenate TEDOR and SPECIFIC-CP transfers into a single pulse sequence. Specifically, we designed new 2D and 3D experiments (2D TEDOR-NCX, 3D TEDOR-NCOCX, and 3D TEDOR-NCACX) to obtain distance measurements and heteronuclear chemical shift correlations for resonance assignments using only one experiment. We successfully tested these experiments on N-Acetyl-Val-Leu dipeptide, microcrystalline U-13C,15N ubiquitin, and single- and multi-span membrane proteins reconstituted in lipid membranes. These pulse sequences can be implemented on any ssNMR spectrometer equipped with standard solid-state hardware using only one receiver. Since these new POEs speed up data acquisition considerably, we anticipate their broad application to fibrillar, microcrystalline, and membrane-bound proteins.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ader C et al (2009) Structural rearrangements of membrane proteins probed by water-edited solid-state NMR spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc 131:170–176
Andreas LB, Le Marchand T, Jaudzems K, Pintacuda G (2015) High-resolution proton-detected NMR of proteins at very fast MAS. J Magn Reson 253:36–49
Andrew W, Hing S, Schaefer J (1992) Transferred-echo double-resonance NMR. J Magn Reson 96:205–209
Baldus M, Petkova AT, Herzfeld J, Griffin RG (1998) Cross polarization in the tilted frame: assignment and spectral simplification in heteronuclear spin systems. Mol Phys 95:1197–1207
Banigan JR, Traaseth NJ (2012) Utilizing afterglow magnetization from cross-polarization magic-angle-spinning solid-state NMR spectroscopy to obtain simultaneous heteronuclear multidimensional spectra. J Phys Chem B 116:7138–7144
Barnes AB et al (2008) High-field dynamic nuclear polarization for solid and solution biological NMR. Appl Magn Reson 34:237–263
Bellstedt P et al (2012) Solid state NMR of proteins at high MAS frequencies: symmetry-based mixing and simultaneous acquisition of chemical shift correlation spectra. J Biomol NMR 54:325–335
Buck B et al (2003) Overexpression, purification, and characterization of recombinant Ca-ATPase regulators for high-resolution solution and solid-state NMR studies. Protein Expr Purif 30:253–261
Castellani F et al (2002) Structure of a protein determined by solid-state magic-angle-spinning NMR spectroscopy. Nature 420:98–102
Das BB, Opella SJ (2016) Simultaneous cross polarization to (13)C and (15)N with (1)H detection at 60 kHz MAS solid-state NMR. J Magn Reson 262:20–26
Daviso E, Eddy MT, Andreas LB, Griffin RG, Herzfeld J (2013) Efficient resonance assignment of proteins in MAS NMR by simultaneous intra- and inter-residue 3D correlation spectroscopy. J Biomol NMR 55:257–265
Demers JP, Chevelkov V, Lange A (2011) Progress in correlation spectroscopy at ultra-fast magic-angle spinning: Basic building blocks and complex experiments for the study of protein structure and dynamics. Solid State Nucl Magn Reson 40:101–113
Ekanayake EV, Fu R, Cross TA (2016) Structural influences: cholesterol, drug, and proton binding to full-length influenza A M2 protein. Biophys J 110:1391–1399
Franks WT, Kloepper KD, Wylie BJ, Rienstra CM (2007) Four-dimensional heteronuclear correlation experiments for chemical shift assignment of solid proteins. J Biomol NMR 39:107–131
Fung BM, Khitrin AK, Ermolaev K (2000) An improved broadband decoupling sequence for liquid crystals and solids. J Magn Reson 142:97–101
Gopinath T, Veglia G (2009) Sensitivity enhancement in static solid-state NMR experiments via single- and multiple-quantum dipolar coherences. J Am Chem Soc 131:5754–5756
Gopinath T, Veglia G (2012a) Dual acquisition magic-angle spinning solid-state NMR-spectroscopy: simultaneous acquisition of multidimensional spectra of biomacromolecules. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 51:2731–2735
Gopinath T, Veglia G (2012b) 3D DUMAS: simultaneous acquisition of three-dimensional magic angle spinning solid-state NMR experiments of proteins. J Magn Reson 220:79–84
Gopinath T, Veglia G (2013) Orphan spin operators enable the acquisition of multiple 2D and 3D magic angle spinning solid-state NMR spectra. J Chem Phys 138:184201
Gopinath T, Veglia G (2015) Multiple acquisition of magic angle spinning solid-state NMR experiments using one receiver: application to microcrystalline and membrane protein preparations. J Magn Reson 253:143–153
Gopinath T, Veglia G (2016a) Multiple acquisitions via sequential transfer of orphan spin polarization (MAeSTOSO): How far can we push residual spin polarization in solid-state NMR? J Magn Reson 267:1–8
Gopinath T, Veglia G (2016b) Orphan spin polarization: A catalyst for high-throughput solid-state NMR spectroscopy of proteins. Ann Rep NMR Spectrosc 89:103–121
Gopinath T, Veglia G (2018) Experimental aspects of polarization optimized experiments (POE) for magic angle spinning solid-state NMR of microcrystalline and membrane-bound proteins. Methods Mol Biol 1688:37–53
Gopinath T, Mote KR, Veglia G (2011) Proton evolved local field solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance using Hadamard encoding: theory and application to membrane proteins. J Chem Phys 135:074503
Gor’kov PL et al (2007) Using low-E resonators to reduce RF heating in biological samples for static solid-state NMR up to 900 MHz. J Magn Reson 185:77–93
Gullion T, Schaefer J (1989) Development of REDOR rotational-echo double-resonance NMR. J Magn Reson 81:196
Gullion T, Baker DB, Conradi MS (1990) New, compensated Carr-Purcell sequences. J Magn Reson 89:479–484
Gustavsson M et al (2013) Allosteric regulation of SERCA by phosphorylation-mediated conformational shift of phospholamban. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:17338–17343
Hartmann SR, Hahn EL (1962) Nuclear double resonance in the rotating frame. Phys Rev 128:2042–2053
Hing AW, Schaefer J (1993) Two-dimensional rotational-echo double resonance of Val1-[1-13C]Gly2-[15N]Ala3-gramicidin A in multilamellar dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine dispersions. Biochemistry 32:7593–7604
Hong M, Griffin RG (1998) Resonance assignments for solid peptides by dipolar-mediated C-13/N-15 correlation solid-state NMR. J Am Chem Soc 120:7113–7114
Hong M, Zhang Y, Hu F (2012) Membrane protein structure and dynamics from NMR spectroscopy. Annu Rev Phys Chem 63:1–24
Hu F, Luo W, Hong M (2010) Mechanisms of proton conduction and gating in influenza M2 proton channels from solid-state NMR. Science 330:505–508
Igumenova TI et al (2004) Assignments of carbon NMR resonances for microcrystalline ubiquitin. J Am Chem Soc 126:6720–6727
Jain S, Bjerring M, Nielsen NC (2012) Efficient and robust heteronuclear cross-polarization for high-speed-spinning biological solid-state NMR spectroscopy. J Phys Chem Lett 3:703–708
Jaroniec CP, Filip C, Griffin RG (2002) 3D TEDOR NMR experiments for the simultaneous measurement of multiple carbon–nitrogen distances in uniformly (13)C,(15)N-labeled solids. J Am Chem Soc 124:10728–10742
Manu VS, Veglia G (2016) Optimization of identity operation in NMR spectroscopy via genetic algorithm: application to the TEDOR experiment. J Magn Reson 273:40–46
McNeill SA, Gor’kov PL, Shetty K, Brey WW, Long JR (2009) A low-E magic angle spinning probe for biological solid state NMR at 750 MHz. J Magn Reson 197:135–144
Mote KR, Gopinath T, Veglia G (2013) Determination of structural topology of a membrane protein in lipid bilayers using polarization optimized experiments (POE) for static and MAS solid state NMR spectroscopy. J Biomol NMR 57:91–102
Paulson EK, Martin RW, Zilm KW (2004) Cross polarization, radio frequency field homogeneity, and circuit balancing in high field solid state NMR probes. J Magn Reson 171:314–323
Pines A, Waugh JS, Gibby MG (1972) Proton-enhanced nuclear induction spectroscopy—method for high-resolution NMR of dilute spins in solids. J Chem Phys 56:1776
Qiu B et al (2018) Succinate–acetate permease from Citrobacter koseri is an anion channel that unidirectionally translocates acetate. Cell Res 28:644–654
Reif B (2012) Ultra-high resolution in MAS solid-state NMR of perdeuterated proteins: implications for structure and dynamics. J Magn Reson 216:1–12
Rienstra CM et al (2002) De novo determination of peptide structure with solid-state magic-angle spinning NMR spectroscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:10260–10265
Sa-Pessoa J et al (2013) SATP (YaaH), a succinate–acetate transporter protein in Escherichia coli. Biochem J 454:585–595
Sharma K, Madhu PK, Mote KR (2016) A suite of pulse sequences based on multiple sequential acquisitions at one and two radiofrequency channels for solid-state magic-angle spinning NMR studies of proteins. J Biomol NMR 65:127–141
Stringer JA et al (2005) Reduction of RF-induced sample heating with a scroll coil resonator structure for solid-state NMR probes. J Magn Reson 173:40–48
Struppe J et al (2017) Expanding the horizons for structural analysis of fully protonated protein assemblies by NMR spectroscopy at MAS frequencies above 100 kHz. Solid State Nucl Magn Reson 87:117–125
Sun P et al. (2018) Crystal structure of the bacterial acetate transporter SatP reveals that it forms a hexameric channel. J Biol Chem 293:19492–19500
Takegoshi KN, S; and Terao T (2001) 13C–1H dipolar-assisted rotational resonance in magic-angle spinning NMR. Chem Phys Lett 344:631–637
Tang W, Nevzorov AA (2011) Repetitive cross-polarization contacts via equilibration-re-equilibration of the proton bath: sensitivity enhancement for NMR of membrane proteins reconstituted in magnetically aligned bicelles. J Magn Reson 212:245–248
Tekely P, Goldman M (2001) Radial-field sidebands in MAS. J Magn Reson 148:135–141
Tosner Z et al (2017) Radiofrequency fields in MAS solid state NMR probes. J Magn Reson 284:20–32
Tosner Z et al (2018) Overcoming volume selectivity of dipolar recoupling in biological solid-state NMR spectroscopy. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 57:14514–14518
Traaseth NJ et al (2008) Structural and dynamic basis of phospholamban and sarcolipin inhibition of Ca(2+)-ATPase. Biochemistry 47:3–13
Wang S, Ladizhansky V (2014) Recent advances in magic angle spinning solid state NMR of membrane proteins. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc 82C:1–26
Wang S et al (2015) Nano-mole scale sequential signal assignment by (1)H-detected protein solid-state NMR. Chem Commun 51:15055–15058
Wickramasinghe NP et al (2009) Nanomole-scale protein solid-state NMR by breaking intrinsic 1HT1 boundaries. Nat Methods 6:215–218
Zhang Y et al (2010) Resonance assignment and three-dimensional structure determination of a human alpha-defensin, HNP-1, by solid-state NMR. J Mol Biol 397:408–422
Zhang R, Mroue KH, Ramamoorthy A (2017) Proton-based ultrafast magic angle spinning solid-state NMR spectroscopy. Acc Chem Res 50:1105–1113
Zhou DH et al (2007) Proton-detected solid-state nmr spectroscopy of fully protonated proteins at 40 kHz magic-angle spinning. J Am Chem Soc 129:11791–11801
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Institute of Health (GM 64742 to G.V. and R35 GM118047 to H.A.). Many thanks to Dr. D. Weber for critical reading and editing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gopinath, T., Wang, S., Lee, J. et al. Hybridization of TEDOR and NCX MAS solid-state NMR experiments for simultaneous acquisition of heteronuclear correlation spectra and distance measurements. J Biomol NMR 73, 141–153 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-019-00237-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-019-00237-5