Abstract
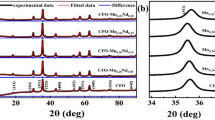
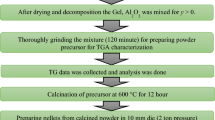
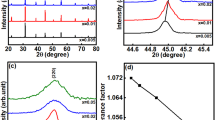
The regulation of Fe2+ in yttrium iron garnet is a crucial factor in determining its dielectric and magnetic properties. This study successfully prepared Y3Mn0.2Fe4.8O12 ceramics, and studied their microstructure, magnetism, dielectric properties, and ferromagnetic linewidth through Mnn+ ion doping. The microstructural analysis revealed that the doping of low-valence Mn led to an increase in the grain size and density of ceramics, while the Mn4+–YIG showed the emergence of the second phase of YFeO3. Chemical composition analysis confirmed that the Fe2+ content was regulated by the Mn valence and that the lowest value was observed in Mn2+–YIG. The hysteresis loop demonstrated that the saturation magnetization decreased with the increase of Mn valence. In addition, low-valence Mn doping also reduced the dielectric loss and ferromagnetic resonance linewidth. Therefore, this study confirmed that low-valence metal doping could be a promising approach for regulating the Fe2+ content in YIG.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on request.
References
See https://www.digitaltrends.com/mobile/what-is-5g/for some background information acquired from C. de Looper, “What is 5G? The Next-Generation Network Explained, Digital Trends” (last retrieved May 25, 2021).
S.J. Zhang, B. Cheng, Z.G. Gao, D. Lan, Z.W. Zhao, F.C. Wei, Q.S. Zhu, X.P. Lu, G.L. Wu, Two-dimensional nanomaterials for high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption: an overview of recent advances and prospects. J. Alloy. Compd. 893, 162343 (2022)
R.C. Pullar, Hexagonal ferrites: a review of the synthesis, properties and applications of hexaferrite ceramics. Progr. Mater. Sci. 57, 1191–1334 (2012)
V.G. Harris, Modern microwave ferrites. IEEE Trans. Magn. 48, 1075–1104 (2012)
V.G. Harris, A. Geiler, Y. Chen, S.D. Yoon, W. Mingzhong, A. Yang, Z. Chen, P. He, P.V. Parimi, Xu. Zuo, C.E. Patton, M. Abe, O. Acher, C. Vittoria, Recent advances in processing and applications of microwave ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, 2035–2047 (2009)
V.G. Harris, Ba-hexaferrite films for next generation microwave devices. J. Appl. Phys. 99, 08M911 (2006)
V.G. Harris, A.S. Sokolov, The self-biased circulator: ferrite materials design and process considerations. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 32, 97–108 (2019)
C. Yu, P. Andalib, A. Sokolov et al., Interface-engineered barium magnetoplumbite-wide-bandgap semiconductor integration enabling 5G system-on-wafer solutions for full-duplexing phased arrays. Appl. Phys. Lett. 5, 119 (2021)
E.J.J. Mallmann, A.S.B. Sombra, J.C. Goes, P.B.A. Fechine, Yttrium iron garnet: properties and applications review. Solid State Phenom. 202, 65–96 (2013)
H.C. Cao, H. Zheng, L.N. Fan, Z.F. Cheng, J.W. Zhou, Q. Wu, P. Zheng, L. Zheng, Y. Zhang, Structural, morphological, dielectric and magnetic properties of Zn–Zr co-doping yttrium iron garnet. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 17(2), 813–822 (2020)
J. Li, Y. Sun, F. Gao, X. Han, Z. Liang, H. Zhang, Q. Li, Enhanced FMR linewidth and magnetic properties of In3+-doped YIG ferrite materials for microwave devices applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 538, 168318 (2021)
J. Wang, Y. Jin, J. Yang, T. Qiu, Effect of manganese addition on the microstructure and electromagnetic properties of YIG. J. Rare Earths 29(6), 562 (2011)
X.R. Ji, K. Zhou, Y. Zhao, M.L. Sun, S.J. Dong, H.B. Zhang, H.C. Cao, H. Zheng, Q. Wu, Y. Zhang, Crystal structure, magnetic, dielectric and ferromagnetic resonance properties of Pr–Zn–Zr Co-doped yttrium iron garnet. J. Electron. Mater. 51, 1180–1188 (2022)
R.P. Garcia, Y. Guerra, D.M. Buitrago, L.R.F. Leal, F.E.P. Santos, E.P. Hernández, Synthesis and characterization of yttrium iron garnet nanoparticles doped with cobalt. Ceram. Int. 44, 11314 (2018)
E. Baños-López, C.A. Cortés-Escobedo, F. Sánchez-De Jesús, A. Barba-Pingarrón, A.M. Bolarín-Miró, Crystal structure and magnetic properties of cerium-doped YIG: effect of doping concentration and annealing temperature. J. Alloy. Compd. 730, 127 (2018)
F.W. Aldbea, N.B. Ibrahim, M. Yahya, Effect of adding aluminum ion on the structural, optical, electrical and magnetic properties of terbium doped yttrium iron garnet nanoparticles films prepared by sol-gel method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 321, 150–157 (2014)
R. Peña-Garcia, A. Delgado, Y. Guerra, B.V.M. Farias, D. Martinze, E. Skovroinski, A. Galembeck, E. Padrón-Hernández, Magnetic and structural properties of Zn-doped yttrium iron garnet nanoparticles. Phys. Status Solidi A 213, 2485–2491 (2016)
S. Khanra, A. Bhaumik, Y.D. Kolekar, P. Kahol, K. Ghosh, Structural and magnetic studies of Y3Fe5-5xMo5xO12. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 369, 14–22 (2014)
K. Bouziane, A. Yousif, H.M. Widatallah, J. Amighian, Site occupancy and magnetic study of Al3+ and Cr3+ co-substituted Y3Fe5O12. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 320, 2330–2334 (2008)
C.C. Huang, C.C. Mo, Y.H. Hung, W.Z. Zuo, J.Y. Huang, H.H. Hsu, C.H. Cheng, Effect of particle size of as-milled powders on microstructural and magnetic properties of Y3MnxAl0.8−xFe4.2O12 ferrites. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 102, 3525–3534 (2019)
Z.Z. Zhang, H.L. Lv, Z.K. Feng, Y. Nie, Study on the magnetically tunable filters based on Mnn+ and Al3+ co-doped YIG ferrite. IEEE Trans. Magn. 51, 2802704 (2015)
F. Chen, Q. Li, X. Wang, Z. Feng, Y. Chen, V.G. Harris, Magnetic spectra and richter after effect relaxation in zirconium-doped yttrium iron garnet ferrites. IEEE Trans. Magn. 51(11), 1–4 (2015)
T.C. Mao, J.C. Chen, Influence of the addition of CeO2 on the microstructure and the magnetic properties of yttrium iron garnet ceramic. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 302(1), 74–81 (2006)
J.S. Zhu, H.R. Wu, R.X. Ti, F.Z. Huang, Y.M. Jin, Grain size and Fe2+ concentration-dependent magnetic, dielectric, and magnetodielectric properties of Y3Fe5O12 ceramics. Phys. Status Solidi A (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/pssa.201532582
S.J. Dong, R.Q. Li, J.P. Wu, W.X. Zhong, Y. Zhao, X.R. Ji, H. Zheng, P. Zheng, H. He, L. Zheng, Microstructure and electromagnetic of tantalum substituted W-type hexagonal barium ferrite based on doping concentration. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 34, 837 (2023)
C.Y. Liu, Q.K. Xu, Y. Tang, Z.R. Wang, R. Ma, N. Ma, P.Y. Du, Zr4+ doping-controlled permittivity and permeability of BaFe12−xZrxO19 and the extraordinary EM absorption power in the millimeter wavelength frequency range. J. Mater. Chem. C 4, 9532–9543 (2016)
C.Y. Liu, Y.J. Chen, Y.Y. Yue, Y. Tang, Z.R. Wang, Formation of BaFe12−xNbxO19 and its high electromagnetic wave absorption properties in millimeter wave frequency range. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 100, 3999–4010 (2017)
X.X. Li, J.J. Zhou, J.X. Deng, H. Zheng, L. Zheng, P. Zheng, H.B. Qin, Synthesis of dense, fine-grained YIG ceramics by two-step sintering. J. Electron. Mater. 45(10), 4973–4978 (2016)
E. Zhou, H. Zheng, L. Zheng, P. Zheng, Z.H. Ying, J.X. Deng, J.J. Zhou, Synthesis of dense, fine-grained hexagonal barium ferrite ceramics by two-step sintering process. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 15, 1023–1029 (2018)
I.W. Chen, X.H. Wang, Sintering dense nanocrystalline ceramics without final-stage grain growth. Nature 404, 168 (2000)
H. Su, X.L. Tang, H.W. Zhang, Y.L. Jing, F.M. Bai, Z.Y. Zhong, J. Appl. Phys. 113, 17B301 (2013)
H.W. Nesbitt, M. Scaini, H. Höchst, G.M. Bancroft, A.G. Schaufuss, R. Szargan, Synchrotron XPS evidence for Fe2+–S and Fe3+–S surface species on pyrite fracture-surfaces, and their 3D electronic states. Am. Miner. 85(5–6), 850–857 (2000)
W.B. Soltan, S. Nasri, M.S. Lassoued, S. Ammar, Structural, optical properties, impedance spectroscopy studies and electrical conductivity of SnO2 nanoparticles prepared by polyol method. J. Mater. Sci. 28, 6649 (2017)
X.D. Li, Z.N. Chen, L.S. Sheng, L.L. Li, W.F. Bai, F. Wen, P. Zheng, W. Wu, L. Zheng, Y. Zhang, Remarkable piezoelectric activity and high electrical resistivity in Cu/Nb co-doped Bi4Ti3O12 high temperature piezoelectric ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 39, 2050–2057 (2019)
Y. Yang, J. Li, J.X. Zhao, X. Chen, G.W. Gan, G. Wang, L.F. He, Synthesis of nickel zinc ferrite ceramics on enhancing gyromagnetic properties by a novel low-temperature sintering approach for LTCC applications. J. Alloy. Compd. 778, 8 (2019)
Y.J. Siao, X. Qi, C.R. Lin, J. Huang, Dielectric and magnetic properties of Y3−xTbxFe5O12 ferrimagnets. J. Appl. Phys. 111(7), 317 (2012)
H.B. Zhang, L.N. Fan, H.C. Cao, Y.S. Yu, T.C. Zhang, Q.Q. Feng, H. Zheng, Q. Wu, Y. Zhang, Microstructure, magnetic, and dielectric properties of Co–Zr co-doped hexagonal barium ferrites based on the sintering temperature and doping concentration. J. Mater. Sci. 32, 2685–2695 (2021)
A. Verma, D.C. Dube, Processing of nickel–zinc ferrites via the citrate precursor route for high-frequency applications. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 88, 519 (2005)
X.T. Tang, G.T. Wei, T.X. Zhu, L.M. Sheng, K. An, L.M. Yu, Y. Liu, X.L. Zhao, Microwave absorption performance enhanced by high-crystalline graphene and BaFe12O19 nanocomposites. J. Appl. Phys. 119, 204301 (2016)
C.J. Wu, W. Wang, Q. Li, M. Wei, Q. Luo, Y. Fan, X. Jiang, Z. Lan, Z. Jiao, Y. Tian, K. Sun, Z. Yu, Barium hexaferrites with narrow ferrimagnetic resonance linewidth tailored by site-controlled Cu doping. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 105, 7492–7501 (2022)
Y.Y. Song, S. Kalarickal, C.E. Patton, Optimized pulsed laser deposited barium ferrite thin films with narrow ferromagnetic resonance linewidths. J. Appl. Phys. 94, 5103–5110 (2003)
P.E. Seiden, J.G. Grunberg, Ferrimagnetic resonance linewidth in dense polycrystalline ferrites. J. Appl. Phys. 34, 1696 (1963)
A.V. Nazarov, D. Ménard, J.J. Green, C.E. Patton, G.M. Argentina, Near theoretical microwave loss in hot isostatic pressed (hipped) polycrystalline yttrium iron garnet. J. Appl. Phys. 94, 7227 (2003)
Acknowledgements
This work is funded by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Provincial Universities of Zhejiang (Grant No. GK239909299001-402), National Key Research and Development Project (Grant No. 2019YFF0217205), Key R&D Program of Zhejiang Province of China (Grant No. 2021C01190).
Funding
Funding was provided by Fundamental Research Funds for the Provincial Universities of Zhejiang (Grant No. GK239909299001-402), National Key Research and Development Project (Grant No. 2019YFF0217205), Key R&D Program of Zhejiang Province of China (Grant No. 2021C01190).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors of the current manuscript contributed equally.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, W., Chen, K., Nan, Y. et al. Regulation of Fe2+ contents in yttrium iron garnet by doping with different valence states of Mn and its dielectric and magnetic properties. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 35, 984 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12742-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12742-x