Abstract
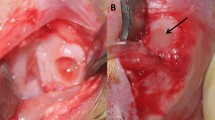
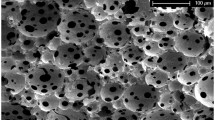
This study used porous polyethylene (PE) as a scaffold in an animal model system. The surface of the scaffolds was either modified with collagen II coating or first functionalized by oxygen plasma treatment and then coated with collagen II. The specimens were inoculated with autologous chondrocytes and transplanted into the concha of guinea pigs. Bare scaffolds were used as controls. Periods of 1, 6, and 12 months after implantation, samples of cells containing specimens and control samples were evaluated microscopically. As a result, the pre-seeded specimens were better integrated into the surrounding tissue than cell-free PE-specimens. Also a weaker immune reaction and an improved cartilage generation could be detected in the pre-seeded specimen. Compared to the other surface modifications, no further improvement of cartilage development was observed in the long term in vivo animal experimental study.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lin Z, Willers C, Xu J, Zheng MH. The chondrocyte: biology and clinical application. Tissue Eng. 2006;12:1971–4. doi:10.1089/ten.2006.12.1971.
Praveen J, Patel MA, Rees HC, Olver JM. Fibrovascularization of porous polyethylene orbital floor implants in humans. Arch Ophthalmol. 2003;121:400–3.
Romo TIII, Sclafani A, Sabini P. Use of porous high-density polyethylene in revision rhinoplasty and in the platyrrhine nose. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 1998;22:211–21. doi:10.1007/s002669900193.
Romo TIII, Sonne J, Choe KS, Sclafani A. Revision rhinoplasty. Facial Plast Surg. 2003;19:299–307. doi:10.1055/s-2004-815649.
Nam SB, Bae YC, Kang YS. Analysis of the postoperative outcome in 405 cases of orbital fracture using two synthetic implants. Ann Plast Surg. 2006;56:263–7. doi:10.1097/01.sap.0000199173.73610.bc.
Cui HG, Li HY, Chen YH. Analysis of high density porous polyethylene (Medpor) orbital implant in 266 cases. Zhonghua Zheng Xing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2006;22:133–5.
Carboni A, Cerulli G, Perugini M, Renzi G. Long-term-follow-up of 105 porous polyethylene implants used to correct facial deformity. Eur J Plast Surg. 2002;25:310–4. doi:10.1007/s00238-002-0407-3.
Berghaus A. Implantate für die rekonstruktive Chirurgie der Nase und des Ohres. Laryngorhinootologie. 2007;86:S67–76. doi:10.1055/s-2007-966301.
Blaydon SM, Shepler TR, Neuhaus RW, White WL, Shore JW. The porous polyethylene (Medpor) sperical orbital implant: a retrospective study of 136 cases. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003;19:364–71. doi:10.1097/01.IOP.0000083643.36461.84.
Shin H, Jo S, Mikos AG. Biomimetic materials for tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2003;24:4353–4. doi:10.1016/S0142-9612(03)00339-9.
Isogai N, Kusuhara H, Ikada Y, Ohtani H, Jacquet R, Hillyer J, et al. Comparison of different chondrocytes for use in tissue engineering of cartilage structures. Tissue Eng. 2006;12:691–3. doi:10.1089/ten.2006.12.691.
Perka C, Schultz O, Sittinger M, Zippel H. Chondrozytentransplantation in PGLA/Polydioxanon-Vliesen. Orthopade. 2000;29:112–9.
Cao Y, Vacanti MP, Paiqe KT, Upton J, Vacanti CA. Transplantation of chondrocytes utilizing a polymer-cell construct to produce tissue-engineered cartilage in the shape of a human ear. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1997;100:297–302. doi:10.1097/00006534-199708000-00001.
Aigner J, Tegeler J, Hutzler P, Campoccia D, Pavesio A, Hammer C, et al. Cartilage tissue engineering with novel nonwoven structured biomaterial based on hyaluronic acid benzyl ester. J Biomed Mater Res. 1998;42:172–81. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4636(199811)42:2<172::AID-JBM2>3.0.CO;2-M.
Lee CR, Grodzinsky, Hsu H-P, Spector M. Effects of a cultured autologous chondrocytes-seeded type II collagen scaffold on the healing of a chondral defect in a canine model. J Orthop Res. 2003;21:272–81. doi:10.1016/S0736-0266(02)00153-5.
Nehrer S, Breinan HA, Ramappa A, Young G, Shortkroff S, Louie LK, et al. Matrix collagen type and pore size influence behavior of seeded canine Chondrozytes. Biomaterials. 1997;18:769–76. doi:10.1016/S0142-9612(97)00001-X.
Angele P, Abke J, Kujat R, Faltermeier H, Schumann D, Nerlich M, et al. Influence of different collagen species on physico chemical properties of crosslinked collagen matrices. Biomaterials. 2004;25:2831–41. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2003.09.066.
Rotter N, Haisch A, Bücheler M. Cartilage and bone tissue engineering for reconstructive head and neck surgery. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2005;262:539–45. doi:10.1007/s00405-004-0866-1.
Bryant SJ, Durand KL, Anseth KS. Manipulations in hydrogel chemistry control photoencapsulated chondrocytes behavior and their extracellular matrix production. J Biomed Mater Res. 2003;67A:1430–6. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.20003.
Baek CH, Ko YJ. Characteristics of tissue-engineered cartilage on macroporous biodegradedable PLGA scoffold. Laryngoscope. 2006;116:1829–34. doi:10.1097/01.mlg.0000233521.49393.0d.
Röpke E, Schön I, Vogel J, Jamali J, Bloching M, Berghaus A. Screening of modified polyethylene surfaces for tissue engineering of chondrocytes. Laryngo-Rhino-Otol. 2007;86:37–43. doi:10.1055/s-2006-945025.
Vats A, Tolley NS, Polak JM, Gough JE. Scaffold and Biomaterials for tissue engineering: a review of clincal applications. Clin Otolaryngol. 2003;28:165–72. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2273.2003.00686.x.
Cancedda R, Dozin B, Giannoni P, Quarto R. Tissue engineering and cell therapy of cartilage and bone. Matrix Biol. 2003;22:81–91. doi:10.1016/S0945-053X(03)00012-X.
Rickert D, Lendlein A, Peters I, Moses MA, Franke RP. Biocompatibility testing of novel multifunctional polymeric biomaterials for tissue engineering applications in head and neck surgery: an overview. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2006;263:215–22. doi:10.1007/s00405-005-0950-1.
Dayss E, Leps G, Meinhardt J, Wutzler A. Biokompatible Polymerschichten. In: Leps G, Kausche H, editors. 40 Jahre Werkstofftechnik. Merseburg; 1999, p. 84.
Harlow E, Lane D. Antibodies: a laboratory manual. New York: Cold Spring Harbour laboratory; 1988.
Freshney RI. Culture of animal cells. A manual of basic technique. 2nd ed. Berlin, New York: de Gruyter; 1990.
Romeis B. Mikroskopische Technik. 17th ed. München: Urban und Schwarzenberg; 1989.
Custers RJ, Creemers LB, Verbout AJ, van Rijen MH, Dhert WJ, Saris DB. Reliabaility, reproducibility and variability of the traditional Histologic/Histochemical Grading System vs the new OARSI Osteoarthritis Cartilage Histopathology Assessment System. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2007;15:1241–8. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2007.04.017.
Petersen JP, Ueblackker P, Goepfert C, Adamietz P, Baumbach K, Stork A, et al. Long term results after implantation of tissue engineered cartilage for the treatment of osteochondral lesions in a minipig model. J Mater Sci: Mater Med. 2008;19:2029–38. doi:10.1007/s10856-007-3291-3.
Kusuhara H, Isogai N, Enjo M, Otani H, Ikada Y, Jacquet R, et al. Tissue engineering a model for the human ear: assessment of size, shape, morphology, and gene expression following seeding of different chondrocytes. Wound Rep Reg. 2009;17:136–46.
Cenzi R, Farina A, Zuccarino L, Carinci F. Clinical Note Clinical outcome of 285 Medpor grafts used for craniofacial reconstruction. J Craniofac Surg. 2005;16:526–33. doi:10.1097/01.scs.0000168761.46700.dc.
Hilborn J, Bjursten LM. A new and evolving paradigm for biocompatibility. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2007;1:110–9. doi:10.1002/term.4.
Tigli RS, Gümüsdereioglu M. Evaluation of alginate-chitosan semi IPNs as cartilage scaffolds. J Mater Sci: Mater Med. 2009;20:699–709. doi:10.1007/s10856-008-3624-x.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Jürgen Vogel from the Department of Bioengineering of the MLU Halle-Wittenberg for performing the surface modification of the PE materials. This project has been funded by ministry of education of Sachsen-Anhalt Grant No. 3308A/0080B.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schoen, I., Rahne, T., Markwart, A. et al. Cartilage replacement by use of hybrid systems of autologous cells and polyethylene: an experimental study. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 20, 2145–2154 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-009-3775-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-009-3775-4