Abstract
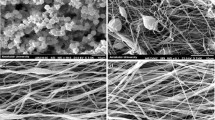
Electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds in neural tissue engineering provide an alternative approach for neural regeneration. Since the topography of a surface affects the microscopic behaviour of material; the creation of nanoscale surface features, which mimic the natural roughness of live tissue, on polymer surfaces can promote an appropriate cell growth and proliferation. In this research, a unique PLGA nanofibrous structure was fabricated without any post-electrospinning treatment. Scaffolds were prepared in two general groups: cylindrical and ribbon-shaped electrospun fibres, with smooth and rough (porous and grooved) surfaces. The experiments about nerve cell culture have demonstrated that the nanoroughness of PLGA electrospun scaffolds can increase the cell growing rate to 50 % in comparison with smooth and conventional electrospun scaffolds. SEM and AFM images and MTT assay results have shown that the roughened cylindrical scaffolds enhance the nerve growth and proliferation compared to smooth and ribbon-shaped nanofibrous scaffolds. A linear interaction has been found between cell proliferation and surface features. This helps to approximate MTT assay results by roughness parameters.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao H, Liu T, Chew SY. The application of nanofibrous scaffolds in neural tissue engineering. J Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2009;61:1055–64.
Tabesh H, Amoabediny G, Salehi Nik N, Heydari M, Yosefifard M, Ranaei Siadat SO, Mottaghy K. The role of biodegradable engineered scaffolds seeded with Schwann cells for spinal cord regeneration. Neurochem Int. 2009;54:73–83.
Huang ZM, Zhang YZ, Kotaki M, Ramakrishna S. A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites. Compos Sci Technol. 2003;63:2223–53.
Liang D, Hsiao BS, Chu B. Functional electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds for biomedical applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2007;59:1392–412.
Lowery JL, Datta N, Routledge GC. Effect of fiber diameter, pore size and seeding method on growth of human dermal fibroblasts in electrospun poly(var epsilon-caprolactone) fibrous mats. Biomaterials. 2010;31:491–504.
Zhou J, Cao C, Ma X. A novel three-dimensional tubular scaffold prepared from silk fibroin by electrospinning. Int J Biol Macromol. 2009;45:504–10.
Teixeira A, Abrams GA, Bertics PJ, Murphy CJ, Nealey PF. Epithelial contact guidance on well-defined micro- and nanostructured substrates. J Cell Sci. 2003;116:1881–9.
Ikada Y. Tissue engineering fundamentals and applications interface science and technology. Tokyo: Elsevier Academic; 2008. p. 41–65.
Kim G, Park J, Park S. Surface-treated and multilayered poly(e-caprolactone) nanofiber webs exhibiting enhanced hydrophilicity. J Polym Sci Polym Phys. 2007;45:2038–45.
Xiong Y, et al. Synaptic transmission of neural stem cells seeded in 3-dimensional PLGA scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2009;30:3711–22.
Wen X, Tresco PA. Fabrication and characterization of permeable degradable poly(dl-lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) hollow fiber phase inversion membranes for use as nerve tract guidance channels. Biomaterials. 2006;27:3800–9.
Yuan-yuan D, Jun J, Shao-hai W, Wei Y, Lei J, Zhong-yi W. Preparation of PLGA electrospun nanofibers for tissue engineering applications. J US China Med Sci. 2007;4:41–4.
Krych AG, Rooney GE, Schermerhorn BC. Relationship between scaffold channel diameter and number of regenerating axons in the transected rat spinal cord. Acta Biomater. 2009;5:2551–9.
Moore MJ, Friedman A, Lewellyn EB. Multiple-channel scaffolds to promote spinal cord axon regeneration. Biomaterials. 2006;27:419–29.
Yao L, Wang S, Cui W, Sherlock R, O’Connell C, Damodaran G, Gorman A, Windebank A, Pandit A. Effect of functionalized micropatterned PLGA on guided neurite growth. Acta Biomater. 2009;5:580–8.
Bible E, Chau DYS, Alexander MR, Price J, Shakesheff KM, Modo M. The support of neural stem cells transplanted into stroke-induced brain cavities by PLGA particles. Biomaterials. 2009;30:2985–94.
Bini TB, Gao S, Tan TC, Wang S, Lim A, Hai LB, Ramakrishna S. Electrospun poly(l-lactide-co-glycolide) biodegradable polymer nanofibre tubes for peripheral nerve regeneration. Nanotechnology. 2004;15:1459–64.
Zheng YF, Li C, Li CJ, Cai W, Zhao LC. Surface characteristics and biological properties of paclitaxel-embedding PLGA coating on TiNi alloy. Mater Sci Eng A. 2005;438–440:1119–23.
Yang J, Shi G, Bei J, Wang S, Cao Y, Shang Q, Yang G, Wang W. Fabrication and surface modification of macroporous poly(l-lactic acid) and poly(l-lactic-co-glycolic acid)(70/30) cell scaffolds for human skin fibroblast cell culture. J Biomed Mater Res. 2002;62:438–46.
Yang J, Bei J, Wang S. Enhanced cell affinity of poly(d, l-lactide) by combing plasma treatment with collagen anchorage. Biomaterials. 2002;23:2607–14.
Chung TW, Liu DZ, Wang SY, Wang SS. Enhancement of the growth of human endothelial cells by surface roughness at nanometer scale. Biomaterials. 2003;24:4655–61.
Xinghua Z, Chuanbao C, Xilan M, Yanan L. Optimization of macroporous 3-D silk fibroin scaffolds by salt-leaching procedure in organic solvent-free conditions. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2012;23:315–24.
Tze-Wen C, Shoei-Shen W, Yen-Zen W, Chien-Hung H. Enhancing growth and proliferation of human gingival fibroblasts on chitosan grafted poly(e-caprolactone) films is influenced by nano-roughness chitosan surfaces. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2009;20:397–404.
Chun YW, Khang D, Haberstroh KM, Webstermah TJ. The role of polymer nanosurface roughness and submicron pores in improving bladder urothelial cell density and inhibiting calcium oxalate stone formation. Nanotechnology. 2009;20(8):085104.
Miller DC, Haberstroh KM, Webster TJ. PLGA nanometer surface features manipulate fibronectin interactions for improved vascular cell adhesion. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2007;81:678–84.
Wang GJ, Lin YC, Li CW, Hsueh CC. Fabrication of orderly nanostructured PLGA scaffolds using anodic aluminum oxide templates. Biomed Microdevices. 2009;11:843–50.
Lampin M, Warocquier-Clerout R, Legris C, Degrange M, Sigot-Luizard MF. Correlation between substratum roughness and wettability, cell adhesion, and cell migration. J Biomed Mater Res. 1997;36:99–108.
Deitzel JM, Kleinmeyer J, Harris D, Beak-Tan NC. The effect of processing variables on the morphology of electrospun nanofibers and textiles. Polymer. 2001;42:261–72.
Thompson CJ, Chase GG, Yarin AL, Reneker DH. Effects of parameters on nanofiber diameter determined from electrospinning model. Polymer. 2007;48:6913–22.
Vrieze SD, Camp TV, Nelvig A, Hagstrom B, Westbroek P, Clerck KD. The effects of temperature and humidity on electrospinning. J Mater Sci. 2009;44:1357–62.
Ramakrishna S, Fujihara K, Teo WE, Lim TC, Ma Z. An introduction to electrospinning and nanofibers. Singapore: World Scientific; 2005. p. 90-154.
Shalumon KT, Binulal NS, Selvamurugan N, Nair SV, Menon D, Furuike T, Tamura H, Jayakumar R. Electrospinning of carboxymethyl chitin/poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofibrous scaffolds for tissue engineering applications carbohydrate. Polymers. 2009;77:863–9.
Ghasemi-Mobarakeh L, Prabhakaran MP, Morshed M, Nasr-Esfahani MH, Ramakrishn S. Electrospun poly(3-caprolactone)/gelatin nanofibrous scaffolds for nerve tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2008;29:4532–9.
Gadelmawla ES, Koura MM, Maksoud TMA, Elewa IM, Soliman HH. Roughness parameters. J Mater Process Technol. 2002;123:133–45.
Dong WP, Sullivan PJ, Stout KJ. Comprehensive study of parameters for characterising three-dimensional surface topography III: parameters for characterising amplitude and some functional. Wear. 1994;178:29–43.
Deligianni DD, Katsala ND, Koutsoukos PG, MissirlisYF. Effect of surface roughness of hydroxyapatite on human bone marrow cell adhesion, proliferation, differentiation and detachment strength. Biomaterials. 2000;22:87–96.
Rosales-Leala JI, Rodríguez-Valverdeb MA, Mazzagliaa G, Ramón-Torregrosab PJ, Díaz-Rodríguezc L, García-Martínezc O, Vallecillo-Capillaa M, Ruizc C, Cabrerizo-Vílchezb MA. Effect of roughness, wettability and morphology of engineered titanium surfaces on osteoblast-like cell adhesion. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Aspects. 2010;365:222–9.
Zan Q, Wang C, Dong L, Cheng P, Yian J. Effect of surface roughness of chitosan-based microspheres on cell adhesion. Appl Surf Sci. 2008;255:401–3.
Whitehouse DJ. Handbook of surface and nanometrology. 2nd ed. New York: CRC Press Taylor & Francis; 1994. p. 493–622.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zamani, F., Amani-Tehran, M., Latifi, M. et al. The influence of surface nanoroughness of electrospun PLGA nanofibrous scaffold on nerve cell adhesion and proliferation. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 24, 1551–1560 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-013-4905-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-013-4905-6