Abstract
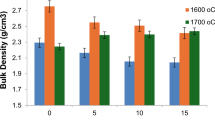
Hydrothermal treatment is traditionally employed to improve the sinterability of powder compacts by reducing porosity and increasing apparent density. The effect of hydrothermal treatment on green powder compacts has been assessed in order to better understand how treatment may affect the sinterability of the bodies. Laboratory synthesised nano sized hydroxyapatite (HA) and a commercial zirconia (ZrO2) powder have been ball milled together to create composite mixtures containing 0–5 wt% ZrO2 loadings. Disc shaped bodies have been formed using uniaxial and subsequent isostatic pressure. The resultant coherent samples were subjected to hydrothermal treatment at either 120 or 250°C for 10 h in order to assess the effect of this processing technique on the physical, mechanical and microstructural properties of the green composites. ZrO2 loadings up to 3 wt% increased apparent density from 90 to 92%, whereas increased loading to 5 wt% increased flexural strength, from 6 to 9 MPa. Increasing the hydrothermal treatment temperature increased open porosity, from ~44 to ~48% and reduced biaxial flexural strengths of the treated bodies compared to those of their room temperature isostatically pressed counterparts (~10 to ~6 MPa).








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bettinelli A, Guille J, et al. Densification of alumins at 1400°C. Ceram Intl. 1998;14(1):31–4.
Kingery WD, Bowen HK. Introduction to ceramics. New york: Wiley; 1976.
Cheng JP, Agrawal D, et al. Microwave sintering of transparent alumina. Mater Lett. 2002;56(4):587–92.
Upadhyaya DD, Ghosh A, et al. Microwave sintering of zirconia ceramics. J Mater Sci. 2001;36(19):4701–7.
Kumar R, Prakash KH. Microstructure and mechanical properties of spark plasma sintering zirconia-hydroxyapatite nano-composite powders. Acta Mater. 2005;53(8):2327–35.
Que W, Khor KA, et al. Hydroxyapatite/titania nanocomposites derived by combining high-energy ball milling with spark plasma sintering processes. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2005;28:3083–90.
Nagaranjan VS, Rao KJ. Structural, mechanical and biocompatibility studies of hydroxyapatite-derived composites toughened by zirconia addition. J Mater Chem. 1993;3:43–51.
Hing KA, Gibson IR, Di-silvio L, Best SM, Bonfield W (1998) Effect of variation of Ca:P ratio on the cellular response of primary human osteoblast-like cells to hydroxyapatite based ceramics. In: LeGeros RZ, LeGeros, JP, editors. Proceedings of the 11th international symposium on ceramics in medicine. New York: World Scientific Publishing Co; 1998. pp. 293–296.
Rao WR, Boehm RF. A study of sintered apatites. J Dent Res. 1974;53:1351–4.
Towler MR. Processing, characterisation and mechanical properties of hydroxyapatite-zirconia composites for skeletal implants. London: University of London; 1997.
Towler MR, Gibson IR, Best SM. Novel processing of hydroxyapatite-zirconia composites using nano-sized particles. J Mater Sci Lett. 2000;19(24):2209–11.
Xin-bo X, Xie-rong Z, Chun-li Z. Preparation of enhanced HA coating on H2O2-treated carbon/carbon composite by induction heating and hydrothermal treatment methods. Mater Chem Phy. 2009;114(1):434–8.
Ji S, Murakami S, Kamitakahara M, Ioku K. Fabrication of titania/hydroxyapatite composite granules for photo-catalyst. Mater Res Bull. 2009;44(4):768–74.
Jarcho M, Bolen CH, Thomas MB, Bobick J, Kay JF, Doremus RH. Hydroxylapatite synthesis and characterisation in dense polycrystalline form. J Mater Sci. 1976;11:2027–35.
Kunio Ishikawa PD, Shulamic R. Determination of the Ca/P ratio in calcium-deficient hydroxyapatite using X-ray diffraction analysis. J Mater Sci: Mater Med. 1993;4(2):165–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Curran, D.J., Fleming, T.J., Kawachi, G. et al. Characterisation and mechanical testing of hydrothermally treated HA/ZrO2 composites. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 20, 2235–2241 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-009-3801-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-009-3801-6