Abstract
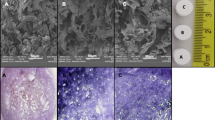
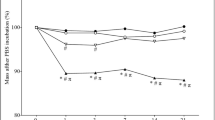
Biodegradable and biocompatible materials are the basis for tissue engineering. As an initial step for developing bone tissue engineering scaffolds, the in vitro biocompatibility of degradable and bioactive composites consisting of polyhydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate (PHBV) and wollastonite (W) was studied by culturing osteoblasts on the PHBV/W substrates, and the cell adhesion, morphology, proliferation, and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity were evaluated. The results showed that the incorporation of wollastonite benefited osteoblasts adhesion and the osteoblasts cultured on the PHBV/W composite substrates spread better as compared to those on the pure PHBV after culturing for 3 h. In the prolonged incubation time, the osteoblasts cultured on the PHBV/W composite substrates revealed a higher proliferation and differentiation rate than those on the pure PHBV substrates. In addition, an increase of proliferation and differentiation rate was observed when the wollastonite content in the PHBV/W composites increased from 10 to 20 wt%. All of the results showed that the addition of wollastonite into PHBV could stimulate osteoblasts to proliferate and differentiate and the PHBV/W composites with wollastonite up to 20 wt% were more compatible than the pure PHBV materials for bone repair and bone tissue engineering.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. WANG, Biomaterials 24 (2003) 2133–2151
S. GOGOLEWSKI, M. JOVANOVIC, S. M. PERREN, J. G. DILLON and K. HUGHES, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 27 (1993) 1135–1148
G. T. KOSE, H. KENAR, N. HASIRCI and V. HASIRCI, Biomaterials 24 (2003) 1949–1958
L. J. CHEN and M. WANG, Biomaterials 23 (2002) 2631–2639
H. Li and J. CHANG, Biomaterials 25 (2004) 5473–5480
H. Li and J. CHANG, Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 87 (2005) 301–307
D. F. WILLIAMS, Medical, Dental Materials, edited by R. W. CAHN, P. HAASEN and E. KRAMER J. Mater. Sci. Technol.—a comprehensive treatment. (Weinheim, New York, Basel, Cambridge: VCH, 1992) p.1–27
S. L. ABBONDANZO, V. L. YOUNG, M. Q. WEI and F. W. MILLER, Mod. Pathol. 12 (1999) 706–713
D. F. WILLIAMS, The Williams Dictionary of Biomaterials. (Liverpool, UK: University Press, 1999) p. 40
S. VERRIER, J. J. BLAKER, V. MAQUET, L. L. HENCH and A. R. Boccaccini, Biomaterials 25 (2004) 3013–3021
O. H. LOWRY, N. R. ROBERTS, M. WU, W. S. HIXTON and E. J. CRAWFORD, J. Biol. Chem. 207 (1954) 19–37
H.F. WANG An ATLAS of Bone of Cells and Cell Culture Techniques. (Shanghai Science and Technique press, 2001) p. 63
ISO/EN 10993–5: Biological evaluation of medical devices-part 5: Tests for cytotoxicity: in vitro methods, 1992
K. BURRIDGE and K. FATH, Bioessays 4 (1989) 104–108
K. ANSELME, Biomaterials 7 (2000) 667–681
S. VERRIER, R. Bareille, A. Rovira, M. DARD and J. AMEDEE, J Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 7 (1996) 46–51
D. A. ULEO and R. BIZIOS, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 26 (1992) 291–301
A. HUNTER, C. W. ASCHER, P. S. WALKER and G. W. BLUNN, Biomaterials 6 (1995) 287–295
K DERHAMI, J. F. WOLFAARDT, A. WENNERBERG and P. G. SCOTT, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 52 (2000) 315–322
C. H. THOMAS, C. D. Mcfarland, M. L. JENKINS, A. REZANIA, J. C. STEELE, K. E. HEALY, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 37 (1997) 81–93
K. WEBB, V. HLASY and P. A. TRESCO, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 41 (1984) 422–430
M. YANG, S. ZHU, Y. CHEN, Z. CHANG, G. CHEN, Y. GONG, N. ZHAO and X. ZHANG, Biomaterials. 25 (2004) 1365–1373
J. G. STEELE, C. MCFARLAND, B. A. DALTON, G. JOHNSON, M. D. EVANS and C. R. HOWLETT, J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 5 (1993) 245–257
B. FENG, J. WENG, B. C. YANG, S. X. QU and X. D. ZHANG, Biomaterials 17 (2004) 3421–3428
I. D. XYNOS, M. V. J. HUKKANEN, J. J. BATTEN, L. D. K. BUTTERY, L. L. Hench and J. M. Polak, Calcif. Tissue. Inter. 67 (2000) 321–329
I. A. SILVER, J. DEAS and M. ERECINSKA, Biomaterials 22 (2001) 175–185
J. E. GOUGH, J. R. JONES, L. L. HENCH, Biomaterials 25 (2004) 2039–2046
A. EL-GHANNAM, P. DUCHEYNE and I.M. SHAPIRO, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 36 (1997) 167–180
C. LOTY, J. M. SAUTIER, H. BOULEKACHE, T. KOKUBO and H. M. KIM, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 49 (2000) 423–434
N. OLMO, A. I. MARTÍN, A. J. SALINAS, J. TURNAY, V. R. MARÍA and M. A. LIZARBE, Biomaterials 24 (2003) 3383–3393
G. R. BECK Jr, E. C. Sullivan, E. MORAN and B. ZERLER, J. Cell. Biochem. 68 (1998) 269–280
J. E. AUBIN, F. Liu, L. MALAVAL and A. K. GUPTA, Bone 17 (2 Suppl) (1995) 77S–83S
L. MALAVAL, F. LIU, P. ROCHE and J. E. AUBIN, J. Cell. Biochem. 74 (1999) 616–627
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Basic Science Research Program of China (973 Program) (Grant No: 2005CB522700) and the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (Grant No: 02JC14009 and 05DJ14005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Zhai, W. & Chang, J. In vitro biocompatibility assessment of PHBV/Wollastonite composites. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 19, 67–73 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-007-3170-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-007-3170-y