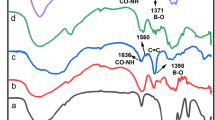
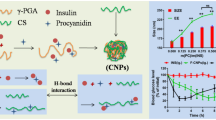
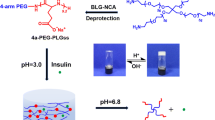
Abstract
The glucose-responsive nanocapsules [CS-NAC/p(GAMA-r-AAPBA)] were readily fabricated with modified chitosan (CS-NAC) and random glycopolymer poly(d-gluconamidoethyl methacrylate-r-3-acrylamidophenylboronic acid) p(GAMA-r-AAPBA) as the alternant multilayered polyelectrolyte hybrid shell via layer-by-layer self-assembly after etching the amino functionalized SiO2 spheres by NH4F/HF. The spherical and hollow structure of nanocapsules was confirmed by TEM analysis and there was no clear collapse found after removal of the sacrificial cores. The reversible zeta potential changes of the nanocapsule materials evaluated the reversible glucose sensitivity. Besides, this system demonstrated a good capacity for encapsulation and loading insulin entrapped in nanocapsules as model protein drug. A good biocompatibility of the material was confirmed by the cell viability. In vitro release of insulin experiments revealed that no obvious release was found in acidic condition and the release could be normally conducted at physiological pH. These results implied that it was feasible for nanocapsules to be used in controlled release drug delivery system.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ivanov AE, Larsson H, Galaev IY, Mattiasson B. Synthesis of boronate-containing copolymers of N,N-dimethylacrylamide, their interaction with poly(vinyl alcohol) and rheological behaviour of the gels. Polymer. 2004;45:2495–505.
Schofield CL, Haines AH, Field RA, Russell DA. Silver and gold glyconanoparticles for colorimetric bioassays. Langmuir. 2006;22:6707–11.
Kikuchi A, Suzuki K, Okabayashi O, Hoshino H, Kataoka K, Sakurai Y, Okano T. Glucose-sensing electrode coated with polymer complex gel containing phenylboronic acid. Anal Chem. 1996;68:823–8.
Matsumoto A, Yoshida R, Kataoka K. Glucose-responsive polymer gel bearing phenylborate derivative as a glucose-sensing moiety operating at the physiological pH. Biomacromolecules. 2004;5:1038–45.
Phillips MD, James TD. Boronic acid based modular fluorescent sensors for glucose. J Fluoresc. 2004;14:549–59.
Decher G, Hong JD, Chmitt J. Buildup of ultrathin multilayer films by a self-assembly process: III. Consecutively alternating adsorption of anionic and cationic polyelectrolytes on charged surfaces. Thin Solid Films. 1992;210:831–5.
Sukhishvili SA. Responsive polymer films and capsules via layer-by-layer assembly. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci. 2005;10:37–44.
Mu B, Liu P, Li XR, Du PC, Dong Y, Wang YJ. Fabrication of flocculation-resistant pH/ionic strength/temperature multiresponsive hollow microspheres and their controlled release. Mol Pharm. 2012;9:91–101.
Del Mercato LL, Rivera-Gil P, Abbasi AZ, Ochs M, Ganas C, Zins I, Sönnichsen C, Parak WJ. LbL multilayer capsules: recent progress and future outlook for their use in life sciences. Nanoscale. 2010;2:458–67.
Ariga K, Hill JP, Lee MV, Vinu A, Charvet R, Acharya S. Challenges and breakthroughs in recent research on self-assembly. Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2008;9:014109. doi:10.1088/1468-6996/9/1/014109.
Donath E, Sukhorukov GB, Caruso F, Davis SA, Möhwald H. Novel hollow polymer shells by colloid-templated assembly of polyelectrolytes. Angew Chem Int Ed. 1998;37:2201–5.
Quintanar-Guerrero D, Allémann E, Fessi H, Doelker E. Preparation techniques and mechanisms of formation of biodegradable nanoparticles from preformed polymers. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 1998;24:1113–28.
Mazumder MAJ, Shen F, Burke NAD, Potter MA, Stvöer HDH. Self-cross-linking polyelectrolyte complexes for therapeutic cell encapsulation. Biomacromolecules. 2008;9:2292–300.
Lin YH, Chen CT, Chang WC, Peng SF, Liang HF, Sung HW. Preparation and characterization of nanoparticles shelled with chitosan for oral insulin delivery. Biomacromolecules. 2007;8:146–52.
Chen HY, Moore T, Qi B, Colvin DC, Jelen EK, Hitchcock DA, He J, Mefford OT, Gore JC, Alexis F, Anker JN. Monitoring pH-triggered drug release from radioluminescent nanocapsules with X-ray excited optical luminescence. ACS Nano. 2013;7:1178–87.
Shchukin DG, Sukhorukov GB. Nanoparticle synthesis in engineered organic nanoscale reactors. Adv Mater. 2004;16:671–82.
Horgan AM, Marshall AJ, Kew SJ, Dean KES, Creasey CD, Kabilan S. Crosslinking of phenylboronic acid receptors as a means of glucose selective holographic detection. Biosens Bioelectron. 2006;21:1838–43.
Wang YX, Zhang XG, Han YC, Cheng C, Li CX. pH- and glucose-sensitive glycopolymer nanoparticles based on phenylboronic acid for triggered release of insulin. Carbohyd Polym. 2012;89:124–31.
Jin XJ, Zhang XG, Wu ZM, Teng DY, Zhang XJ, Wang YX, Wang Z, Li CX. Amphiphilic random glycopolymer based on phenylboronic acid: synthesis, characterization, and potential as glucose-sensitive matrix. Biomacromolecules. 2009;10:1337–45.
Cui C, Zhang XG, Xiang JX, Wang YX, Zheng C, Lu ZT, Li CX. Development of novel self-assembled poly(3-acrylamidophenylboronic acid)/poly(2-lactobionamidoethyl methacrylate) hybrid nanoparticles for improving nasal adsorption of insulin. Soft Matter. 2012;8:765–73.
Wu ZM, Zhang XG, Guo HL, Li CX, Yu DM. An injectable and glucose-sensitive nanogel for controlled insulin release. J Mater Chem. 2012;22:22788–96.
Motwani SK, Chopra S, Talegaonkar S, Kohli K, Ahmad FJ, Khar RK. Chitosan-sodium alginate nanoparticles as submicroscopic reservoirs for ocular delivery: formulation, optimisation and in vitro characterization. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2008;68:513–25.
Guzmán E, Cavallo JA, Chuliá-Jordán R, Gómez C, Strumia MC, Ortega F, Rubio RG. pH-induced changes in the fabrication of multilayers of poly(acrylic acid) and chitosan: fabrication, properties, and tests as a drug storage and delivery system. Langmuir. 2011;27:6836–45.
Gong M, Wang YB, Li M, Hu BH, Gong YK. Fabrication and hemocompatibility of cell outer membrane mimetic surfaces on chitosan by layer by layer assembly with polyanion bearing phosphorylcholine groups. Colloid Surface B. 2011;85:48–55.
Gemene KL, Meyerhoff ME. Reversible detection of heparin and other polyanions by pulsed chronopotentiometric polymer membrane electrode. Anal Chem. 2010;82:1612–5.
Cado G, Kerdjoudj H, Chassepot A, Lefort M, Benmlih K, Hemmerlé J, Voegel JC, Jierry L, Schaaf P, Frère Y, Boulmedais F. Polysaccharide films built by simultaneous or alternate spray: a rapid way to engineer biomaterial surfaces. Langmuir. 2012;28:8470–8.
Yang Q, Xu ZK, Dai ZW, Wang JL, Ulbricht M. Surface modification of polypropylene microporous membranes with a novel glycopolymer. Chem Mater. 2005;17:3050–8.
Narain R, Armes SP. Synthesis and aqueous solution properties of novel sugar methacrylate-based homopolymers and block copolymers. Biomacromolecules. 2003;4:1746–58.
Lee MC, Kabilan S, Hussain A, Yang XP, Blyth J, Lowe CR. Glucose-sensitive holographic sensors for monitoring bacterial growth. Anal Chem. 2004;76:5748–55.
Krauland AH, Hoffer MH, Bernkop-Schnurch A. Viscoelastic properties of a new in situ gelling thiolated chitosan conjugate. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2005;31:885–93.
Stöber W, Fink A, Bohn EJ. Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J Colloid Interface Sci. 1968;26:62–9.
Ibisate M, Zou AQ, Xia YN. Arresting, Fixing, and separating dimers composed of uniform silica colloidal spheres. Adv Funct Mater. 2006;16:1627–32.
Shu SJ, Zhang XG, Wu ZM, Wang Z, Li CX. Gradient cross-linked biodegradable polyelectrolyte nanocapsules for intracellular protein drug delivery. Biomaterials. 2010;31:6039–49.
Zelikin AN, Quinn JF, Caruso F. Disulfide cross-linked polymer capsules: en route to biodeconstructible systems. Biomacromolecules. 2006;7:27–30.
Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–54.
Fernandez-Urrusuno R, Calvo P, Remunan-Lopez C, Vila-Jato JL, Alouso MJ. Enhancement of nasal absorption of insulin using chitosan nanoparticles. Pharm Res. 1999;26:1576–81.
Amidi M, Romeijn SG, Borchard G, Junginger HE, Hennink WE, Jiskoot W. Preparation and characterization of protein-loaded N-trimethyl chitosan nanoparticles as nasal delivery system. J Control Release. 2006;111:107–16.
Shiomi Y, Saisho M, Tsukagoshi K, Shinkai S. Specific complexation of glucose with a diphenylmethane-3,3′-diboronic acid derivative: correlation between the absolute configuration of mono- and di-saccharides and the circular dichroic activity of the complex. J Chem Soc Perkin Trans. 1993;17:2111–7.
Kondo K, Shiomi Y, Saisho M, Harada T, Shinkai S. Specific complexation of disaccharides with diphenyl-3,3′-diboronic acid that can be detected by circular dichroism. Tetrahedron. 1992;48:8239–52.
Qureshi S, Al-Shabanah OA, Al-Harbi MM, Al-Bekairi AM, Raza M. Boric acid enhances in vivo Ehrlich ascites carcinoma cell proliferation in Swiss albino mice. Toxicology. 2001;165:1–11.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grants (81000683 to Z. M. W.) from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and Grant (863 Program: 2012AA022602 to K. X. X.) from the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, H., Guo, Q., Chu, T. et al. Glucose-sensitive polyelectrolyte nanocapsules based on layer-by-layer technique for protein drug delivery. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 25, 121–129 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-013-5055-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-013-5055-6