Abstract
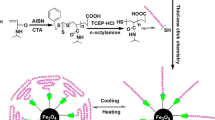
A new strategy for assembling multifunctional nanocomposites with magnetic particles and amino dendrimers was reported. In this strategy, the amino terminated PAMAM G5.0 and Fe3O4 NPs prepared by co-deposition method and further modified by aminosilane by two sol–gel processes were combined with the hydrophilic spacer of PEG dicarboxylate by amidation. The nanocomposites were characterized by means of X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), atom force microscopy (AFM), superconducting quantum interference device (SQUID) magnetometer, and hydrophilicity analysis. The results showed that the multifunctional nanocomposites were spherical with the mean diameter of 180 nm and exhibited good dispersion and hydrophilicity. The new strategy put forward here provides an effective route to functionalizing Fe3O4 NPs with various amino dendrimers for drug and gene delivery as well as biological detection.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang ZD. Nanocapsules. In: Nalwa HS, editor. Encyclopedia of nanoscience and nanotechnology, vol 6. Stevenson Ranch, California: American Scientific Publishers; 2004. p. 77–160.
HW Gu, KM Xu, CJ Xu, B Xu, Biofunctional magnetic nanoparticles for protein separation and pathogen detection. Chem Commun. 2006; 941–9. doi:10.1039/b514130c.
Oscar BM, María PM, Pedro T, Jesus RC, Pierre B, Martín S, et al. Fe-based nanoparticles metallic alloys as contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging. Biomaterials. 2005;26:5695–703. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2005.02.020.
Xie HY, Zuo C, Liu Y, Zhang ZL, Pang DW, Li XL, et al. Cell-targeting multifunctional nanospheres with both fluorescence and magnetism. Small. 2005;1:506–9. doi:10.1002/smll.200400136.
Yang Y, Jiang JS, Du B, Gan ZF, Qian M, Zhang P. Preparation and properties of a novel drug delivery system with both magnetic and biomolecular targeting. J Mater Sci: Mater Med. 2009;20:301–7. doi:10.1007/s10856-008-3577-0.
Gou ML, Qian ZY, Wang H, Tang YB, Huang MJ, Kan B, et al. Preparation and characterization of magnetic poly(ε-caprolactone)-poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(ε-caprolactone) microspheres. J Mater Sci: Mater Med. 2008;19:1033–41. doi:10.1007/s10856-007-3230-3.
Tanaka H, Sugita T, Yasunaga YJ, Shimose SJ, Deie M, Kubo T, et al. Efficiency of magnetic liposomal transforming growth factor-β 1 in the repair of articular cartilage defects in a rabbit model. J Biomed Mater Res. 2005;73A:255–63. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.30187.
Aulenta F, Hayes W, Rannard S. Dendrimers: a new class of nanoscopic containers and delivery devices. Eur Polym J. 2003;39:1741–71. doi:10.1016/S0014-3057(03)00100-9.
Boas U, Heegaard PMH. Dendrimers in drug research. Chem Soc Rev. 2004;33:43–63. doi:10.1039/b309043b.
Paleos CM, Tsiourvas D, Sideratou Z. Molecular engineering of dendritic polymers and their application as drug and gene delivery systems. Mol Pharmacol. 2007;4:169–88. doi:10.1021/mp060076n.
Kim TI, Seo HJ, Choi JS, Jang HS, Baek JU, Kim K, et al. PAMAM-PEG-PAMAM: novel triblock copolymer as a biocompatible and efficient gene delivery carrier. Biomacromolecules. 2004;5:2487–92. doi:10.1021/bm049563j.
Majoros IJ, Myc A, Thomas T, Mehta CB, Baker JR Jr. PAMAM dendrimer-based multifunctional conjugate for cancer therapy: synthesis, characterization, and functionality. Biomacromolecules. 2006;7:572–9. doi:10.1021/bm0506142.
Myc A, Majoros IJ, Thomas TP, Baker JR Jr. Dendrimer-based targeted delivery of an apoptotic sensor in cancer cells. Biomacromolecules. 2007;8:13–8. doi:10.1021/bm060815l.
Shi XY, Wang SH, Sasha M, Mary EVA, Bi XD, Lee IH, et al. Dendrimer-entrapped gold nanoparticles as a platform for cancer-cell targeting and imaging. Small. 2007;3:1245–52. doi:10.1002/smll.200700054.
Scott RWJ, Datye AK, Crooks RM. Bimetallic palladium-platinum dendrimer-encapsulated catalysts. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125:3708–9. doi:10.1021/ja034176n.
Jiang YJ, Jiang JH, Gao QM, Ruan ML, Yu HM, Qi LJ. A novel nanoscale catalyst system composed of nanosized Pd catalysts immobilized on Fe3O4@SiO2–PAMAM. Nanotechnology. 2008;19:1–6. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/19/7/075714.
Mandal D, Maran A, Yaszemski MJ, Bolander ME, Sarkar G. Cellular uptake of gold nanoparticles directly cross-linked with carrier peptides by osteosarcoma cells. J Mater Sci: Mater Med. 2009;20:347–50. doi:10.1007/s10856-008-3588-x.
Strable E, Bulte JWM, Moskowitz B, Vivekanandan K, Allen M, Douglas T. Synthesis, characterization, and intracellular uptake of carboxyl-terminated poly(amidoamine) dendrimer-stabilized iron oxide nanoparticles. Chem Mater. 2001;13:2201–9. doi:10.1021/cm010125i.
Shi XY, Thomas TP, Myc LA, Kotlyar A, Baker JR Jr. Synthesis, characterization, and intracellular uptake of carboxyl-terminated poly(amidoamine) dendrimer-stabilized iron oxide nanoparticles. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2007;9:5712–20. doi:10.1039/b709147h.
Bulte JWM, Douglas T, Witwer B, Zhang SCh, Strable E, Lewis BK, et al. Magnetodendrimers allow endowsomal magnetic labeling and in vivo stracking of stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2001;19:1141–7. doi:10.1038/nbt1201-1141.
Wang SH, Shi XY, Antwerp MV, Cao ZY, Swanson SD, Bi XD, et al. Dendrimer-functionalized iron oxide nanoparticles for specific targeting and imaging of cancer cells. Adv Funct Mater. 2007;17:3043–50. doi:10.1002/adfm.200601139.
Jevprasesphant R, Penny J, Jalal R, Attwood D, McKeown NB, Demanuele A. The influence of surface modification on the cytotoxicity of PAMAM dendrimers003. Int J Pharm. 2003;252:263–6. doi:10.1016/S0378-5173(02)00623-3.
Yamazaki M, Ito T. Deformation and instability of membrane structure of phospholipid vesicles caused by osmophobic association: mechanical stress model for the mechanism of poly(ethylene glycol)-induced membrane fusion. Biochemistry. 1990;29:1309–14. doi:10.1021/bi00457a029.
Boni LT, Hah JS, Hui SW, Mukherjee P, Ho JT, Jung CY. Aggregation and fusion of unilamellar vesicles by poly(ethylene glycol). Biochem Biophys Acta-Biomembranes. 1984;775:409–18. doi:10.1016/0005-2736(84)90387-0.
Yoon TJ, Kim JS, Kim BG, Yu KN, Cho MH, Lee JK. Multifunctional nanoparticles possessing a “magnetic motor effect” for drug or gene delivery. Angew Chem. 2005;44:1092–5. doi:10.1002/anie.200461910.
Guo J, Yang WL, Deng YH, Wang CC, Fu SK. Organic-dye-coupled magnetic nanoparticles encaged inside thermoresponsive PNIPAM microcapsules. Small. 2005;1:737–43. doi:10.1002/smll.200400145.
Zhang Y, Wang SN, Ma S, Guan JJ, Li D, Zhang XD, et al. Self-assembly multifunctional nanocomposites with Fe3O4 magnetic core and CdSe/ZnS quantum dots shell. J Biomed Mater Res. 2008;85A:840–6. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.31609.
Souza KC, Ardisson JD, Sousa EMB. Study of mesoporous silica/magnetite systems in drug controlled release. J Mater Sci: Mater Med. 2009;20:507–9. doi:10.1007/s10856-008-3592-1.
Stöber W, Fink A, Bohn E. Controlled growth of monodisperse silica sphere in micro size range. J Colloid Interface Sci. 1968;26:62–9. doi:10.1016/0021-9797(68)90272-5.
Wei XL, Fahlman M, Epstein KJ. XPS study of highly sulfonated polyaniline. Macromolecules. 1999;32:3114–7. doi:10.1021/ma981386p.
Jiang P, Zhou JJ, Li R, Gao Y, Sun TL, Zhao XW, et al. PVP-capped twinned gold plates from nanometer to micrometer. J Nanopart Res. 2006;8:927–34. doi:10.1007/s11051-005-9046-5.
J. Ren, J. Shen, S.C. Lu. In: Xing T, editor. Dispersion science and technology of particles. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press; 2005. p. 175.
Driffield M, Goodall DM, Klute AS, Smith DK, Wilson K. Synthesis and characterization of silica-supported L-lysine-based dendritic branches. Langmuir. 2002;18:8660–5. doi:10.1021/la0203842.
Lee J, Isobe T, Senna M. Preparation of ultrafine Fe3O4 particles by precipitation in the presence of PVA at high pH. J Colloid Interface Sci. 1996;177:490–4. doi:10.1006/jcis.1996.0062.
Ding Y, Hu Y, Zhang LY, Chen Y, Jiang XQ. Synthesis and magnetic properties of biocompatible hybrid hollow spheres. Biomacromolecules. 2006;7:1766–72. doi:10.1021/bm060085h.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 50331030 and 50831006.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Liu, JY., Yang, F. et al. A new strategy for assembling multifunctional nanocomposites with iron oxide and amino-terminated PAMAM dendrimers. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 20, 2433–2440 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-009-3808-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-009-3808-z