Abstract
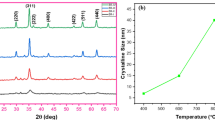
The monodisperse core-shell silica magnetic microspheres (MMS) were synthesized by sol–gel method gelling in the emulsion. Optical microscope (OM), field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM), nitrogen adsorption and desorption Brunauer Emmett Teller Procedure (BET) isotherms and Barrett-Joyner-Halenda (BJH) pore size distribution measurements, X-ray diffraction (XRD), energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS) and vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) were used to characterize the appearance, size distribution, phase, specific surface area, chemical composition and magnetic property of silica MMS. The results showed that silica MMS prepared through sol–gel method with acid-alkali two-step catalyze and gelling in emulsion exhibited the superior core-shell structure and size distribution of the microspheres concentrated in about 20 μm. The main phase of microspheres was amorphous silica and spinel ferroferric oxide. Meanwhile, the microspheres remained the superparamagnetic behavior and could be used as biomaterials.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. JINYUAN and P. TUZHI, Preparation and Properties of a Magnetic-nanometer TiO2/Fe3O4 Composite Photocatalyst. Acta Chim. Sin. 62(20) (2004) 2093–2097
L. ZHENHUA, C. JIANJUN, Y. KEFU, et al., Preparation and Characterization of Nanometer-sized Magnetic Photocatalyst TiO2/SiO2/Fe3O4. J. Inorg. Mater. 19(4) (2004) 749–754
P. REIMER and R. WEISSLEDER, Development and Experimental Application of Receptir-specific MR Contrast Media. Der Radiologe. 36(2) (1996) 153
C. CHOULY, D. POULIQUEN, I. LUCET, et al., Development of Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles for MRI: Effect of Particles Size, Charge and Surface Nature on Biodistribution. J. Microencapsul. 13(3) (1996) 245–255
T. KUBO, T. SUGITA, S. SHIMOSE, et al., Targeted Delivery of Anticancer Drugs with Intravenously Administered Magnetic Liposomes in Osteosarcoma Bearing Hamsters. Int. J. Oncol. 17(2) (2000) 309–315
R. F. H. DEKKER, Application of a magnetic immobilized α-glucosidase in the enzymatic saccharification of steam-exploded lignocellulosic residues. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol 23(1) (1990) 25–39
S. C. GOODWIN, C. A. BITTNER, C. L. PETERSON, et al., Single-dose Toxicity Study of Hepatic Intra-arterial Infusion of Doxorubicin Coupled to a Novel Magnetically Targeted Drug Carrier. Toxical. Sci. 60(1) (2001) 177–183
D. F. MCCOLE, M. L. DOHERTY, A. W. BAIRD, et al., Concanavalin Astimulated Proliferation of T Cell Subset-depleted Lymphocyte Populations Isolated from Fasciola Hepatica-infected Cattle. Vet. Immune. Immunopathol. 66(3) (1998) 289–293
A. RALF and P. MARTIN GEOFFREY, Preparation of Spherical Multiplayer Magnetic Particles for the Separation of Nucleic Acids, Biotin and Biotinylated Molecules from Aqueous Solutions. WO Patent 9812717, 1998-03-26
H. UEMATSU, K. DAIMON, et al., Method for Isolating Nucleic Acids using Silica-coated Magnetic Particles. US Patent, 5945525, 1999-8-31
D. C. F. CHAN, D. KIRPOTIN and P. A. BUNN, Synthesis and Evaluation of Colloidal Magnetic Iron-oxides for the Site-specific Radiofrequency Induced Hyperthermai of Cancer. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 122(8) (1993) 374–379
A. JORDAN, P. WUST, R. SCHOLZ, et al., (1997) Scientific and Clinical Applications of Magnetic Carriers. (New York: Plenum Press) 569–575
I. SAFARIK, M. SAFARIKOVA, Use of Magnetic Techniques for the Isolation of Cells. J. Chromatogr. B, 722(1) (1999) 33–53
J. UGELSTAD, P.C. MORK, K.H. KAGGERUD, T. ELLINGSEN and A. BERGE, New Methods of Preparation of Emulsion and Polymer Dispersions. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 13(2) (1980) 101–140
S. SANTRA, R. TAPEC, N. THEODOROPOULOU, et al., Synthesis and Characterization of Silica-coated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles in Microemulsion: The Effect of Non-ionic Surfactants. Langmuir. 17(10) (2001) 2900–2906
M. J. ZHANG, T. ITOH and M. ABE, Ultrasonic Visualization of Still and Flowing Waters Using Contrast Agents of Magnetite-encapsulated Porous Silica Microspheres. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 36(1A) (1997) 243–246
Y. SHOICHI and K. KIYOSHI, Magnetic Silica Gel And Manufacturing Method Thereof. JP Patent, 10-214710, 1998-11-08
H. TAO, Preparation of Low Density Silica by Means of Sol-Gel. Electron. Compon. Mater. 15(3) (1995) 52–55
Y.MINGZHI, Y. XI and Z. LIANGYING, Fabrication and Characterization of Nanoporous Silica Film. J. Funct. Mater. 1(34) (2003) 103–105
S. ZHONG, Z. ZHENGUO and W. GUOTING, Colloid and Surface Chemistry, 3rd edn (Beijing: Chemical Industry Press) 313–399 (2004)
Z. XUEYAN, C. MINGQING, L. XIAOYA, et al, Progress in preparations of microspheres with core/shell structure. Chem. Res. Appl. 16(3) (2004) 309–313
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China with award mumber 50272041 and also supported by Science & Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (STCSM) with award number 0452nm059.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work is supported by both National Science Foundation 50572072 and Science & Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (STCSM) 0452nm059.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lou, My., Jia, Ql., Wang, Dp. et al. The preparation and properties of monodisperse core-shell silica magnetic microspheres. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 19, 217–223 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-007-3094-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-007-3094-6