Abstract
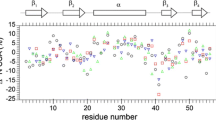
We present a comprehensive analysis of protein dynamics for a micro-crystallin protein in the solid-state. Experimental data include 15N T 1 relaxation times measured at two different magnetic fields as well as 1H–15N dipole, 15N CSA cross correlated relaxation rates which are sensitive to the spectral density function J(0) and are thus a measure of T 2 in the solid-state. In addition, global order parameters are included from a 1H,15N dipolar recoupling experiment. The data are analyzed within the framework of the extended model-free Clore–Lipari–Szabo theory. We find slow motional correlation times in the range of 5 and 150 ns. Assuming a wobbling in a cone motion, the amplitude of motion of the respective amide moiety is on the order of 10° for the half-opening angle of the cone in most of the cases. The experiments are demonstrated using a perdeuterated sample of the chicken α-spectrin SH3 domain.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal V, Reif B (2008) Residual methyl protonation in perdeuterated proteins for multidimensional correlation experiments in MAS solid-state NMR spectroscopy. J Magn Reson 194:16–24
Agarwal V, Xue Y, Skrynnikov NR, Reif B (2008) Protein side-chain dynamics as observed by solution- and solid-state NMR: a similarity revealed. J Am Chem Soc 130:16611–16621
Andronesi OC, Becker S, Seidel K, Heise H, Young HS, Baldus M (2005) Determination of membrane protein structure and dynamics by magic-angle-spinning solid-state NMR spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc 127:12965–12974
Bouvignies G, Bernado P, Meier S, Cho K, Grzesiek S, Bruschweiler R, Blackledge M (2005) Identification of slow correlated motions in proteins using residual dipolar and hydrogen-bond scalar couplings. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:13885–13890
Cavanagh J, Fairbrother WJ, Palmer AG, Skelton NJ (1996) Protein NMR spectroscopy: principles and practice. Academic Press, San Diego
Chekmenev EY, Zhang Q, Waddell KW, Mashuta MS, Wittebort RJ (2004) 15N chemical shielding in glycyl tripeptides: measurement by solid-state NMR and correlation with X-ray structure. J Am Chem Soc 126:379–384
Chevelkov V, Reif B (2008) TROSY effects in MAS solid-state NMR. Concepts NMR 32A:143–156
Chevelkov V, van Rossum BJ, Castellani F, Rehbein K, Diehl A, Hohwy M, Steuernagel S, Engelke F, Oschkinat H, Reif B (2003) 1H detection in MAS solid state NMR spectroscopy employing pulsed field gradients for residual solvent suppression. J Am Chem Soc 125:7788–7789
Chevelkov V, Faelber K, Diehl A, Heinemann U, Oschkinat H, Reif B (2005) Detection of dynamic water molecules in a microcrystalline sample of the SH3 domain of alpha-spectrin by MAS solid-state NMR. J Biomol NMR 31:295–310
Chevelkov V, Rehbein K, Diehl A, Reif B (2006) Ultra-high resolution in proton solid-state NMR at high levels of deuteration. Angew Chem Int Ed 45:3878–3881
Chevelkov V, Diehl A, Reif B (2007a) Quantitative measurement of differential 15N-Hα/β T2 relaxation times in a perdeuterated protein by MAS solid-state NMR spectroscopy. Magn Res Chem 45:S156–S160
Chevelkov V, Faelber K, Schrey A, Rehbein K, Diehl A, Reif B (2007b) Differential line broadening in MAS solid-state NMR due to dynamic interference. J Am Chem Soc 129:10195–10200
Chevelkov V, Zhuravleva AV, Xue Y, Reif B, Skrynnikov NR (2007c) Combined analysis of 15N relaxation data from solid- and solution-state NMR spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc 129:12594–12595
Chevelkov V, Diehl A, Reif B (2008) Measurement of 15N–T1 relaxation rates in a perdeuterated protein by MAS solid-state NMR spectroscopy. J Chem Phys 128:052316
Chevelkov V, Fink U, Reif B (2009) Accurate determination of order parameters from 1H,15N dipolar couplings in MAS solid-state NMR experiments. J Am Chem Soc (submitted)
Clore GM, Szabo A, Bax A, Kay LE, Driscoll PC, Gronenborn AM (1990) Deviations from the Simple 2-parameter model-free approach to the interpretation of N-15 nuclear magnetic relaxation of proteins. J Am Chem Soc 112:4989–4991
Cole HBR, Torchia DA (1991) An NMR-study of the backbone dynamics of Staphylococcal nuclease in the crystalline state. Chem Phys 158:271–281
Dvinskikh SV, Zimmermann H, Maliniak A, Sandstrom D (2003) Heteronuclear dipolar recoupling in liquid crystals and solids by PISEMA-type pulse sequences. J Magn Reson 164:165–170
Dvinskikh SV, Zimmermann H, Maliniak A, Sandström D (2005) Heteronuclear dipolar recoupling in solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance by amplitude-, phase-, and frequency-modulated Lee–Goldburg cross-polarization. J Chem Phys 122:044512
Eichmüller C, Skrynnikov NR (2005) A new amide proton R-1 rho experiment permits accurate characterization of microsecond time-scale conformational exchange. J Biomol NMR 32:281–293
Eichmüller C, Skrynnikov NR (2007) Observation of mu s time-scale protein dynamics in the presence of Ln(3+)stop ions: application to the N-terminal domain of cardiac troponin C. J Biomol NMR 37:79–95
Eisenmesser EZ, Bosco DA, Akke M, Kern D (2002) Enzyme dynamics during catalysis. Science 295:1520–1523
Franks WT, Zhou DH, Wylie BJ, Money BG, Graesser DT, Frericks HL, Gurmukh S, Rienstra CM (2005) Magic-angle spinning solid-state NMR spectroscopy of the beta 1 immunoglobulin binding domain of protein G (GB1): 15N and 13C chemical shift assignments and conformational analysis. J Am Chem Soc 127:12291–12305
Frederick KK, Marlow MS, Valentine KG, Wand AJ (2007) Conformational entropy in molecular recognition by proteins. Nature 448:325–330
Fushman D, Cowburn D (1998) Model-independent analysis of 15N chemical shift anisotropy from NMR relaxation data. Ubiquitin as a test example. J Am Chem Soc 120:7109–7110
Giraud N, Böckmann A, Lesage A, Penin F, Blackledge M, Emsley L (2004) Site-specific backbone dynamics from a crystalline protein by solid-state NMR spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc 126:11422–11423
Giraud N, Blackledge M, Goldman M, Böckmann A, Lesage A, Penin F, Emsley L (2005) Quantitative analysis of backbone dynamics in a crystalline protein from nitrogen-15 spin-lattice relaxation. J Am Chem Soc 127:18190–18201
Giraud N, Sein J, Pintacuda G, Böckmann A, Lesage A, Blackledge M, Emsley L (2006) Observation of heteronuclear overhauser effects confirms the 15N–1H dipolar relaxation mechanism in a crystalline protein. J Am Chem Soc 128:12398–12399
Giraud N, Blackledge M, Böckmann A, Emsley L (2007) The influence of nitrogen-15 proton-driven spin diffusion on the measurement of nitrogen-15 longitudinal relaxation times. J Magn Reson 184:51–61
Grey MJ, Tang YF, Alexov E, McKnight CJ, Raleigh DP, Palmer AG (2006) Characterizing a partially folded intermediate of the villin headpiece domain under non-denaturing conditions: contribution of His41 to the pH-dependent stability of the N-terminal subdomain. J Mol Biol 355:1078–1094
Hall JB, Fushman D (2006) Variability of the N-15 chemical shielding tensors in the B3 domain of protein G from N-15 relaxation measurements at several fields. Implications for backbone order parameters. J Am Chem Soc 128:7855–7870
Helmus JJ, Surewicz K, Nadaud PS, Surewicz WK, Jaroniec CP (2008) Molecular conformation and dynamics of the Y145Stop variant of human prion protein in amyloid fibrils. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:6284–6289
Henzler-Wildman K, Kern D (2007) Dynamic personalities of proteins. Nature 450:964–972
Hologne M, Faelber K, Diehl A, Reif B (2005) Characterization of dynamics of perdeuterated proteins by MAS solid-state NMR. J Am Chem Soc 127:11208–11209
Hologne M, Chen Z, Reif B (2006a) Characterization of dynamic processes using deuterium in uniformly 2H, 13C, 15N enriched peptides by MAS solid-state NMR. J Magn Res 179:20–28
Hologne M, Chevelkov V, Reif B (2006b) Deuteration of peptides and proteins in MAS solid-state NMR. Prog NMR Spect 48:211–232
Hoogstraten CG, Wank JR, Pardi A (2000) Active site dynamics in the lead-dependent ribozyme. Biochemistry 39:9951–9958
Huster D, Xiao LS, Hong M (2001) Solid-state NMR investigation of the dynamics of the soluble and membrane-bound colicin Ia channel-forming domain. Biochemistry 40:7662–7674
Korzhnev DM, Salvatella X, Vendruscolo M, Di Nardo AA, Davidson AR, Dobson CM, Kay LE (2004) Low-populated folding intermediates of Fyn SH3 characterized by relaxation dispersion NMR. Nature 430:586–590
Lakomek NA, Fares C, Becker S, Carlomagno T, Meiler J, Griesinger C (2005) Side-chain orientation and hydrogen-bonding imprint supra-tauc motion on the protein backbone of ubiquitin. Angew Chem Int Ed 117:7954–7956
Lange OF, Lakomek N-A, Fares C, Schroeder GF, Walter KFA, Becker S, Meiler J, Grubmueller H, Griesinger C, de Groot BL (2008) Recognition dynamics up to microseconds revealed from an RDC-derived ubiquitin ensemble in solution. Science 320:1471–1475
Linser R, Fink U, Reif B (2008) Proton-detected scalar coupling based assignment strategies in MAS solid-state NMR spectroscopy applied to perdeuterated proteins. J Magn Reson 193:89–93
Lipari G, Szabo A (1981) Pade approximants to correlation-functions for restricted rotational diffusion. J Chem Phys 75:2971–2976
Lipari G, Szabo A (1982) Model-free approach to the interpretation of nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation in macromolecules. 1. Theory and range of validity. J Am Chem Soc 104:4546–4559
Lorieau JL, McDermott AE (2006) Conformational flexibility of a microcrystalline globular protein: order parameters by solid-state NMR spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc 128:11505–11512
Lorieau JL, Day LA, McDermott AE (2008) Conformational dynamics of an intact virus: order parameters for the coat protein of Pf1 bacteriophage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:10366–10371
Mack JW, Usha MG, Long J, Griffin RG, Wittebort RJ (2000) Backbone motions in a crystalline protein from field-dependent H-2-NMR relaxation and line-shape analysis. Biopolymers 53:9–18
Maricq MM, Waugh JS (1979) NMR in rotating solids. J Chem Phys 70:3300–3316
Martinez JC, Pisabarro T, Serrano L (1998) Obligatory steps in protein folding and the conformational diversity of the transition state. Nat Struct Biol 5:721–729
Palmer-III AG, Williams J, McDermott AE (1996) Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of biopolymer dynamics. J Phys Chem 100:13293–13310
Pauli J, Van Rossum B-J, Förster H, De Groot HJM, Oschkinat H (2000) Sample optimization and identification of signal patterns of amino acid side chains in 2D-RFDR spectra of the a-spectrin SH3 domain. J Magn Reson 143:411–416
Redfield AG (1957) On the theory of relaxation processes. IBM J Res Dev 1:19–31
Reif B, Griffin RG (2003) 1H detected 1H, 15N correlation spectroscopy in rotating solids. J Magn Reson 160:78–83
Reif B, Jaroniec CP, Rienstra CM, Hohwy M, Griffin RG (2001) 1H–1H MAS correlation spectroscopy and distance measurements in a deuterated peptide. J Magn Reson 151:320–327
Reif B, Xue Y, Agarwal V, Pavlova MS, Hologne M, Diehl A, Ryabov YE, Skrynnikov NR (2006) Protein side-chain dynamics observed by solution- and solid-state NMR: comparative analysis of methyl 2H relaxation data. J Am Chem Soc 128:12354–12355
Sackewitz M, Scheidt HA, Lodderstedt G, Schierhorn A, Schwarz E, Huster D (2008) Structural and dynamical characterization of fibrils from a disease-associated alanine expansion domain using proteolysis and solid-state NMR spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc 130:7172–7173
Skrynnikov NR (2007) Asymmetric doublets in MAS NMR: coherent and incoherent mechanisms. Magn Res Chem 45:S161–S173
Tjandra N, Szabo A, Bax A (1996) Protein backbone dynamics and 15N chemical shift anisotropy from quantitative measurement of relaxation interference effects. J Am Chem Soc 118:6986–6991
Torchia DA, Szabo A (1982) Spin-lattice relaxation in solids. J Magn Reson 49:107–121
Vallurupalli P, Hansen DF, Kay LE (2008) Structures of invisible, excited protein states by relaxation dispersion NMR spectroscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:11766–11771
Wasmer C, Lange A, Van Melckebeke H, Siemer AB, Riek R, Meier BH (2008) Amyloid fibrils of the HET-s(218–289) prion form a beta solenoid with a triangular hydrophobic core. Science 319:1523–1526
Williams JC, McDermott AE (1995) Dynamics of the flexible loop of triosephosphate isomerase—the loop motion is not ligand-gated. Biochemistry 34:8309–8319
Wu XL, Zilm KW (1993) Cross-polarization with high-speed magic-angle spinning. J Magn Reson A 104:154–165
Wylie BJ, Franks WT, Rienstra CM (2006) Determinations of N-15 chemical shift anisotropy magnitudes in a uniformly N-15, C-13-labeled microcrystalline protein by three-dimensional magic-angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Phys Chem B 110:10926–10936
Wylie BJ, Sperling LJ, Frericks HL, Shah GJ, Franks WT, Rienstra CM (2007) Chemical-shift anisotropy measurements of amide and carbonyl resonances in a microcrystalline protein with slow magic-angle spinning NMR spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc 129:5318–5319
Xu J, Xue Y, Skrynnikov NR (2009) Detection of nanosecond time scale side-chain jumps in water/glycerol solvent. J Biomol NMR (in press) (topical issue on dynamics)
Yao L, Vögeli B, Ying J, Bax A (2008) NMR determination of amide N–H equilibrium bond length from concerted dipolar coupling measurements. J Am Chem Soc 130:16518–16520
Zeeb M, Jacob MH, Schindler T, Balbach J (2003) N-15 relaxation study of the cold shock protein CspB at various solvent viscosities. J Biomol NMR 27:221–234
Zhang Q, Sun XY, Watt ED, Al-Hashimi HM (2006) Resolving the motional modes that code for RNA adaptation. Science 311:653–656
Acknowledgments
We thank Nikolai Skrynnikov for many stimulating discussions. This work was supported by the Leibniz-Gemeinschaft and the DFG (grants Re1435, SFB 449, SFB 740).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chevelkov, V., Fink, U. & Reif, B. Quantitative analysis of backbone motion in proteins using MAS solid-state NMR spectroscopy. J Biomol NMR 45, 197–206 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-009-9348-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-009-9348-5