Abstract
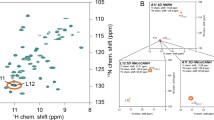
The ability to simultaneously measure many long-range distances is critical to efficient and accurate determination of protein structures by solid-state NMR (SSNMR). So far, the most common distance constraints for proteins are 13C–15N distances, which are usually measured using the rotational-echo double-resonance (REDOR) technique. However, these measurements are restricted to distances of up to ~ 5 Å due to the low gyromagnetic ratios of 15N and 13C. Here we present a robust 2D 13C–19F REDOR experiment to measure multiple distances to ~ 10 Å. The technique targets proteins that contain a small number of recombinantly or synthetically incorporated fluorines. The 13C–19F REDOR sequence is combined with 2D 13C–13C correlation to resolve multiple distances in highly 13C-labeled proteins. We show that, at the high magnetic fields which are important for obtaining well resolved 13C spectra, the deleterious effect of the large 19F chemical shift anisotropy for REDOR is ameliorated by fast magic-angle spinning and is further taken into account in numerical simulations. We demonstrate this 2D 13C–13C resolved 13C–19F REDOR technique on 13C, 15N-labeled GB1. A 5-19F-Trp tagged GB1 sample shows the extraction of distances to a single fluorine atom, while a 3-19F-Tyr labeled GB1 sample allows us to evaluate the effects of multi-spin coupling and statistical 19F labeling on distance measurement. Finally, we apply this 2D REDOR experiment to membrane-bound influenza B M2 transmembrane peptide, and show that the distance between the proton-selective histidine residue and the gating tryptophan residue differs from the distances in the solution NMR structure of detergent-bound BM2. This 2D 13C–19F REDOR technique should facilitate SSNMR-based protein structure determination by increasing the measurable distances to the ~ 10 Å range.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bak M, Nielsen NC (1997) REPULSION, a novel approach to efficient powder averaging in solid-state NMR. J Magn Reson 125:132–139
Bak M, Rasmussen JT, Nielsen NC (2000) SIMPSON: a general simulation program for solid-state NMR spectroscopy. J Magn Reson 147:296–330
Bennett AE, Rienstra CM, Auger M, Lakshmi KV, Griffin RG (1995) Heteronuclear decoupling in rotating solids. J Chem Phys 103:6951–6958
Bennett AE, Rienstra CM, Griffiths JM, Zhen WG, Lansbury PT, Griffin RG (1998) Homonuclear radio frequency-driven recoupling in rotating solids. J Chem Phys 108:9463–9479
Cady SD, Wang T, Hong M (2011) Membrane-dependent effects of a cytoplasmic helix on the structure and drug binding of the influenza virus M2 protein. J Am Chem Soc 133:11572–11579
Cegelski L (2013) REDOR NMR for drug discovery. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 23:5767–5775
Dürr HN, Grage SL, Witter R, Ulrich AS (2008) Solid state 19F NMR parameters of fluorine-labeled amino acids. Part I: aromatic substituents. J Magn Reson 191:7–15
Franks WT et al (2005) Magic-angle spinning solid-state NMR spectroscopy of the beta 1 immunoglobulin binding domain of protein G (GB1): N-15 and C-13 chemical shift assignments and conformational analysis. J Am Chem Soc 127:12291–12305
Ghosh M, Rienstra CM (2017) H-1-detected REDOR with fast magic-angle spinning of a deuterated protein. J Phys Chem B 121:8503–8511
Goetz JM et al (1999) Investigation of the binding of fluorolumazines to the 1-MDa capsid of lumazine synthase by 15N{19F} REDOR NMR. J Am Chem Soc 121:7500–7508
Graesser DT, Wylie BJ, Nieuwkoop AJ, Franks WT, Rienstra CM (2007) Long-range F-19-N-15 distance measurements in highly-C-13, N-15-enriched solid proteins with F-19-dephased REDOR shift (FRESH) spectroscopy. Magn Reson Chem 45:S129–S134
Gullion T, Schaefer J (1989) Rotational-echo double-resonance NMR. J Magn Reson 81:196–200
Hong M, Griffin RG (1998) Resonance assignment for solid peptides by dipolar-mediated 13C/15N correlation solid-state NMR. J Am Chem Soc 120:7113–7114
Hong M, Schmidt-Rohr K (2013) Magic-angle-spinning NMR techniques for measuring long-range distances in biological macromolecules. Acc Chem Res 46:2154–2163
Jaroniec CP, Tounge BA, Rienstra CM, Herzfeld J, Griffin RG (2000) Recoupling of heteronuclear dipolar interactions with rotational-echo double-resonance at high magic-angle spinning frequencies. J Magn Reson 146:132–139
Kim SJ, Cegelski L, Preobrazhenskaya M, Schaefer J (2006) Structures of Staphylococcus aureus cell-wall complexes with vancomycin, eremomycin, and chloroeremomycin derivatives by 13C{19F} and 15N{19F} rotational-echo double resonance. Biochemistry 45:5235–5250
Lehninger AL, Nelson DL, Cox MM (1993) Principles of biochemistry, 2nd edn. Worth Publishers, New York
Luo W, Cady SD, Hong M (2009) Immobilization of the influenza A M2 transmembrane peptide in virus-envelope mimetic lipid membranes: a solid-state NMR investigation. Biochemistry 48:6361–6368
Mani R, Cady SD, Tang M, Waring AJ, Lehrer RI, Hong M (2006a) Membrane-dependent oligomeric structure and pore formation of a beta-hairpin antimicrobial peptide in lipid bilayers from solid-state NMR. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:16242–16247
Mani R, Tang M, Wu X, Buffy JJ, Waring AJ, Sherman MA, Hong M (2006b) Membrane-bound dimer structure of a β-hairpin antimicrobial peptide from rotational-echo double-resonance solid-state NMR. Biochemistry 45:8341–8349
Pan Y, Gullion T, Schaefer J (1990) Determination of C-N internuclear distances by rotational-echo double-resonance NMR of solids. J Magn Reson 90:330
Ravichandran KR, Liang L, Stubbe J, Tommos C (2013) Formal reduction potential of 3,5-difluorotyrosine in a structured protein: insight into multistep radical transfer. Biochemistry 52:8907–8915
Rienstra CM et al (2002) De novo determination of peptide structure with solid-state magic-angle spinning NMR spectroscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:10260–10265
Roos M, Wang T, Shcherbakov AA, Hong M (2018) Fast magic-angle-spinning F-19 spin exchange NMR for determining nanometer distances in proteins and pharmaceutical compounds. J Phys Chem B 122:2900–2911
Sack II, Goldbourt A, Vega S, Buntkowsky G (1999) Deuterium REDOR: principles and applications for distance measurements. J Magn Reson 138:54–65
Sinha N, Hong M (2003) X-1H rotational-echo double-resonance NMR for torsion angle determination of peptides. Chem Phys Lett 380:742–748
Sinha N, Schmidt-Rohr K, Hong M (2004) Compensation for pulse imperfections in rotational-echo double-resonance NMR by composite pulses and EXORCYCLE. J Magn Reson 168:358–365
Tang M, Waring AJ, Hong M (2007) Phosphate-mediated arginine insertion into lipid membranes and pore formation by a cationic membrane peptide from solid-state NMR. J Am Chem Soc 129:11438–11446
Wang J, Pielak RM, McClintock MA, Chou JJ (2009) Solution structure and functional analysis of the influenza B proton channel. Nat Struct Mol Biol 16:1267–1271
Wi S, Sinha N, Hong M (2004) Long-range 1H-19F distance measurement in peptides by solid-state NMR. J Am Chem Soc 126:12754–12755
Williams JK, Tietze D, Lee M, Wang J, Hong M (2016) Solid-state NMR investigation of the conformation, proton conduction, and hydration of the influenza B virus M2 transmembrane proton channel. J Am Chem Soc 138:8143–8155
Williams JK, Shcherbakov AA, Wang J, Hong M (2017) Protonation equilibria and pore-opening structure of the dual-histidine influenza B virus M2 transmembrane proton channel from solid-state NMR. J Biol Chem 292:17876–17884
Wylie BJ, Sperling LJ, Nieuwkoop AJ, Franks WT, Oldfield E, Rienstra CM (2011) Ultrahigh resolution protein structures using NMR chemical shift tensors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:16974–16979
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Matthias Roos for useful discussions. This work is supported by National Institutes of Health Grants GM066976 and GM088204 to M.H.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shcherbakov, A.A., Hong, M. Rapid measurement of long-range distances in proteins by multidimensional 13C–19F REDOR NMR under fast magic-angle spinning. J Biomol NMR 71, 31–43 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-018-0187-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-018-0187-0